
Paraguay, officially the Republic of Paraguay, is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to the east and northeast, and Bolivia to the northwest. It has a population of around 6.1 million, nearly 2.3 million of whom live in the capital and largest city of Asunción, and its surrounding metro area.

Paraguayan foreign policy has concentrated on maintaining good relations with its neighbors, and it has been an active proponent of regional co-operation. It is a member of the United Nations and has served one term in the UN Security Council in 1967-1969. It maintains membership in several international financial institutions, including the World Bank, the Inter-American Development Bank, and the International Monetary Fund. It also belongs to the Organization of American States, the Latin American Integration Association (ALADI), the Rio Group, INTERPOL, MERCOSUR and UNASUR.
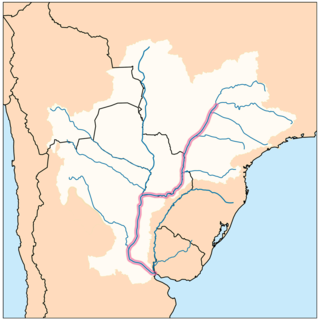
The Paraná River is a river in south-central South America, running through Brazil, Paraguay, and Argentina for some 4,880 kilometres (3,030 mi). Among South American rivers, it is second in length only to the Amazon River. It merges with the Paraguay River and then farther downstream with the Uruguay River to form the Río de la Plata and empties into the Atlantic Ocean.

The Paraguay national football team, nicknamed La Albirroja, represents Paraguay in men's international football competitions, and are controlled by the Paraguayan Football Association. Paraguay is a member of CONMEBOL. The Albirroja has qualified for eight FIFA World Cup competitions, with their best performance coming in 2010 when they reached the quarter-finals. A regular participant at the Copa América, Paraguay have been crowned champions of the competition on two occasions. Paraguay's highest FIFA World Rankings was 8th and their lowest was 103. Paraguay was awarded second place with Best Move of the Year in 1996 for their rise in the FIFA Rankings.

Roque Luis Santa Cruz Cantero is a Paraguayan professional footballer who plays as a striker for Paraguayan Primera División club Libertad. He is the record goal scorer and has earned over 100 caps for the Paraguay national team, thus he is regarded as one of the best players in the nation's history. Santa Cruz has scored goals at a professional level in each of the last four decades.

Club Olimpia is a Paraguayan professional football club based in the city of Asunción. It promotes the practice of various sports, with most importance given to the football, rugby and basketball sides, football being the most successful. The club was founded on July 25, 1902, by a group of young Paraguayans, and the name stems from the idea of its principal founding member, William Paats, a Dutchman based in Paraguay, who is considered the father of Paraguayan football for having introduced the practice of the sport in the South American country. Internationally, the club is referred to as Olimpia Asunción in order to distinguish it from other Latin American football clubs of the same name.

Club Cerro Porteño is a professional Paraguayan football club, based in the neighbourhood of Obrero in Asunción. Founded in 1912, Cerro has won 34 Primera División titles and is one of the most popular football clubs in Paraguay. Its president is Raúl Zapag and the manager is Carlos Jara Saguier. Cerro Porteño plays the Paraguayan derby with its main rival Club Olimpia. They play their home games at the 45,000-seat General Pablo Rojas Stadium, also known as La Nueva Olla, the biggest in the country.
Ever Hugo Almeida Almada is a Paraguayan football manager and former player who played as a goalkeeper. He is the current manager of Ecuadorian club Mushuc Runa.

Club Sportivo Luqueño is a Paraguayan football club, based in the city of Luque on the outskirts of the capital Asunción. It currently plays in the Paraguayan Primera División, the country's top tier of football, where it has won thrice, in 1951, 1953 and 2007-A.

Club Libertad is a Paraguayan professional football club based in Asunción that currently plays in the Paraguayan Primera División. The club plays its home games at Estadio Tigo La Huerta; which holds 10,100 people.

Club Guaraní is a Paraguayan football team, based in the neighbourhood of Pinozá in outer Asunción. Founded on 12 October 1903, it is one of the oldest and one of the most successful in the country, with eleven Primera División titles, and has never been relegated to a lower division.

Club Nacional is a Paraguayan professional football club based in the neighbourhood of Obrero in Asunción. Founded in 1904, the club currently plays in the Paraguayan Primera División, and holds its home games at Estadio Arsenio Erico.

Club Tacuary is a Paraguayan First Division football team, based in the neighborhood of Jara in Asunción. The club was founded in 1923.

Nelson Antonio Haedo Valdez commonly known as Nelson Valdez or Nelson Haedo in Spanish speaking countries, is a Paraguayan professional football coach and a former player who played as a striker for clubs in Paraguay, Germany, Spain, Russia, the United Arab Emirates, Greece, the US and for the Paraguay national team between 2000 and 2021. He is an assistant coach with the German club Werder Bremen II.

Club Sol de América is a Paraguayan sports club, mostly known for its football team. The club is located in Barrio Obrero, Asunción, and was founded in 1909. The stadium Sol de America uses for most of its games is located in the suburb city of Villa Elisa on the border of the capital city, Asunción. Sol de America have won the Paraguayan First Division title on two occasions, in 1986 and then again in 1991. They also have a strong basketball team and an athletics department.

The Paraguayan Football Association, is the omnibus governing body of football in Paraguay. It organizes the Paraguayan football league, including futsal and beach soccer, as well as and the Paraguay national football team. It is based in the city of Luque, near the capital city, Asunción. Football is the most popular sport in Paraguay.

The División Intermedia, also known as the Segunda División, is the third highest professional football league in Paraguay. It is organized by the Asociación Paraguaya de Fútbol.

Fernando Armindo Lugo Méndez is a Paraguayan politician and laicized Catholic bishop who was President of Paraguay from 2008 to 2012. Previously, he was a Roman Catholic priest and bishop, serving as Bishop of the Diocese of San Pedro from 1994 to 2005. He was elected as president in 2008, an election that ended 61 years of rule by the Colorado Party.

The 2011 Copa América final was the final match of the 2011 Copa América, an international football tournament that was played in Argentina from 1 to 24 July 2011. The match was played on 24 July at Estadio Monumental Antonio Vespucio Liberti in Buenos Aires, between Uruguay and Paraguay.

Women in Paraguay face challenges to their rights. Faced by socioeconomic inequalities and gender pay gap, they experienced significant cultural changes since 1990 as a result of constitutional and legal expansions of women's rights and evolving cultural attitudes. The legal and government institutions currently existing in Paraguay were developed in part through the efforts of feminist organizations in the country that held significant awareness-raising campaigns during the 1990s to formalize the guarantees of women's rights. UN Women supports the Paraguayan State in the challenge to extend women's rights, to fight for gender equality, as well as women's empowerment. It also ensures that women's voices are heard and create more opportunities for women.


















