
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and development of both hardware and software. Computing has scientific, engineering, mathematical, technological and social aspects. Major computing disciplines include computer engineering, computer science, cybersecurity, data science, information systems, information technology and software engineering.
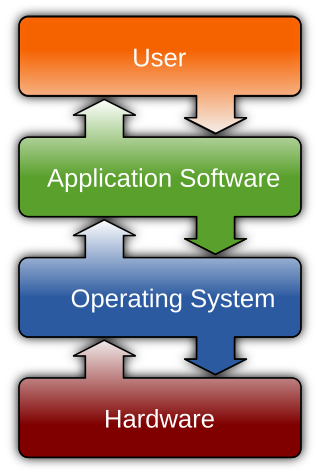
Software is a set of computer programs and associated documentation and data. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work.
Computer vision tasks include methods for acquiring, processing, analyzing and understanding digital images, and extraction of high-dimensional data from the real world in order to produce numerical or symbolic information, e.g. in the forms of decisions. Understanding in this context means the transformation of visual images into descriptions of the world that make sense to thought processes and can elicit appropriate action. This image understanding can be seen as the disentangling of symbolic information from image data using models constructed with the aid of geometry, physics, statistics, and learning theory.

The International Commission on Illumination is the international authority on light, illumination, colour, and colour spaces. It was established in 1913 as a successor to the Commission Internationale de Photométrie, which was founded in 1900, and is today based in Vienna, Austria.

Machine vision (MV) is the technology and methods used to provide imaging-based automatic inspection and analysis for such applications as automatic inspection, process control, and robot guidance, usually in industry. Machine vision refers to many technologies, software and hardware products, integrated systems, actions, methods and expertise. Machine vision as a systems engineering discipline can be considered distinct from computer vision, a form of computer science. It attempts to integrate existing technologies in new ways and apply them to solve real world problems. The term is the prevalent one for these functions in industrial automation environments but is also used for these functions in other environment vehicle guidance.

Theoretical computer science (TCS) is a subset of general computer science and mathematics that focuses on mathematical aspects of computer science such as the theory of computation, lambda calculus, and type theory.
Color science is the scientific study of color including lighting and optics; measurement of light and color; the physiology, psychophysics, and modeling of color vision; and color reproduction.
The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as indexed by Clarivate's Web of Science.

Gesture recognition is a topic in computer science and language technology with the goal of interpreting human gestures via mathematical algorithms. It is a subdiscipline of computer vision. Gestures can originate from any bodily motion or state, but commonly originate from the face or hand. Focuses in the field include emotion recognition from face and hand gesture recognition since they are all expressions. Users can make simple gestures to control or interact with devices without physically touching them. Many approaches have been made using cameras and computer vision algorithms to interpret sign language, however, the identification and recognition of posture, gait, proxemics, and human behaviors is also the subject of gesture recognition techniques. Gesture recognition can be seen as a way for computers to begin to understand human body language, thus building a better bridge between machines and humans than older text user interfaces or even GUIs, which still limit the majority of input to keyboard and mouse and interact naturally without any mechanical devices.

Google Scholar is a freely accessible web search engine that indexes the full text or metadata of scholarly literature across an array of publishing formats and disciplines. Released in beta in November 2004, the Google Scholar index includes peer-reviewed online academic journals and books, conference papers, theses and dissertations, preprints, abstracts, technical reports, and other scholarly literature, including court opinions and patents.

Tetrahedron is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering the field of organic chemistry. According to the Journal Citation Reports, Tetrahedron has a 2020 impact factor of 2.457. Tetrahedron and Elsevier, its publisher, support an annual symposium. In 2010, complaints were raised over its high subscription cost.
CSA was a division of Cambridge Information Group and provider of online databases, based in Bethesda, Maryland before merging with ProQuest of Ann Arbor, Michigan in 2007. CSA hosted databases of abstracts and developed taxonomic indexing of scholarly articles. These databases were hosted on the CSA Illumina platform and were available alongside add-on products like CSA Illustrata. The company produced numerous bibliographic databases in different fields of the arts and humanities, natural and social sciences, and technology. Thus, coverage included materials science, environmental sciences and pollution management, biological sciences, aquatic sciences and fisheries, biotechnology, engineering, computer science, sociology, linguistics, and other areas.
IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the IEEE Computer Society.

Statistical Applications in Genetics and Molecular Biology is a bimonthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering the application of statistics to problems in computational biology. It was established in 2002 and is published by de Gruyter. The editor-in-chief is Guido Sanguinetti. According to the Journal Citation Reports, the journal has a 2012 impact factor of 1.717.
Biotechnology and Bioengineering is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering biochemical engineering science that was established in 1959. In 2009, the BioMedical & Life Sciences Division of the Special Libraries Association listed Biotechnology and Bioengineering as one of the 100 most influential journals in biology and medicine of the past century.

Dlib is a general purpose cross-platform software library written in the programming language C++. Its design is heavily influenced by ideas from design by contract and component-based software engineering. Thus it is, first and foremost, a set of independent software components. It is open-source software released under a Boost Software License.

Optometry and Vision Science is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins on behalf of the American Academy of Optometry. The journal was established in 1924 as the American Journal of Optometry. It was renamed the American Journal of Optometry and Archives of the American Academy of Optometry in 1941, then to the American Journal of Optometry and Physiological Optics in 1974, before obtaining its current title in 1989. The editor-in-chief is Michael D. Twa of the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
Linear Algebra and its Applications is a biweekly peer-reviewed mathematics journal published by Elsevier and covering matrix theory and finite-dimensional linear algebra.

Clarivate Plc is a British-American publicly traded analytics company that operates a collection of subscription-based services, in the areas of bibliometrics and scientometrics; business / market intelligence, and competitive profiling for pharmacy and biotech, patents, and regulatory compliance; trademark protection, and domain and brand protection. In the academy and the scientific community, Clarivate is known for being the company which calculates the impact factor, using data from its Web of Science product family, that also includes services/applications such as Publons, EndNote, EndNote Click, and ScholarOne. Its other product families are Cortellis, DRG, CPA Global, Derwent, MarkMonitor, CompuMark, and Darts-ip, and also the various ProQuest products and services.











