
In computer programming, a macro is a rule or pattern that specifies how a certain input should be mapped to a replacement output. Applying a macro to an input is known as macro expansion.

Scroll Lock is a lock key on most IBM-compatible computer keyboards. Depending on the operating system, it may be used for different purposes, and applications may assign functions to the key or change their behavior depending on its toggling state. The key is not frequently used, and therefore some reduced or specialized keyboards lack Scroll Lock altogether.

A text editor is a type of computer program that edits plain text. An example of such program is "notepad" software. Text editors are provided with operating systems and software development packages, and can be used to change files such as configuration files, documentation files and programming language source code.
In object-oriented programming, the command pattern is a behavioral design pattern in which an object is used to encapsulate all information needed to perform an action or trigger an event at a later time. This information includes the method name, the object that owns the method and values for the method parameters.

An electronic keyboard, portable keyboard, or digital keyboard is an electronic musical instrument based on keyboard instruments. Electronic keyboards include synthesizers, digital pianos, stage pianos, electronic organs and digital audio workstations. In technical terms, an electronic keyboard is a rompler-based synthesizer with a low-wattage power amplifier and small loudspeakers.

A function key is a key on a computer or terminal keyboard that can be programmed to cause the operating system or an application program to perform certain actions, a form of soft key. On some keyboards/computers, function keys may have default actions, accessible on power-on.

In computing, a keyboard shortcut is a software-based assignment of an action to one or more keys on a computer keyboard. Most operating systems and applications come with a default set of keyboard shortcuts, some of which may be modified by the user in the settings.

Caps Lock is a button on a computer keyboard that causes all letters of bicameral scripts to be generated in capital letters. It is a toggle key: each press reverses the previous action. Some keyboards also implement a light to give visual feedback about whether it is on or off. Exactly what Caps Lock does depends on the keyboard hardware, the operating system, the device driver, and the keyboard layout. Usually, the effect is limited to letter keys. Letters of non-bicameral scripts and non-letter characters are generated normally.
Common User Access (CUA) is a standard for user interfaces to operating systems and computer programs. It was developed by IBM and first published in 1987 as part of their Systems Application Architecture. Used originally in the MVS/ESA, VM/CMS, OS/400, OS/2 and Microsoft Windows operating systems, parts of the CUA standard are now implemented in programs for other operating systems, including variants of Unix. It is also used by Java AWT and Swing.
Utility software is a program specifically designed to help manage and tune system or application software. It is used to support the computer infrastructure - in contrast to application software, which is aimed at directly performing tasks that benefit ordinary users. However, utilities often form part of the application systems. For example, a batch job may run user-written code to update a database and may then include a step that runs a utility to back up the database, or a job may run a utility to compress a disk before copying files.

Windows Installer is a software component and application programming interface (API) of Microsoft Windows used for the installation, maintenance, and removal of software. The installation information, and optionally the files themselves, are packaged in installation packages, loosely relational databases structured as COM Structured Storages and commonly known as "MSI files", from their default filename extensions. The packages with the file extensions mst contain Windows Installer "Transformation Scripts", those with the msm extensions contain "Merge Modules" and the file extension pcp is used for "Patch Creation Properties". Windows Installer contains significant changes from its predecessor, Setup API. New features include a GUI framework and automatic generation of the uninstallation sequence. Windows Installer is positioned as an alternative to stand-alone executable installer frameworks such as older versions of InstallShield and NSIS.
Hard coding is the software development practice of embedding data directly into the source code of a program or other executable object, as opposed to obtaining the data from external sources or generating it at runtime.

AutoKey is a free, open-source scripting application for Linux.

Winlogon is the component of Microsoft Windows operating systems that is responsible for handling the secure attention sequence, loading the user profile on logon, creates the desktops for the window station, and optionally locking the computer when a screensaver is running. The roles and responsibilities of Winlogon have changed significantly in Windows Vista and later operating systems.

The Gateway AnyKey is a programmable computer keyboard that was sold exclusively by Gateway 2000, Inc., as an option for some of their desktop computers. Introduced in the spring of 1991, the keyboard was manufactured in at least five known versions and incarnations by Tucson, Arizona–based Maxi Switch, Inc., a subsidiary of the Lite-On Technology Corporation. It was also sold by Maxi Switch themselves, as the ProKey II. The AnyKey proved popular, especially among power users and computer programmers, and soon gained a cult following. The AnyKey is no longer manufactured, Gateway having discontinued it by 1998 at the latest.
A macro recorder is software that records macros for playback at a later time. The main advantage of using a macro recorder is that it allows a user to easily perform complex operations much faster and with less effort without requiring custom computer programming or scripting.
A number of computer operating systems employ security features to help prevent malicious software from gaining sufficient privileges to compromise the computer system. Operating systems lacking such features, such as DOS, Windows implementations prior to Windows NT, CP/M-80, and all Mac operating systems prior to Mac OS X, had only one category of user who was allowed to do anything. With separate execution contexts it is possible for multiple users to store private files, for multiple users to use a computer at the same time, to protect the system against malicious users, and to protect the system against malicious programs. The first multi-user secure system was Multics, which began development in the 1960s; it wasn't until UNIX, BSD, Linux, and NT in the late 80s and early 90s that multi-tasking security contexts were brought to x86 consumer machines.
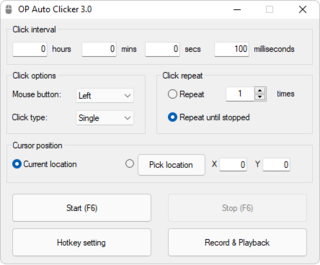
An auto clicker is a type of software or macro that can be used to automate the clicking of a mouse on a computer screen element. Some clickers can be triggered to repeat recorded input.

A mouse button is an electric switch on a computer mouse which can be pressed (“clicked”) to select or interact with an element of a graphical user interface. Mouse buttons are most commonly implemented as miniature snap-action switches.
Emacs, originally named EMACS, is a family of text editors that are characterized by their extensibility. The manual for the most widely used variant, GNU Emacs, describes it as "the extensible, customizable, self-documenting, real-time display editor". Development of the first Emacs began in the mid-1970s, and work on GNU Emacs, directly descended from the original, is ongoing; its latest version is 29.4 , released June 2024.













