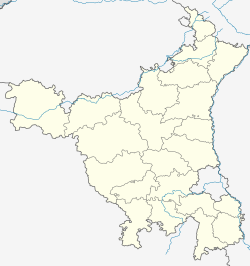
Hisar district is one of the 22 districts of Haryana, India. Hisar city serves as the district headquarters. Hisar district has four sub-divisions that is, Hisar, Barwala, Hansi and Narnaud, each headed by an SDM. The district is also part of Hisar division. Hisar was founded by Firuz Shah Tughlaq.

Rewari district is one of the 22 districts in the state of Haryana, India. It was carved out of Gurgaon district by the Government of Haryana on 1 November 1989. It is also part of the National Capital Region. The administrative headquarter of the district is the city of Rewari, which is also the biggest city in the district. In medieval times, it was an important market town. It is located in southern Haryana. As of 2011, it is the second least populous district of Haryana after Panchkula.

Lucknow district is a district located in the state of Uttar Pradesh in northern India. The city of Lucknow is the district headquarters and the district is part of Lucknow Division. It also is the capital of Uttar Pradesh Lucknow is Bounded on the east by Barabanki district, on the west by Unnao and Hardoi districts, on the south by Raebareli district and in the north by Sitapur district.

Mian Channu, alternately spelled Mian Chunnun, is the capital city of Mian Channu Tehsil in Khanewal District, Punjab province of Pakistan.
Narnaund is an emerging city on Hansi–Chandigarh highway, a municipal committee and Narnaund, in Hisar district in the Indian state of Haryana. The city Hansi is approximately 22 km away and another city Jind is 25 km. Narnaund is famous for its 'Main Bazar' as people from adjacent villages used to go there for purchases. The market has now developed to outer regions of the city also. Narnaund has famous Devraj-Mandir where people flock in large numbers on Ekadashi.
Safidon is a city and a municipal committee in Jind district in the Indian state of Haryana.Safidon was anciently known as "Sarp Daman"
Kharif crops, also known as monsoon crops or autumn crops, are domesticated plants that are cultivated and harvested in India, Pakistan and Bangladesh during the Indian subcontinent's monsoon season, which lasts from June to November depending on the area. Monsoon rains may begin as early as May in some parts of the Indian subcontinent, and crops are generally harvested from the third week of September to October. Rice, maize, and cotton are some of the major Kharif crops in India. Unlike the Rabi crops, which are grown in the winter, the kharif crops require good rainfall.
Morsand is a village in Sitamarhi district, Bihar state, India. It is situated 18 km. to the southeast of the town of Sitamarhi on the banks of the river - Lakhandei, and is connected to the district headquarters via National Highway 77 Sitamarhi- Hajipur. The nearest railway stations are Sitamarhi and Muzaffarpur, and the nearest airport is in Patna. Now a new railway station is established in the village itself with the name "Runni Saidpur", which will be providing rail connectivity from this village to the rest of India.

Rajasthan is a mineral-rich state and has a diversified economy having agriculture, mining and tourism as its main engines of growth. The state mines produce gold, silver, sandstone, limestone, marble, rock phosphate, copper and lignite. It is the second-largest producer of cement and contributes one tenth of the salt produced in India.

Rabi crops or rabi harvest, also known as winter crops, are agricultural crops that are sown in winter and harvested in the spring in India, Pakistan and Bangladesh. Complementary to the rabi crop is the kharif crop, which is grown after the rabi and zaid (zaa-id) crops are harvested one after another respectively.
Kanwari, also spelled Kunwari, or Kwari, is a village of 7,000 population, in Hansi-I Tehsil, Hisar-1 Rural Development Block, Hansi and Hisar of Hisar District of Hisar Division in the Haryana state of India. It is part of the saat bas bhaichara grouping of 7 villages. The village has 4 panna/patti (subdivisions), named as Nangalia Panna , upparla Panna , parla Panna , etc. with a total revenue land area of 43903 kanal or 5487 acre as per HALRIS records.

GSDP of Haryana state is estimated to be US$140 billion in 2023-2034 which had grown at 12.96% CAGR between 2012–17, boosted by the fact that this state on DMIC in NCR contributes 7% of India's agricultural exports and 60% of India's Basmati rice export, with 7 operational SEZs and additional 23 formally approved SEZs. Haryana also produces India's 67% of passenger cars, 60% of motorcycles, 50% of tractors and 50% of the refrigerators, which places Haryana on 14th place on the list of Indian states and union territories by GDP behind only much bigger states that are significantly larger in both area and population.
Datta is a village located in Hisar district in Haryana, India. Datta is a village in Hansi Tehsil of Hisar district in Haryana State of India. It is situated 36 km from Hisar city and 20 km from Hansi city on the road to Datta which also leads to Barwala. At Datta there is another road that leads to Narnaund. It is 15 km from Narnaund Tehsil and only 16 km from Barwala town. Datta comes under Roghi Khap Panchayat. There is an oil depot of HPCL situated on bianakhera road.
Kular is a village in Firozpur District, Punjab, India. It is located in south western Punjab, lying in close proximity with the Rajasthan State's Hanumangarh and Sri Ganganagar districts. Many farmers of the village own land in both Punjab and Rajasthan. The village, unlike its other counterparts of Punjab, including neighboring villages, has a very low population of Sikh community. This is one of the bases on which neighboring Haryana lays its claim on the region, repeatedly denied by the Punjab government. The land here is very productive and though the average holding size is small-except for a few landlords holding huge estates with an annual turnover of crores of rupees-people in general are prosperous.

Farming systems in India are strategically utilized, according to the locations where they are most suitable. The farming systems that significantly contribute to the agriculture of India are subsistence farming, organic farming, industrial farming. Regions throughout India differ in types of farming they use; some are based on horticulture, ley farming, agroforestry, and many more. Due to India's geographical location, certain parts experience different climates, thus affecting each region's agricultural productivity differently. India is very dependent on its monsoon cycle for large crop yields. India's agriculture has an extensive background which goes back to at least 9 thousand years. In India, in the alluvial plains of the Indus River in Pakistan, the old cities of Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa experienced an apparent establishment of an organized farming urban culture. That society, known as the Harappan or Indus civilization, flourished until shortly after 4000 BP; it was much more comprehensive than those of Egypt or Babylonia and appeared earlier than analogous societies in northern China. Currently, the country holds the second position in agricultural production in the world. In 2007, agriculture and other industries made up more than 16% of India's GDP. Despite the steady decline in agriculture's contribution to the country's GDP, agriculture is the biggest industry in the country and plays a key role in the socio-economic growth of the country. India is the second-largest producer of wheat, rice, cotton, sugarcane, silk, groundnuts, and dozens more. It is also the second biggest harvester of vegetables and fruit, representing 8.6% and 10.9% of overall production, respectively. The major fruits produced by India are mangoes, papayas, sapota, and bananas. India also has the biggest number of livestock in the world, holding 281 million. In 2008, the country housed the second largest number of cattle in the world with 175 million.
Bihar lies in the river plains of the basin of the river Ganga. It is endowed with fertile alluvial soil ground water resources. This makes the agriculture of Bihar rich and diverse. Rice, wheat, and maize are the major cereal crops. Arhar, urad, moong, gram, pea, lentils, and khesaria are some of the pulses cultivated in Bihar. Bihar is the largest producer of vegetables, which is dominated by potato, onion, eggplant, and cauliflower. In fruit cultivation, it is the largest producer of lychee and the third largest producer of pineapple, as well as a major producer of mango, banana, and guava. Sugar cane and jute are two other major cash crops of Bihar.
Moth Rangran, and Moth Karnail are two Panchayats of Moth village in Narnaund Tehsil in District Hisar of Haryana state in India. Sarpanch of Moth Rangran Is Jaswant Bhayana.
Nasopur is a village in Kotkasim, Tehsil Alwar district, in the Indian state of Rajasthan. It is located around 75 km south of Delhi, 75 km north of Alwar, and about 200 km north of Jaipur, the capital of Rajasthan. Nasopur is part of Greater Bhiwadi and National Capital Region (NCR).
Sahuwala is a village located in Bhadra Tehsil, within the Hanumangarh district in the state of Rajasthan, India. It is located near Haryana in the northern part of Rajasthan. It belongs to the Bikaner Division. Sahuwala has a few schools which are well rated and utilized by locals. The Sahuwala pincode is 335511.
Shop is also known as soap and sop, a village located in Uniara Tehsil of Tonk, a district of the state of Rajasthan in Western India.