
Ore is natural rock or sediment that contains one or more valuable minerals concentrated above background levels, typically containing metals, that can be mined, treated and sold at a profit. The grade of ore refers to the concentration of the desired material it contains. The value of the metals or minerals a rock contains must be weighed against the cost of extraction to determine whether it is of sufficiently high grade to be worth mining and is therefore considered an ore. A complex ore is one containing more than one valuable mineral.

Turquoise is an opaque, blue-to-green mineral that is a hydrous phosphate of copper and aluminium, with the chemical formula CuAl6(PO4)4(OH)8·4H2O. It is rare and valuable in finer grades and has been prized as a gemstone for millennia due to its hue.

The Berkeley Pit is a former open pit copper mine in the western United States, located in Butte, Montana. It is one mile (1.6 km) long by one-half mile (800 m) wide, with an approximate maximum depth of 1,780 feet (540 m). It is filled to a depth of about 900 feet (270 m) with water that is acidic, about the acidity of beer or tomatoes. As a result, the pit's water is laden with heavy metals and dissolved metals that leach from the rock in a natural process known as acid rock drainage. The dissolved metals include but are not limited to copper, arsenic, cadmium, zinc, and sulfuric acid.

Chuquicamata is the largest open pit copper mine in terms of excavated volume in the world. It is located in the north of Chile, just outside Calama, at 2,850 m (9,350 ft) above sea level. It is 215 km (134 mi) northeast of Antofagasta and 1,240 km (770 mi) north of the capital, Santiago. Flotation and smelting facilities were installed in 1952, and expansion of the refining facilities in 1968 made 500,000 tons annual copper production possible in the late 1970s. Previously part of Anaconda Copper, the mine is now owned and operated by Codelco, a Chilean state enterprise, since the Chilean nationalization of copper in the late 1960s and early 1970s. Its depth of 850 metres (2,790 ft) makes it the second deepest open-pit mine in the world, after Bingham Canyon Mine in Utah, United States.

Copper extraction refers to the methods used to obtain copper from its ores. The conversion of copper ores consists of a series of physical, chemical, and electrochemical processes. Methods have evolved and vary with country depending on the ore source, local environmental regulations, and other factors.

The National Copper Corporation of Chile, abbreviated as Codelco, is a Chilean state-owned copper mining company. It was formed in 1976 from foreign-owned copper companies that were nationalised in 1971.

The Ranau District is an administrative district in the Malaysian state of Sabah, part of the West Coast Division which includes the districts of Kota Belud, Kota Kinabalu, Papar, Penampang, Putatan, Ranau and Tuaran. The capital of the district is in Ranau Town. The landlocked district bordering the Sandakan Division to the east until it meets the Interior Division border. Ranau sits 108 km (67 mi) east of Kota Kinabalu and 227 km (141 mi) west of Sandakan. As of the 2010 Census, the population of the district was 94,092, an almost entirely Dusun ethnic community.

Mining in Japan is minimal because Japan does not possess many on-shore mineral resources. Many of the on-shore minerals have already been mined to the point that it has become less expensive to import minerals. There are small deposits of coal, oil, iron and minerals in the Japanese archipelago. Japan is scarce in critical natural resources and has been heavily dependent on imported energy and raw materials. There are major deep sea mineral resources in the seabed of Japan. This is not mined yet due to technological obstacles for deep sea mining.

Porphyry copper deposits are copper ore bodies that are formed from hydrothermal fluids that originate from a voluminous magma chamber several kilometers below the deposit itself. Predating or associated with those fluids are vertical dikes of porphyritic intrusive rocks from which this deposit type derives its name. In later stages, circulating meteoric fluids may interact with the magmatic fluids. Successive envelopes of hydrothermal alteration typically enclose a core of disseminated ore minerals in often stockwork-forming hairline fractures and veins. Because of their large volume, porphyry orebodies can be economic from copper concentrations as low as 0.15% copper and can have economic amounts of by-products such as molybdenum, silver, and gold. In some mines, those metals are the main product.

The Bingham Canyon Mine, more commonly known as Kennecott Copper Mine among locals, is an open-pit mining operation extracting a large porphyry copper deposit southwest of Salt Lake City, Utah, in the Oquirrh Mountains. The mine is the largest human-made excavation, and deepest open-pit mine in the world, which is considered to have produced more copper than any other mine in history – more than 19,000,000 short tons. The mine is owned by Rio Tinto Group, a British-Australian multinational corporation. The copper operations at Bingham Canyon Mine are managed through Kennecott Utah Copper Corporation which operates the mine, a concentrator plant, a smelter, and a refinery. The mine has been in production since 1906, and has resulted in the creation of a pit over 0.75 miles (1,210 m) deep, 2.5 miles (4 km) wide, and covering 1,900 acres. It was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1966 under the name Bingham Canyon Open Pit Copper Mine. The mine experienced a massive landslide in April 2013 and a smaller slide in September 2013.

Silver mining is the extraction of silver by mining. Silver is a precious metal and holds high economic value. Because silver is often found in intimate combination with other metals, its extraction requires the use of complex technologies. In 2008, approximately 25,900 metric tons of silver were consumed worldwide, most of which came from mining. Silver mining has a variety of effects on the environment, humans, and animals.
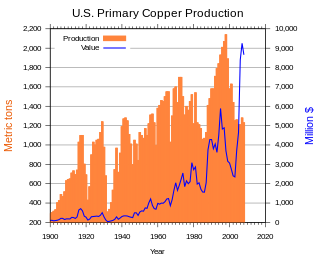
In the United States, copper mining has been a major industry since the rise of the northern Michigan copper district in the 1840s. In 2017, the US produced 1.27 million metric tonnes of copper, worth $8 billion, making it the world's fourth largest copper producer, after Chile, China, and Peru. Copper was produced from 23 mines in the US. Top copper producing states in 2014 were Arizona, Utah, New Mexico, Nevada, and Montana. Minor production also came from Idaho and Missouri. As of 2014, the US had 45 million tonnes of known remaining reserves of copper, the fifth largest known copper reserves in the world, after Chile, Australia, Peru, and Mexico.

The Leadville mining district, located in the Colorado Mineral Belt, was the most productive silver-mining district in the state of Colorado and hosts one of the largest lead-zinc-silver deposits in the world. Oro City, an early Colorado gold placer mining town located about a mile east of Leadville in California Gulch, was the location to one of the richest placer gold strikes in Colorado, with estimated gold production of 120,000–150,000 ozt, worth $2.5 to $3 million at the then-price of $20.67 per troy ounce.

Tajikistan has rich deposits of gold, silver, and antimony. The largest silver deposits are in Sughd Province, where Tajikistan's largest gold mining operation is also located. Russia's Norilsk nickel company has explored a large new silver deposit at Bolshoy Kanimansur. More than 400 mineral deposits of some 70 different minerals have been discovered in Tajikistan, including strontium, tungsten, molybdenum, bismuth, salt, lead, zinc, fluorspar, and mercury. These minerals have been found suitable for mining. Uranium, an important mineral in the Soviet era, remains in some quantity but is no longer being extracted. The Tajikistan Aluminium Company (TALCO), an aluminium smelter, is the country's only large-scale production enterprise in the mining sector. Tajikistan hosts the annual Mining World Tajikistan, an international exhibition on mining in Dushanbe.

The San Manuel Copper Mine was a surface and underground porphyry copper mine located in San Manuel, Pinal County, Arizona. Frank Schultz was the original discoverer, in 1879, but the main body of the deposits were discovered by Henry W. Nichols in 1942. The exploration drilling went on from 1943 to 1948, with the first mine shaft built 1948. Louis Lesser developed a mining city to service Nichols’ newly discovered deposits, and the development was completed about 1954. The first major production began in 1955. The mine and smelter were permanently closed in 2003.

The Toquepala mine is a large porphyry copper mine in the Tacna Province, Tacna Department, Peru. The mine is an open-pit mine producing copper, molybdenum, rhenium and silver with minor gold and zinc.
The Robinson Mine is a porphyry copper deposit located at Ruth, White Pine County, Nevada, in the Egan Range, 4 miles (6.4 km) west of Ely. The mine comprises three large open pits: Liberty, Tripp-Veteran and Ruth. The ore is extracted using conventional surface methods, and is then processed into a copper-gold concentrate, and a molybdenum concentrate in a concentrating plant. Since 2012 the mine has been owned and operated by Polish copper miner KGHM Polska Miedź

The Majdanpek mine is a large copper mine located in the east of Serbia in Bor District. Majdanpek represents one of the largest porphyry copper reserves in Serbia and in the world having estimated reserves of 619.5 million tonnes of ore grading 0.33% copper. The mine also has gold reserves amounting to 7.68 million oz and silver reserves of 56 million oz.
The Çöpler mine is a gold mine located in Erzincan Province, eastern Turkey. It is owned and operated by the Anagold Mining Inc., established in 2009. Explored in 1999, it is on an epithermal gold-silver-copper ore deposit, one of the largest in Turkey and in the world. The Çöpler mine started production in 2010.
The NorthMet Deposit is a deposit of minerals located in northeastern Minnesota contained within the geological region known as the Duluth Complex. The minerals contained in the deposit include copper, nickel, platinum, silver, palladium, and titanium.



















