
Interstate 97 (I-97) is a north-south Interstate Highway in the eastern United States. It runs entirely within Anne Arundel County, Maryland, for 17.62 miles (28.36 km) from U.S. Route 50/U.S. Route 301 (US 50/US 301) in Parole near Annapolis north to I-695 and I-895 in Brooklyn Park near Baltimore. The interstate is the primary highway between Baltimore and Annapolis. I‑97 connects Annapolis with Baltimore/Washington International Airport and links the northern Anne Arundel County communities of Crownsville, Millersville, Severna Park, Glen Burnie, and Ferndale. It is the second shortest primary Interstate Highway after I-87 in North Carolina.

Maryland Route 450 is a state highway in the U.S. state of Maryland. The state highway runs 30.19 miles (48.59 km) from U.S. Route 1 Alternate in Bladensburg east to US 50/US 301 and MD 2 near Arnold. MD 450 forms a local complement to US 50 from near Washington, D.C. through Annapolis. In Prince George's County, the highway is a four- to six-lane divided highway that serves Bladensburg, Landover Hills, New Carrollton, Lanham, and Bowie. In Anne Arundel County, MD 450 connects Crofton with Parole and Annapolis with the portion of the county east of the Severn River. The highway serves as one of the main streets of Annapolis, including the state capital's historic core, and is the primary vehicular access to the U.S. Naval Academy.

Maryland Route 18 (MD 18) is a state highway in the U.S. state of Maryland. The state highway runs 20.37 miles (32.78 km) from the beginning of state maintenance at Love Point east to MD 213 in Centreville. MD 18 is the main east–west local highway on Kent Island and east to Centreville, serving the centers of Stevensville, Chester, Kent Narrows, Grasonville, and Queenstown that are bypassed by U.S. Route 50 (US 50)/US 301. What is signed as MD 18 is actually a set of four suffixed highways: MD 18A, MD 18B, MD 18S, and MD 18C. There are also several unsigned segments of MD 18 scattered along the length of the signed portions.
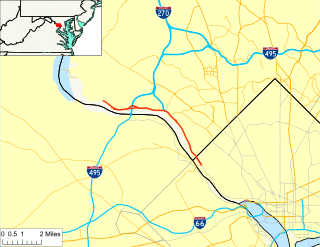
Clara Barton Parkway is an automobile parkway in the U.S. state of Maryland and the District of Columbia. The highway runs 6.8 miles (10.9 km) from MacArthur Boulevard in Carderock, Maryland, east to Canal Road at the Chain Bridge in Washington. Clara Barton Parkway is a two- to four-lane parkway that parallels the Potomac River and the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal (C&O) in southwestern Montgomery County, Maryland, and the far western corner of Washington. The parkway provides access to the communities of Cabin John and Glen Echo and several units of the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal National Historical Park. The Maryland portion of the George Washington Memorial Parkway was constructed from Carderock past Interstate 495 (I-495) to Glen Echo in the early to mid-1960s. The parkway was proposed to continue west to Great Falls and east to Georgetown. However, these proposals never came to fruition and the parkway was extended only to the Chain Bridge in the early 1970s. The Maryland portion of the George Washington Memorial Parkway was renamed in 1989 for Clara Barton, the founder of the American Red Cross, and whose original headquarters is located in Glen Echo.

Maryland Route 10 is a state highway in the U.S. state of Maryland. Known as the Arundel Expressway, the highway runs 7.17 miles (11.54 km) from MD 2 in Pasadena north to Interstate 695 (I-695) near Glen Burnie. MD 10 is a four- to six-lane freeway that serves as a bypass of MD 2 through Pasadena and Glen Burnie in northeastern Anne Arundel County. The Arundel Expressway was planned as a Baltimore–Annapolis freeway to provide relief to MD 2 between the cities as early as the 1950s. However, the portion of MD 10 south of Pasadena was removed from state plans when the I-97 corridor was chosen for the intercity freeway in the 1970s. MD 10 was constructed from I-695 to MD 710 in the early 1970s and continued south to MD 648 in the late 1970s. The freeway was extended south to MD 100 and completed to MD 2 in the late 1980s and early 1990s, respectively.

Maryland Route 3, part of the Robert Crain Highway, is the designation given to the former alignment of U.S. Route 301 from Bowie, Maryland, United States, to Baltimore. It is named for Robert Crain of Baltimore. It is unique in Maryland in that it has a business route and a truck route which do not connect to their parent; however, the business route is also a part of the Robert Crain Highway. MD 3's current orientation is vestigial from the construction of Maryland's freeway system.

Maryland Route 404 (MD 404) is a major highway on Maryland's Eastern Shore in the United States. Signed east-west, it runs 24.61 miles (39.61 km) from MD 662 in Wye Mills on the border of Queen Anne's and Talbot counties, southeast to the Delaware state line in Caroline County, where the road continues as Delaware Route 404 (DE 404) to the Five Points intersection near Rehoboth Beach. The Maryland and Delaware state highways together cross the width of the Delmarva Peninsula and serve to connect the Baltimore–Washington Metropolitan Area by way of the Chesapeake Bay Bridge and U.S. Route 50 (US 50) with the Delaware Beaches. Along the way, MD 404 passes through mostly farmland and woodland as well as the towns of Queen Anne, Hillsboro, and Denton. The route is a four-lane divided highway between US 50 and east of Denton, with the remainder of the route a two-lane undivided road.

Maryland Route 90 is a state highway in the U.S. state of Maryland. Known as the Ocean City Expressway, the state highway runs 11.83 miles (19.04 km) from U.S. Route 50 near Whaleyville east to MD 528 in Ocean City. MD 90 is a two-lane expressway that provides one of the main access routes to Ocean City, especially the northern part of the resort town, and thus sees heavy seasonal traffic. The highway was constructed from Ocean City starting in 1970. The state highway was opened west to MD 589 in 1972 and to US 113 in 1975. MD 90 was completed west to US 50 in 1976.

Maryland Route 179 is a state highway in the U.S. state of Maryland. Known for most of its length as St. Margarets Road, the highway runs 3.16 miles (5.09 km) from MD 648 near Annapolis east to the end of state maintenance in Cape St. Claire. MD 179 serves a suburban area near the southern end of the Broadneck Peninsula of northeastern Anne Arundel County. The state highway was paved in the 1920s from its western end to Skidmore near Sandy Point. MD 179 was truncated at what is now U.S. Route 50 /US 301 when their predecessor highway replaced the stretch to Skidmore in the early 1940s. MD 179 was extended into Cape St. Claire in the early 1990s.

U.S. Route 50 is a major east–west route of the U.S. Highway system, stretching just over 3,000 miles (4,800 km) from West Sacramento, California, east to Ocean City, Maryland, on the Atlantic Ocean. In the U.S. state of Maryland, US 50 exists in two sections. The longer of these serves as a major route connecting Washington, D.C., with Ocean City; the latter is the eastern terminus of the highway. The other section passes through the southern end of Garrett County for less than 10 miles (16 km) as part of the Northwestern Turnpike, entering West Virginia at both ends. One notable section of US 50 is the dual-span Chesapeake Bay Bridge across the Chesapeake Bay, which links the Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area with the Eastern Shore region, allowing motorists to reach Ocean City and the Delaware Beaches.

Maryland Route 144 is a collection of state highways in the U.S. state of Maryland. These highways are sections of old alignment of U.S. Route 40 between Cumberland and Baltimore. Along with US 40 Scenic, US 40 Alternate, and a few sections of county-maintained highway, MD 144 is assigned to what was once the main highway between the two cities, connecting those endpoints with Hancock, Hagerstown, Frederick, New Market, Mount Airy, Ellicott City, and Catonsville. MD 144 has seven disjoint sections of mainline highway that pass through the Appalachian Mountains in Allegany and Washington counties and the rolling Piedmont of Frederick, Carroll, Howard, and Baltimore counties.

Maryland Route 197 is a state highway in the U.S. state of Maryland. Known for most of its length as Laurel Bowie Road, the state highway runs 14.64 miles (23.56 km) from U.S. Route 301 in Bowie north to MD 198 in Laurel. MD 197 serves as the main connection between Bowie and Laurel in northern Prince George's County. The highway also provides access to Patuxent Wildlife Research Center and Bowie State University. MD 197 also connects US 50 in Bowie and the Baltimore–Washington Parkway in South Laurel with the Bowie State MARC station.

Maryland Route 704 is a state highway in the U.S. state of Maryland. Known as Martin Luther King Jr. Highway, the highway runs 6.53 miles (10.51 km) from Eastern Avenue at the District of Columbia boundary in Seat Pleasant east to MD 450 in Lanham. MD 704 is a four- to six-lane divided highway that connects the northern Prince George's County communities of Seat Pleasant, Landover, Glenarden, and Lanham. The highway was constructed along the right of way of the abandoned Washington, Baltimore and Annapolis Electric Railway (WB&A) in the early 1940s. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, MD 704 served as a temporary routing of U.S. Route 50 while the U.S. Highway's freeway was under construction from Washington to Lanham. The route was expanded to a divided highway between Seat Pleasant and US 50 in the late 1960s and early 1970s. MD 704 was completed as a divided highway when the portion east of US 50 was expanded in the late 1990s.

U.S. Route 301 (US 301) in the state of Maryland is a major highway that runs 122.85 miles (197.71 km) from the Governor Harry W. Nice Memorial Bridge over the Potomac River into Virginia northeast to Delaware. It passes through three of Maryland's four main regions: Southern Maryland, the Baltimore-Washington Metropolitan Area, and the Eastern Shore. US 301 serves mainly as a bypass of Baltimore and Washington, D.C. from Virginia to Delaware.

Maryland Route 214 is a state highway in the U.S. state of Maryland. Known for most of its length as Central Avenue, the highway runs 24.97 miles (40.19 km) from Southern Avenue and East Capitol Street at the District of Columbia boundary in Capitol Heights east to Beverley Beach. MD 214 connects the central Prince George's County suburbs of Capitol Heights, Seat Pleasant, Largo, and Bowie with the southern Anne Arundel County communities of Davidsonville and Edgewater and several beach villages along the Chesapeake Bay. The highway connects Interstate 95 (I-95)/I-495 to FedExField, Six Flags America, and several stations of the Washington Metro's Blue and Silver lines, which the route parallels between Capitol Heights and Largo.

Maryland Route 180 is a state highway in the U.S. state of Maryland. Known for most of its length as Jefferson Pike, the state highway runs 14.95 miles (24.06 km) from U.S. Route 340 in Knoxville east to Ballenger Creek Pike and Interstate 70 (I-70) in Frederick. MD 180 is the old alignment of US 340 through Knoxville, Petersville, and Jefferson in the Middletown Valley of western Frederick County. The state highway was originally constructed in the early 1910s and designated US 340 in 1927. MD 180 was assigned to the highway bypassed by the US 340 freeway between Sandy Hook in far southern Washington County and Jefferson in the mid-1960s. The state highway was extended east to Frederick and south along Ballenger Creek Pike after the US 340 freeway was completed in the late 1960s. MD 180 was rolled back to Frederick and removed from Washington County in 1989.

Interstate 70 (I-70) is a part of the Interstate Highway System that runs from Cove Fort, Utah, to Woodlawn just outside of Baltimore, Maryland. In Maryland, the Interstate Highway runs 91.85 miles (147.82 km) from the Pennsylvania state line in Hancock east to the Interstate's eastern terminus at its junction with I-695. I-70 is the primary east–west Interstate in Maryland; the Interstate Highway connects Baltimore—and Washington, D.C., via I-270—with Western Maryland. The Interstate serves Frederick and Hagerstown directly and provides access to Cumberland via its junction with I-68 at Hancock. I-70 runs concurrently with its predecessor highway, U.S. Route 40 (US 40), from Hancock to Indian Springs in Washington County and from Frederick to West Friendship in Howard County.

U.S. Route 40 in the U.S. state of Maryland runs from Garrett County in Western Maryland to Cecil County in the state's northeastern corner. With a total length of 221 miles (356 km), it is the longest numbered highway in Maryland. Almost half of the road overlaps or parallels with Interstate 68 (I-68) or I-70, while the old alignment is generally known as US 40 Alternate, US 40 Scenic, or Maryland Route 144. West of Baltimore, in the Piedmont and Appalachian Mountains / Blue Ridge region of the Western Maryland panhandle of the small state, the portions where it does not overlap an Interstate highway are mostly two-lane roads. The portion northeast of Baltimore going toward Wilmington in northern Delaware and Philadelphia in southeastern Pennsylvania is a four-lane divided highway, known as the Pulaski Highway. This section crosses the Susquehanna River at the north end of the Chesapeake Bay on the Thomas J. Hatem Memorial Bridge.

Maryland Route 665 is a state highway in the U.S. state of Maryland. Known as Aris T. Allen Boulevard, the state highway runs 2.68 miles (4.31 km) from U.S. Route 50 /US 301 in Parole east to Bywater Road and Forest Drive in Annapolis. MD 665 is a four-lane divided highway that connects US 50/US 301 and Interstate 97 (I-97) with MD 2 and the southern part of Annapolis and adjacent unincorporated communities on the Annapolis Neck in central Anne Arundel County. MD 665 was assigned to Forest Drive from MD 2 east to Bay Ridge Avenue circa 1950. The highway was relocated at its intersections with MD 387 and Bay Ridge Road in the 1960s. The Forest Drive iteration of MD 665 was removed from the state highway system in the late 1980s immediately before construction began on modern MD 665, which opened in 1992.





















