Related Research Articles
The Kujargé language is spoken in seven villages in eastern Chad near Jebel Mirra, and in villages scattered along the lower Wadi Salih and Wadi Azum in Darfur, Sudan. It is estimated to have about 1,000 speakers.
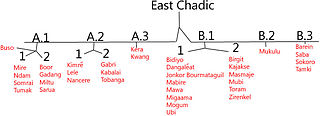
The three dozen East Chadic languages of the Chadic family are spoken in Chad and Cameroon.
The Agaw or Central Cushitic languages are Afro-Asiatic languages spoken by several groups in Ethiopia and, in one case, Eritrea. They form the main substratum influence on Amharic and other Ethiopian Semitic languages.
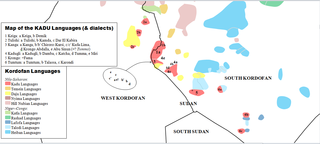
The Kadu languages, also known as Kadugli–Krongo or Tumtum, are a small language family of the Kordofanian geographic grouping, once included in Niger–Congo. However, since Thilo Schadeberg (1981), Kadu is widely seen as Nilo-Saharan. Evidence for a Niger-Congo affiliation is rejected, and a Nilo-Saharan relationship is controversial. A conservative classification would treat the Kadu languages as an independent family.
Mono is a language spoken by about 65,000 people in the northwestern corner of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is one of the Banda languages, a subbranch of the Ubangian branch of the Niger–Congo languages. It has five dialects: Bili, Bubanda, Mpaka, Galaba, and Kaga.
Baldemu, or Mbazlam, is a nearly extinct Afro-Asiatic language spoken in northern Cameroon. Baldamu is spoken in Bogo commune, Diamaré department, Far North Region by only 5 speakers as of 2012. Speakers have been shifting to Fulfulde.
Mbuko is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in the canton of Doulek, Méri subdivision, department of Diamaré, and also in parts of the canton of Serawa, Tokombéré subdivision, department of Mayo-Sava, in the Far North Region of Cameroon.
Bidiyo is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in south central Chad.
Dangaléat is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in central Chad. Speakers make up the majority of the population of Migami Canton in Mongo, Chad.
Mabire is a critically endangered Afro-Asiatic language spoken in Oulek village in Chad.
Ubi is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in Guéra region, Chad.
Mubi is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in central Chad. It forms one of the Mubi languages, a group of East Chadic languages.
Saba is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in south central Chad. Speakers are found in Sorki canton in Chinguil sub-prefecture.
Rendille is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken by the Rendille people inhabiting northern Kenya. It is part of the family's Cushitic branch.
Mundat is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in Plateau State, Nigeria in Mundat village of Bokkos LGA.

Ron is an Afro-Asiatic language cluster spoken in Plateau State, Nigeria. Dialects include Bokkos, Daffo-Mbar-Butura, Monguna/Manguna (Shagau),. Blench (2006) considers these to be separate languages.
Sha is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in Plateau State and Kaduna State, Nigeria. As of 2018, the language is used for face-to-face communication and lacks a standardized written form. It is spoken by approximately 1000 people and is considered sustainable.

The Rashad languages form a small language family in the Nuba Hills of Sudan. They are named after Rashad District of South Kordofan.
Polci is an Afro-Asiatic language of Bauchi State, Nigeria. It is part of the Barawa cluster, which is in turn part of the West Chadic language family.

The Ron, Ronic or Ron–Fyer languages, group A.4 of the West Chadic branch of the Afro-Asiatic language family, are spoken in Plateau State, north-central Nigeria.
References
- Hutchinson, Noelle, and Eric Johnson. 2006. A sociolinguistic survey of the Ubi language of Chad. SIL Electronic Survey Reports 2006-002. Dallas: SIL International. Online. URL: https://sil.org/silesr/abstract.asp?ref=2006-002.
- Jungraithmayr, Herrmann. 1981b. Über die Mawa (Guera, Tschad) – Ethnographische und linguistische Notizen. In: I. Hofmann (ed.), Festschrift zum 60. Geburtstag von P. Anton Vorbichler, 47–70.
- Roberts, James. 2009. Palatalization and Labialization in Mawa (Eastern Chadic). In: Rothmaler, Eva (ed.), Topics in Chadic Linguistics V, 129–140. Cologne: Rüdiger Köppe.
- Roberts, James. 2013. The tone system of Mawa. In: Henry Tourneux (ed.), Topics in Chadic Linguistics VII, Cologne: Rüdiger Köppe.