
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder and is made gas-tight by piston rings. In an engine, its purpose is to transfer force from expanding gas in the cylinder to the crankshaft via a piston rod and/or connecting rod. In a pump, the function is reversed and force is transferred from the crankshaft to the piston for the purpose of compressing or ejecting the fluid in the cylinder. In some engines, the piston also acts as a valve by covering and uncovering ports in the cylinder.

A two-strokeengine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes a power cycle with two strokes of the piston in one revolution of the crankshaft. A four-stroke engine requires four strokes of the piston to complete a power cycle in two crankshaft revolutions. In a two-stroke engine, the end of the combustion stroke and the beginning of the compression stroke happen simultaneously, with the intake and exhaust functions occurring at the same time.

An aircraft engine, often referred to as an aero engine, is the power component of an aircraft propulsion system. Aircraft using power components are referred to as powered flight. Most aircraft engines are either piston engines or gas turbines, although a few have been rocket powered and in recent years many small UAVs have used electric motors.

In internal combustion engines, exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) is a nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions reduction technique used in petrol/gasoline, diesel engines and some hydrogen engines. EGR works by recirculating a portion of an engine's exhaust gas back to the engine cylinders. The exhaust gas displaces atmospheric air and reduces O2 in the combustion chamber. Reducing the amount of oxygen reduces the amount of fuel that can burn in the cylinder thereby reducing peak in-cylinder temperatures. The actual amount of recirculated exhaust gas varies with the engine operating parameters.

A four-strokeengine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either direction. The four separate strokes are termed:
- Intake: Also known as induction or suction. This stroke of the piston begins at top dead center (T.D.C.) and ends at bottom dead center (B.D.C.). In this stroke the intake valve must be in the open position while the piston pulls an air-fuel mixture into the cylinder by producing a partial vacuum in the cylinder through its downward motion.
- Compression: This stroke begins at B.D.C, or just at the end of the suction stroke, and ends at T.D.C. In this stroke the piston compresses the air-fuel mixture in preparation for ignition during the power stroke (below). Both the intake and exhaust valves are closed during this stage.
- Combustion: Also known as power or ignition. This is the start of the second revolution of the four stroke cycle. At this point the crankshaft has completed a full 360 degree revolution. While the piston is at T.D.C. the compressed air-fuel mixture is ignited by a spark plug or by heat generated by high compression, forcefully returning the piston to B.D.C. This stroke produces mechanical work from the engine to turn the crankshaft.
- Exhaust: Also known as outlet. During the exhaust stroke, the piston, once again, returns from B.D.C. to T.D.C. while the exhaust valve is open. This action expels the spent air-fuel mixture through the exhaust port.

The Chevrolet "big-block" engine is a term for a series of large-displacement, naturally-aspirated, 90°, overhead valve, gasoline-powered, V8 engines; that were developed and produced by the Chevrolet Division of General Motors, from the 1950s until present.

The Chevrolet Vega is a subcompact automobile that was manufactured and marketed by GM's Chevrolet division from 1970 to 1977. Available in two-door hatchback, notchback, wagon, and sedan delivery body styles, all models were powered by an inline four-cylinder engine designed specifically for the Vega, with a lightweight, aluminum alloy cylinder block. The Vega first went on sale in Chevrolet dealerships on September 10, 1970. Variants included the Cosworth Vega, a short-lived limited-production performance model, introduced in the spring of 1975.
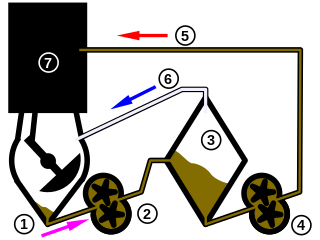
A dry-sump system is a method to manage the lubricating motor oil in four-stroke and large two-stroke piston driven internal combustion engines. The dry-sump system uses two or more oil pumps and a separate oil reservoir, as opposed to a conventional wet-sump system, which uses only the main sump below the engine and a single pump. A dry-sump engine requires a pressure relief valve to regulate negative pressure inside the engine, so internal seals are not inverted.

The Chevrolet Turbo-Air 6 is a flat-six air-cooled automobile engine developed by General Motors (GM) in the late 1950s for use in the rear-engined Chevrolet Corvair of the 1960s. It was used in the entire Corvair line, as well as a wide variety of other applications.

A crankcase is the housing in a piston engine that surrounds the crankshaft. In most modern engines, the crankcase is integrated into the engine block.

The Lamborghini Espada is a 4-seat grand touring coupé built by Italian car manufacturer Lamborghini between 1968 and 1978.

The Bourke engine was an attempt by Russell Bourke, in the 1920s, to improve the two-stroke internal combustion engine. Despite finishing his design and building several working engines, the onset of World War II, lack of test results, and the poor health of his wife compounded to prevent his engine from ever coming successfully to market. The main claimed virtues of the design are that it has only two moving parts, is lightweight, has two power pulses per revolution, and does not need oil mixed into the fuel.

A crankcase ventilation system (CVS) removes unwanted gases from the crankcase of an internal combustion engine. The system usually consists of a tube, a one-way valve and a vacuum source.

The ME Four-Twelve is an American high-performance concept car that was engineered, developed and produced by Chrysler in 2004. The name is a combination of the Mid-Engine with Four turbochargers on a Twelve cylinder engine.

Cox model engines are used to power small model airplanes, model cars and model boats. They were in production for more than 60 years between 1945 and 2006. The business is named for founder Leroy M. Cox. He started L.M. Cox Manufacturing Co. Inc, which later became Cox Hobbies Inc., then Cox Products, before being sold to Estes Industries, when it became Cox Models. On February 7, 2009, Estes Industries stopped producing Cox engines and sold all of their remaining inventory – mainly spare parts – to several private buyers from Canada and the US. One of the new owners of the remaining Cox engine and parts inventory has launched a website with an online store.
Crankcase dilution is a phenomenon of internal combustion engines in which unburned diesel or gasoline accumulates in the crankcase. Excessively rich fuel mixture or incomplete combustion allows a certain amount of fuel to pass down between the pistons and cylinder walls and dilute the engine oil. It is more common in situations where fuel is injected at a very high pressure, such as in a direct-injected diesel engine.
The Rover 16/50 and Rover 16 are mid-sized cars which were produced by Rover from 1926 to 1929 and non-continuously from 1936 to 1947 respectively.

An internal combustion engine is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high-pressure gases produced by combustion applies direct force to some component of the engine. The force is typically applied to pistons, turbine blades, a rotor, or a nozzle. This force moves the component over a distance. This process transforms chemical energy into kinetic energy which is used to propel, move or power whatever the engine is attached to.

Lightweighting is a concept in the auto industry about building cars and trucks that are less heavy as a way to achieve better fuel efficiency, battery range, acceleration, braking and handling. In addition, lighter vehicles can tow and haul larger loads because the engine is not carrying unnecessary weight. Excessive vehicle weight is also a contributing factor to particulate emissions from tyre and brake wear.

















