Related Research Articles

In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing calculations and data processing. By making use of artificial intelligence, algorithms can perform automated deductions and use mathematical and logical tests to divert the code execution through various routes. Using human characteristics as descriptors of machines in metaphorical ways was already practiced by Alan Turing with terms such as "memory", "search" and "stimulus".
The terms foobar, foo, bar, baz, and others are used as metasyntactic variables and placeholder names in computer programming or computer-related documentation. They have been used to name entities such as variables, functions, and commands whose exact identity is unimportant and serve only to demonstrate a concept.

Maxwell's equations, or Maxwell-Heaviside equations, are a set of coupled partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electromagnetism, classical optics, and electric circuits. The equations provide a mathematical model for electric, optical, and radio technologies, such as power generation, electric motors, wireless communication, lenses, radar etc. They describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated by charges, currents, and changes of the fields. The equations are named after the physicist and mathematician James Clerk Maxwell, who, in 1861 and 1862, published an early form of the equations that included the Lorentz force law. Maxwell first used the equations to propose that light is an electromagnetic phenomenon. The modern form of the equations in their most common formulation is credited to Oliver Heaviside.
In probability theory and statistics, a probability distribution is the mathematical function that gives the probabilities of occurrence of different possible outcomes for an experiment. It is a mathematical description of a random phenomenon in terms of its sample space and the probabilities of events.
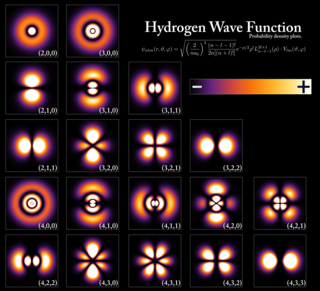
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science.

A regular expression is a sequence of characters that specifies a search pattern in text. Usually such patterns are used by string-searching algorithms for "find" or "find and replace" operations on strings, or for input validation. Regular expression techniques are developed in theoretical computer science and formal language theory.

An electric field is the physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles and exerts force on all other charged particles in the field, either attracting or repelling them. It also refers to the physical field for a system of charged particles. Electric fields originate from electric charges, or from time-varying magnetic fields. Electric fields and magnetic fields are both manifestations of the electromagnetic force, one of the four fundamental forces of nature.

Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes.
Pansexuality is sexual, romantic, or emotional attraction towards people regardless of their sex or gender identity. Pansexual people may refer to themselves as gender-blind, asserting that gender and sex are not determining factors in their romantic or sexual attraction to others.
Grey aliens, also referred to as Zeta Reticulans, Roswell Greys, or Grays, are purported extraterrestrial beings. They are frequent subjects of close encounters and alien abduction claims. The details of such claims vary widely, but typically Greys are described as being human-like with small bodies with smooth, grey-colored skin; enlarged, hairless heads; and large, black eyes. The Barney and Betty Hill abduction claim, which purportedly took place in New Hampshire in 1961, popularized Grey aliens. Precursor figures have been described in science fiction and similar descriptions appeared in early accounts of the 1948 Aztec UFO Hoax and later accounts of the 1947 Roswell UFO incident.

Os Lusíadas, usually translated as The Lusiads, is a Portuguese epic poem written by Luís Vaz de Camões and first published in 1572. It is widely regarded as the most important work of Portuguese-language literature and is frequently compared to Virgil's Aeneid. The work celebrates the discovery of a sea route to India by the Portuguese explorer Vasco da Gama (1469–1524). The ten cantos of the poem are in ottava rima and total 1,102 stanzas.
Representational state transfer (REST) is a software architectural style that describes a uniform interface between decoupled components in the Internet in a Client-Server architecture. REST defines four interface constraints:

Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) is a comprehensive controlled vocabulary for the purpose of indexing journal articles and books in the life sciences. It serves as a thesaurus that facilitates searching. Created and updated by the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), it is used by the MEDLINE/PubMed article database and by NLM's catalog of book holdings. MeSH is also used by ClinicalTrials.gov registry to classify which diseases are studied by trials registered in ClinicalTrials.
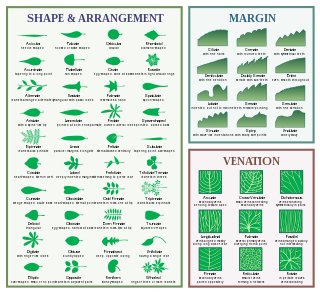
The following is a list of terms which are used to describe leaf morphology in the description and taxonomy of plants. Leaves may be simple or compound. The edge of the leaf may be regular or irregular, may be smooth or bearing hair, bristles or spines. For more terms describing other aspects of leaves besides their overall morphology see the leaf article.
Gaslighting is a colloquialism, loosely defined as making someone question their own reality. The expression, which derives from the title of the 1944 film Gaslight, became popular in the mid-2010s.
Gay is a term that primarily refers to a homosexual person or the trait of being homosexual. The term originally meant 'carefree', 'cheerful', or 'bright and showy'.

The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (UK), since 1922, comprises four constituent countries: England, Scotland, and Wales, as well as Northern Ireland. The UK Prime Minister's website has used the phrase "countries within a country" to describe the United Kingdom. Some statistical summaries, such as those for the twelve NUTS 1 regions of the United Kingdom, refer to Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland as "regions". With regard to Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales particularly, the descriptive name one uses "can be controversial, with the choice often revealing one's political preferences".

Metadata is "data that provides information about other data", but not the content of the data, such as the text of a message or the image itself. There are many distinct types of metadata, including:
JSON-LD is a method of encoding linked data using JSON. One goal for JSON-LD was to require as little effort as possible from developers to transform their existing JSON to JSON-LD. JSON-LD allows data to be serialized in a way that is similar to traditional JSON. It was initially developed by the JSON for Linking Data Community Group before being transferred to the RDF Working Group for review, improvement, and standardization, and is currently maintained by the JSON-LD Working Group. JSON-LD is a World Wide Web Consortium Recommendation.

Anatomical terminology is a form of scientific terminology used by anatomists, zoologists, and health professionals such as doctors.
References
- 1 2 "GlobIZ search". Global Information System on Pyraloidea. Retrieved June 15, 2017.
- ↑ Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London