
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biological species. It uses a set of precise criteria to evaluate the extinction risk of thousands of species and subspecies. These criteria are relevant to all species and all regions of the world. With its strong scientific base, the IUCN Red List is recognized as the most authoritative guide to the status of biological diversity. A series of Regional Red Lists are produced by countries or organizations, which assess the risk of extinction to species within a political management unit.

Sabiaceae is a family of flowering plants that were placed in the order Proteales according to the APG IV system. It comprises three genera, Meliosma, Ophiocaryon and Sabia, with 66 known species, native to tropical to warm temperate regions of southern Asia and the Americas. The family has also been called Meliosmaceae Endl., 1841, nom. rej.

Meliosma is a genus of flowering plants in the family Sabiaceae, native to tropical to warm temperate regions of southern and eastern Asia and the Americas. It is traditionally considered to contain about 100 species; some botanists take a much more conservative view accepting only 20-25 species as distinct. They are trees or shrubs, growing to 10–45 m tall.

A species that is extinct in the wild (EW) is one that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as known only by living members kept in captivity or as a naturalized population outside its historic range due to massive habitat loss.

Loxococcus rupicola is a species of palm tree, and the only species in the genus Loxococcus. It is endemic to Sri Lanka. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Satakentia liukiuensis, is a species of palm tree, endemic to Ishigaki Island and Iriomote Island in the Yaeyama Islands, the southwesternmost of the Ryukyu Islands, Japan. It is the only species in the genus Satakentia.
Tectiphiala ferox, or palmiste bouglé, is a species of flowering plant in the family Arecaceae. It is endemic to Mauritius.

Ceratozamia sabatoi is a species of plant in the family Zamiaceae. It is endemic to Mexico, where it occurs in the states of Hidalgo and Querétaro. It is known from only two localities, one of which is degraded by agriculture and grazing.

Helicia is a genus of 110 species of trees and shrubs, constituting part of the plant family Proteaceae. They grow naturally in rainforests throughout tropical South and Southeast Asia, including India, Sri Lanka, Indochina, Peninsular Malaysia to New Guinea and as far south as New South Wales.

Meliosma cordata is a species of plant in the Sabiaceae family. It is endemic to Panama.
Meliosma linearifolia is a species of plant in the Sabiaceae family. It is endemic to Panama. It is threatened by habitat loss.
Meliosma littlei is a species of plant in the Sabiaceae family. It is endemic to Ecuador.
Meliosma youngii is a species of plant in the Sabiaceae family. It is endemic to Peru.
Terminalia ivorensis is a species of tree in the family Combretaceae, and is known by the common names of Ivory Coast almond, idigbo, black afara, framire and emeri.
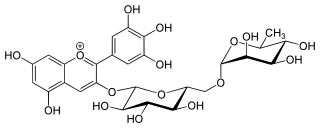
Tulipanin is an anthocyanin. It is the 3-O-rutinoside of delphinidin. It can be found in Alstroemeria spp., Berberis spp., Cissus sicyoides, Hymenocallis spp., Manihot utilissima, Meliosma tenuis, Musa acuminata, Ophiopogon japonicus, Petunia exserta, Petunia reitzii, blackcurrant, Schismatoglottis concinna, Secale cereale, Solanum betaceum, Thaumatococcus daniellii, Tulipa spp and in eggplants.

Ranitomeya sirensis is a species of poison dart frog found in the Amazonian rainforests of northern Bolivia, westernmost Brazil (Acre), and eastern Peru.

Meliosma beusekomii is an extinct species of Meliosma from the middle Eocene Clarno Formation of central Oregon

Meliosma simplicifolia is a species of plant in the family Sabiaceae. It is widely distributed in Asia from India through south-east Asia.

Meliosma rigida, the stiff-leaved meliosma, is a species of flowering plant in the family Sabiaceae. It is native to Laos, Vietnam, southern China, Taiwan, Japan, the Ryukyu Islands, and the Philippines.
Quercus nixoniana is an endangered species of oak tree native to southern Mexico. It is found in humid mountain forests of southwestern Mexico, in the states of Jalisco, Guerrero, and Oaxaca.














