
Bilirubin (BR) is a red-orange compound that occurs in the normal catabolic pathway that breaks down heme in vertebrates. This catabolism is a necessary process in the body's clearance of waste products that arise from the destruction of aged or abnormal red blood cells. In the first step of bilirubin synthesis, the heme molecule is stripped from the hemoglobin molecule. Heme then passes through various processes of porphyrin catabolism, which varies according to the region of the body in which the breakdown occurs. For example, the molecules excreted in the urine differ from those in the feces. The production of biliverdin from heme is the first major step in the catabolic pathway, after which the enzyme biliverdin reductase performs the second step, producing bilirubin from biliverdin.
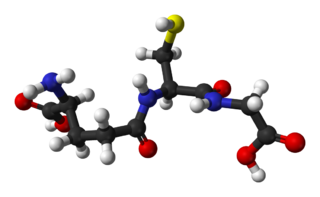
Glutathione is an organic compound with the chemical formula HOCOCH(NH2)CH2CH2CONHCH(CH2SH)CONHCH2COOH. It is an antioxidant in plants, animals, fungi, and some bacteria and archaea. Glutathione is capable of preventing damage to important cellular components caused by sources such as reactive oxygen species, free radicals, peroxides, lipid peroxides, and heavy metals. It is a tripeptide with a gamma peptide linkage between the carboxyl group of the glutamate side chain and cysteine. The carboxyl group of the cysteine residue is attached by normal peptide linkage to glycine.

In organic chemistry, a thiol, or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form R−SH, where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The −SH functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl group, or a sulfanyl group. Thiols are the sulfur analogue of alcohols, and the word is a blend of "thio-" with "alcohol".
Drug metabolism is the metabolic breakdown of drugs by living organisms, usually through specialized enzymatic systems. More generally, xenobiotic metabolism is the set of metabolic pathways that modify the chemical structure of xenobiotics, which are compounds foreign to an organism's normal biochemistry, such as any drug or poison. These pathways are a form of biotransformation present in all major groups of organisms and are considered to be of ancient origin. These reactions often act to detoxify poisonous compounds. The study of drug metabolism is the object of pharmacokinetics. Metabolism is one of the stages of the drug's transit through the body that involves the breakdown of the drug so that it can be excreted by the body.

4-Hydroxynonenal, or 4-hydroxy-2E-nonenal or 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal or 4-HNE or HNE,, is an α,β-unsaturated hydroxyalkenal that is produced by lipid peroxidation in cells. 4-HNE is the primary α,β-unsaturated hydroxyalkenal formed in this process. It is a colorless oil. It is found throughout animal tissues, and in higher quantities during oxidative stress due to the increase in the lipid peroxidation chain reaction, due to the increase in stress events. 4-HNE has been hypothesized to play a key role in cell signal transduction, in a variety of pathways from cell cycle events to cellular adhesion.

Glutathione S-transferases (GSTs), previously known as ligandins, are a family of eukaryotic and prokaryotic phase II metabolic isozymes best known for their ability to catalyze the conjugation of the reduced form of glutathione (GSH) to xenobiotic substrates for the purpose of detoxification. The GST family consists of three superfamilies: the cytosolic, mitochondrial, and microsomal—also known as MAPEG—proteins. Members of the GST superfamily are extremely diverse in amino acid sequence, and a large fraction of the sequences deposited in public databases are of unknown function. The Enzyme Function Initiative (EFI) is using GSTs as a model superfamily to identify new GST functions.

Iproniazid is a non-selective, irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class. It is a xenobiotic that was originally designed to treat tuberculosis, but was later most prominently used as an antidepressant drug. However, it was withdrawn from the market because of its hepatotoxicity. The medical use of iproniazid was discontinued in most of the world in the 1960s, but remained in use in France until its discontinuation in 2015.

Azinphos-methyl (Guthion) is a broad spectrum organophosphate insecticide manufactured by Bayer CropScience, Gowan Co., and Makhteshim Agan. Like other pesticides in this class, it owes its insecticidal properties to the fact that it is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. It is classified as an extremely hazardous substance in the United States as defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act, and is subject to strict reporting requirements by facilities which produce, store, or use it in significant quantities.
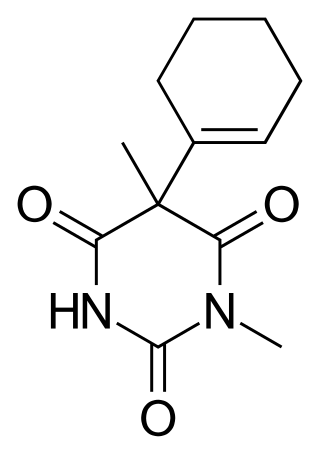
Hexobarbital or hexobarbitone, sold both in acid and sodium salt forms as Citopan, Evipan, and Tobinal, is a barbiturate derivative having hypnotic and sedative effects. It was used in the 1940s and 1950s as an agent for inducing anesthesia for surgery, as well as a rapid-acting, short-lasting hypnotic for general use, and has a relatively fast onset of effects and short duration of action. Modern barbiturates have largely supplanted the use of hexobarbital as an anesthetic, as they allow for better control of the depth of anesthesia. Hexobarbital is still used in some scientific research.

Gliotoxin is a sulfur-containing mycotoxin that belongs to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines produced by several species of fungi, especially those of marine origin. It is the most prominent member of the epipolythiopiperazines, a large class of natural products featuring a diketopiperazine with di- or polysulfide linkage. These highly bioactive compounds have been the subject of numerous studies aimed at new therapeutics. Gliotoxin was originally isolated from Gliocladium fimbriatum, and was named accordingly. It is an epipolythiodioxopiperazine metabolite that is one of the most abundantly produced metabolites in human invasive Aspergillosis (IA).
Glutathione synthetase deficiency (GSD) is a rare autosomal recessive metabolic disorder that prevents the production of glutathione. Glutathione helps prevent damage to cells by neutralizing harmful molecules generated during energy production. Glutathione also plays a role in processing medications and cancer-causing compounds (carcinogens), and building DNA, proteins, and other important cellular components.

In enzymology, maleylacetoacetate isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Xenobiotic metabolism is the set of metabolic pathways that modify the chemical structure of xenobiotics, which are compounds foreign to an organism's normal biochemistry, such as drugs and poisons. These pathways are a form of biotransformation present in all major groups of organisms, and are considered to be of ancient origin. These reactions often act to detoxify poisonous compounds; however, in cases such as in the metabolism of alcohol, the intermediates in xenobiotic metabolism can themselves be the cause of toxic effects.

Felinine, also known as (R)-2-amino-3-(4-hydroxy-2-methylbutan-2-ylthio)propanoic acid, is an amino acid found in cat urine and a precursor via microbial lyase of the putative cat pheromone and thiol called 3-mercapto-3-methylbutan-1-ol (MMB). Felinine is excreted by some Felidae species, including bobcats, Chinese desert cats, the kodkod, and domestic cats.

Glutathione S-transferase, C-terminal domain is a structural domain of glutathione S-transferase (GST).

Glutathione S-transferase A4, also known as GSTA4, is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the GSTA4 gene.

Bacterial glutathione transferases are part of a superfamily of enzymes that play a crucial role in cellular detoxification. The primary role of GSTs is to catalyze the conjugation of glutathione (GSH) with the electrophilic centers of a wide variety of molecules. The most commonly known substrates of GSTs are xenobiotic synthetic chemicals. There are also classes of GSTs that utilize glutathione as a cofactor rather than a substrate. Often these GSTs are involved in reduction of reactive oxidative species toxic to the bacterium. Conjugation with glutathione receptors renders toxic substances more soluble, and therefore more readily exocytosed from the cell.
Arsenic biochemistry is the set of biochemical processes that can use arsenic or its compounds, such as arsenate. Arsenic is a moderately abundant element in Earth's crust, and although many arsenic compounds are often considered highly toxic to most life, a wide variety of organoarsenic compounds are produced biologically and various organic and inorganic arsenic compounds are metabolized by numerous organisms. This pattern is general for other related elements, including selenium, which can exhibit both beneficial and deleterious effects. Arsenic biochemistry has become topical since many toxic arsenic compounds are found in some aquifers, potentially affecting many millions of people via biochemical processes.
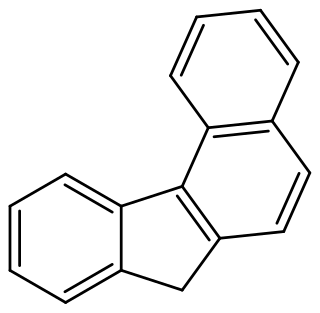
Benzo[c]fluorene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) with mutagenic activity. It is a component of coal tar, cigarette smoke and smog and thought to be a major contributor to its carcinogenic properties. The mutagenicity of benzo[c]fluorene is mainly attributed to formation of metabolites that are reactive and capable of forming DNA adducts. According to the KEGG it is a group 3 carcinogen. Other names for benzo[c]fluorene are 7H-benzo[c]fluorene, 3,4-benzofluorene, and NSC 89264.

Glycidamide is an organic compound with the formula H2NC(O)C2H3O. It is a colorless oil. Structurally, it contains adjacent amides and epoxide functional groups. It is a bioactive, potentially toxic or even carcinogenic metabolite of acrylonitrile and acrylamide. It is a chiral molecule.
















