Related Research Articles

Sukabumi Regency is a regency (kabupaten) in southwestern Java, as part of West Java province of Indonesia. The regency seat is located in Palabuhan Ratu, a coastal district facing the Indian Ocean. The regency fully encircles the administratively separated city of Sukabumi. Covering an area of 4,164.15 km2, the regency is the largest regency in West Java and the second largest regency on Java after the Banyuwangi Regency in East Java. The regency had a population of 2,341,409 at the 2010 census and 2,725,450 at the 2020 census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 2,802,404, with a large proportion of it living in the northeastern part of the regency that encircles Sukabumi City, south of Mount Gede. A plan to create a new regency, the putative North Sukabumi Regency, is currently waiting for the approval of the central government, which has been deferred until the end of the current morotorium on new creations of regencies.
The Batin are a sub-group of Malay people that inhabits the interior parts of Jambi province

Rejang Lebong is a regency of Bengkulu Province, Indonesia, on the island of Sumatra. This regency originally included a much larger part of the inland part of the province, lying to the east of the watershed of the Barisan Mountains, but on 25 February 2003 it was divided in three, with districts in the northwest being split off to form a separate Lebong Regency, and districts in the south being similarly split off to form a new Kepahiang Regency.

Mukomuko is a regency of Bengkulu Province, Indonesia, on the island of Sumatra. It was originally part of the North Bengkulu Regency, but on 25 February 2003 that regency was split into two parts, the northwestern part created as a separate Mukomuko Regency. It covers a land area of 4,146.52 km2 and had a population of 155,753 at the 2010 census, which rose to 190,498 at the 2020 census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 198,794 - comprising 102,576 males and 96,218 females. The administrative centre of the Mukomuko Regency is Mukomuko town.
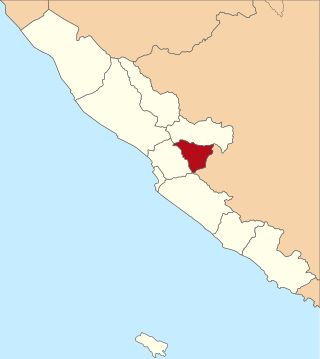
Kepahiang is a regency in Bengkulu Province of Indonesia. It is located on the island of Sumatra, and was created on 25 February 2003 by splitting off the areas of the former southern districts of Rejang Lebong Regency. It covers an area of 710.11 km2, of which a high percentage (27%) is still forest; thus it is the smallest of the province's regencies. It had a population of 124,865 at the 2010 Census and 149,298 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 154,651. The regency seat is Kepahiang town. The local population consists of various ethnic groups such as the Rejang, Serawai, Javanese, Lembak and Sundanese, among which Rejang forms the majority in Kepahiang.

The Mina River is a river of Timor, in the province of East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia, about 2000 km east of the capital Jakarta. Above this river also stretches the Noelmina Bridge which connects Kupang with the South Central Timor Regency.

Lebong is an inland regency of Bengkulu Province, Indonesia, on the island of Sumatra. It lies on the eastern slopes of the Barisan Mountains, the main watershed of Sumatra, thus draining towards the island's east coast. It covers an area of 1,665.28 km2, and had a population of 97,091 at the 2010 Census and 106,293 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 110,347 - comprising 56,410 males and 53,937 females. Contrary to the popularly-held belief that the town of Muara Aman is the seat of the government of Lebong Regency, the regency's capital is actually located in neighboring Tubei District, where all the offices and judiciary institution are situated.

Sumedang Larang is an Islamic Kingdom based in Sumedang, West Java. Its territory consisted of the Parahyangan region, before becoming a vassal state under the Mataram Sultanate.

The Lampung or Lampungese are an indigenous ethnic group native to Lampung and some parts of South Sumatra, Bengkulu, as well as in the southwest coast of Banten. They speak the Lampung language, a Lampungic language estimated to have 1.5 million speakers.

The Muna or Wuna are the indigenous group which primarily inhabit the islands of Buton and Muna. They speak languages from the Muna-Buton language group.

Rejang people are an Austronesian ethnolinguistic group, native to the some parts of Bengkulu Province and South Sumatera Province in the southwestern part of Sumatera Island, Indonesia. They occupied some area in a cool mountain slopes of the Barisan mountain range in both sides of Bengkulu and South Sumatra. With approximately more than 1,3 million people, they form the largest ethnic group in Bengkulu Province. Rejang people predominantly live as a majority in 5 out 10 regencies and city of Bengkulu Province, while the rest of them who lives in South Sumatera resides at 7 villages in the district called as Bermani Ulu Rawas. The Rejangs are predominantly an Islam adherent group with small numbers following a religion other than Islam. According to research, Rejang people are the descendants of the Bukar-Sadong people who migrated from Northern Borneo (Sarawak).

The State of East Java was a federal state (negara bagian) formed on the Indonesian island of Java by the Netherlands in 1948. It subsequently became a component of the United States of Indonesia, but merged into the Republic of Indonesia on 9 March 1950.
Mante people or also spelled as Mantir, are one of the earliest ethnic groups frequently mentioned in legendary folklore to have inhabited Aceh, Indonesia. This ethnic group, along with other indigenous people such as the Illanun people, Sakai people, Jakun people, Senoi and Semang, are the ethnic groups that formed the existing Acehnese people today. The Mante people are regarded as part of the Proto-Malay people group that initially settled around the region of Aceh Besar Regency and in the interior jungle. These indigenous people were thought to have migrated to Aceh through the Malay Peninsula. In the Acehnese legend, the Batak and Mante people were mentioned as the descendants of Kawom Lhèë Reutōïh ; which were also one of the indigenous peoples in Aceh, Indonesia. Today, the Mante people are extinct or have disappeared as a result of intermarriage with other non-indigenous people groups that arrived later. To date, there is no strong scientific evidence for the existence of this people.

Islam in Central Sulawesi, a province of Indonesia, is the majority religion embraced by around 75% of the province's 2,683,722 inhabitants . The propagators of Islam were thought to enter Central Sulawesi through neighboring regions, namely Bone, Wajo, and Mandar from the south and west routes, and through Gorontalo and Ternate from the north and east routes via Tomini Bay and Tolo Bay.
In Indonesian law, the term "city" is generally defined as the second-level administrative subdivision of the Republic of Indonesia, an equivalent to regency. The difference between a city and a regency is that a city has non-agricultural economic activities and a dense urban population, while a regency comprises predominantly rural areas and is larger in area than a city. However, Indonesia historically had several classifications of cities.
Cirebon Sundanese is a variety of conversation in Sundanese in the ex-Residency of Cirebon and its surroundings, which includes Kuningan, Majalengka, Cirebon, Indramayu and Subang as well as Brebes in Central Java.
The Dayak Desa War or Majang Desa War was an armed uprising by the Dayak Desa tribe in West Kalimantan against the Japanese Empire during World War II, and shortly thereafter by Indonesian nationalists against the Dutch East Indies. The war was initially caused by the local population's opposition against the rōmusha system and disappointment with Japanese occupation. In the initial phase of Japanese occupation, several Japanese companies entered the region to gain natural resources in order to support the Japanese war effort in the Pacific. Occupying Japanese forced locals to work for free for these companies, mainly in coal mining and timber production. After that, a Japanese foreman working in a company wanted to marry the daughter of Pang Linggan, a respected Dayak chief in the region, which caused more tension between locals and the Japanese. Dayak tribes in the region initiated mangkuk merah ritual, as a sign to mobilise men from villages and prepare for war. The Japanese were driven out of the Borneo interior in June 1945, but returned on 17 July and continued until 31 August 1945 when Japanese forces there surrendered and left the region, replaced by Allied forces including the Dutch, who would later be opposed again until recognition of Indonesian independence in 1949.

Muhammad Kaharuddin III was an Indonesian politician and royal who was the 16th Sultan of Sumbawa, a senator of the United States of Indonesia, and the regent of Sumbawa Regency between 1959 and 1960. He was also active in the politics of the State of East Indonesia, where he chaired its legislature between 1947 and its dissolution in 1950.
Lembak people, also known as Linggau people, are a local ethnic group that inhabits several areas of Bengkulu Province and South Sumatra Province in Indonesia. Their original settlements are in the border area between the two provinces, in the Barisan mountain range, with densely clustered villages pattern.
References
- 1 2 BPS Kabupaten Kepahiang 2021, pp. 4.
- ↑ "Kecamatan, Kelurahan, dan Desa". Situs Web Resmi Kabupaten Kepahiang. Retrieved 28 March 2022.
- ↑ LeBar 1976, pp. 191.
- ↑ "Mengupas Sejarah Rejang di Kabupaten Lebong". Kupas Bengkulu. 4 July 2014. Retrieved 29 March 2022.
- ↑ Siddik 1980, pp. 51.
- ↑ Proyek Penelitian dan Pencatatan Kebudayaan Daerah 1989, pp. 89.
- ↑ BPS Kabupaten Kepahiang 2021, pp. 3, 13.
- ↑ BPS Kabupaten Kepahiang 2021, pp. 12.
- ↑ Tomi, Bayu Azan (25 June 2021). "Pelatihan TPK di Aula Kantor Camat Merigi" [TPK training in the Simpang Kota Bingin's official hall]. Official Website of Simpang Kota Bingin Village. Retrieved 30 March 2022.
- ↑ BPS Kabupaten Kepahiang 2021, pp. 19.
- ↑ BPS Kabupaten Kepahiang 2021, pp. 20.
- ↑ Mutmaidah 2018, pp. 29.