
Bartonella is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria. It is the only genus in the family Bartonellaceae. Facultative intracellular parasites, Bartonella species can infect healthy people, but are considered especially important as opportunistic pathogens. Bartonella species are transmitted by vectors such as fleas, sand flies, and mosquitoes. At least eight Bartonella species or subspecies are known to infect humans.
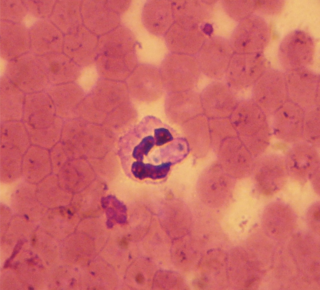
Hepatozoon is a genus of Apicomplexa alveolates which incorporates over 300 species of obligate intraerythrocytic parasites. Species have been described from all groups of tetrapod vertebrates, as well as a wide range of haematophagous arthropods, which serve as both the vectors and definitive hosts of the parasite. By far the most biodiverse and prevalent of all haemogregarines, the genus is distinguished by its unique reciprocal trophic lifecycle which lacks the salivary transmission between hosts commonly associated with other apicomplexans. While particularly prevalent in amphibians and reptiles, the genus is more well known in veterinary circles for causing a tick-borne disease called hepatozoonosis in some mammals.

The Plasmodiidae are a family of apicomplexan parasites, including the type genus Plasmodium, which is responsible for malaria. This family was erected in 1903 by Mesnil and is one of the four families in the order Haemospororida.
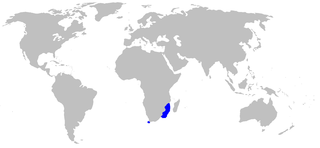
The white-spotted Izak or African spotted catshark is a catshark of the family Scyliorhinidae. It is found in the western Indian Ocean off the coasts of Natal, South Africa, southern Mozambique, Madagascar, Kenya, and Tanzania between latitudes 4° S and 37° S, at depths of between 220 and 440 m. It can grow up to 35 cm in length.
Plasmodium basilisci is a parasite of the genus Plasmodium subgenus Carinamoeba.

Haemoproteus is a genus of alveolates that are parasitic in birds, reptiles, and amphibians. Its name is derived from Greek: haima 'blood' and Proteus, a sea god that had the power to assume various shapes. The name Haemoproteus was first used in the description of H. columbae in the blood of the pigeon Columba livia by Walther Kruse in 1890. This was also the first description of this genus. Two other genera—Halteridium and Simondia—are now considered to be synonyms of Haemoproteus.

The Haemosporida are an order of intraerythrocytic parasitic alveolates.
Karyolysus is a genus of coccidia. With the exception of K. sonomae whose vertebrate host is the yellow-legged frog, species in this genus only infect lizards of the genus Lacerta.
Plasmodium vaughani is a parasite of the genus Plasmodium, and the type species of the subgenus Novyella. As in all Plasmodium species, P. vaughani has both vertebrate and insect hosts. The vertebrate hosts for this parasite are birds.
Plasmodium tropiduri is a parasite of the genus Plasmodium subgenus Lacertaemoba. As in all Plasmodium species, P. tropiduri has both vertebrate and insect hosts. The vertebrate hosts for this parasite are reptiles.
The Channa barb, is a species of cyprinid fish endemic to India where it occurs in hill streams in forested areas. This species can reach a length of 19.6 centimetres (7.7 in) TL. This species is also found in the aquarium trade. This species is the only member of its genus.
Haemosporidiasina (Haemosporidia) is a subclass of apicomplexans described by Jacques Euzéby in 1988. The taxon is very similar to Aconoidasida.
Billbraya is a genus of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexia. It contains a single recognised species, Billbraya australis.
Progarnia is a genus of parasitic alveolates belonging to the phylum Apicomplexa.
Garnia is a genus of parasitic alveolates belonging to the phylum Apicomplexia.
Babesiosoma is a genus of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexia.
Dactylosoma is a genus of parasitic alveolates of the phylum Apicomplexa.
Anthemosoma is a genus of parasites of the phylum Apicomplexa. There is only one species recognised in this genus - a parasite of mammals.
Sauroplasma is a genus of parasites of the phylum Apicomplexa.
Aseptatorina is a suborder of parasitic alveolates of the phylum Apicomplexa





