ATC code C04Peripheral vasodilators is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup C04 is part of the anatomical group C Cardiovascular system.
A rubefacient is a substance for topical application that produces redness of the skin, e.g. by causing dilation of the capillaries and an increase in blood circulation. It has sometimes been used to relieve acute or chronic pain, but there is limited evidence as to its efficacy, and as of 2014 the best evidence does not support using gels and creams containing rubefacients for this purpose.

Maleic acid or cis-butenedioic acid is an organic compound that is a dicarboxylic acid, a molecule with two carboxyl groups. Its chemical formula is HO2CCH=CHCO2H. Maleic acid is the cis isomer of butenedioic acid, whereas fumaric acid is the trans isomer. Maleic acid is mainly used as a precursor to fumaric acid, and relative to its parent maleic anhydride, which has many applications.

Picamilon is a drug formed by a synthetic combination of niacin and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). It was developed in the Soviet Union in 1969 and further studied in both Russia and Japan as a prodrug of GABA.
Ralgex is a brand of topical analgesic sprays and creams for soothing painful muscles and joints in humans when applied to the skin. It is manufactured by GlaxoSmithKline.

In enzymology, a nicotinate-nucleotide-dimethylbenzimidazole phosphoribosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a nicotinate-nucleotide diphosphorylase (carboxylating) (EC 2.4.2.19) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a nicotinate phosphoribosyltransferase (EC 6.3.4.21) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Inositol nicotinate, also known as inositol hexanicotinate or inositol hexaniacinate, is a compound of niacin and inositol. It is marketed in the United States as a "no-flush" form of niacin in dietary supplements.

Xanthinol is a drug prepared from theophylline used as a vasodilator. It is most often used as the salt with niacin, known as xanthinol nicotinate.

Angraecum leonis is a species of flowering plant in the family Orchidaceae.
The molecular formula C7H7NO2 (molar mass: 137.14 g/mol) may refer to:

Chromium(III) nicotinate is an ionic substance used for chromium supplementation in some nutritional products, where it is also referred to as chromium polynicotinate. It appears in products that are referred to as a medical food used for nutritional support for conditions associated with diabetes mellitus type 2. The product is also known as "niacin-bound chromium".

Nicotinate dehydrogenase (cytochrome) (EC 1.17.2.1, nicotinic acid hydroxylase, nicotinate hydroxylase) is an enzyme with systematic name nicotinate:cytochrome 6-oxidoreductase (hydroxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Estrapronicate, also known as estradiol nicotinate propionate is an estrogen medication and estrogen ester which was never marketed. It was studied as a component of the experimental tristeroid combination drug Trophobolene, which contained nandrolone decanoate, estrapronicate, and hydroxyprogesterone heptanoate.

Solute carrier family 22 member 13 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC22A13 gene.
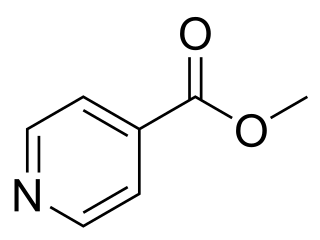
Methyl isonicotinate is a toxic compound, which is used as a semiochemical. Other names for this compound are 4-pyridine carboxylic acid, and isonicotinic acid methyl ester. This compound is slightly toxic to the human body. It has an irritating effect on the eyes, skin, and respiratory tract. Moreover, the compound is used as the active ingredient in several sticky thrip traps to monitor and catch thrips in greenhouses.













