
Operation Peter Pan was a clandestine exodus of over 14,000 unaccompanied Cuban minors ages 6 to 18 to the United States over a two-year span from 1960 to 1962. They were sent by parents who feared, on the basis of unsubstantiated rumors, that Fidel Castro and the Communist party were planning to terminate parental rights and place minors in alleged "communist indoctrination centers", commonly referred to as the Patria Potestad. No such actions by the Castro regime ever took place.

Joan Didion was an American writer and journalist. She is considered one of the pioneers of New Journalism, along with Gay Talese, Hunter S. Thompson, and Tom Wolfe.

A Cuban sandwich is a variation of a ham and cheese sandwich that likely originated in cafes catering to Cuban workers in Tampa or Key West, two early Cuban immigrant communities in Florida centered on the cigar industry. Later on, Cuban exiles and expatriates brought it to Miami, where it is also very popular. The sandwich is made with ham, mojo, roasted pork, Swiss cheese, pickles, mustard, and sometimes salami on Cuban bread. Salami is included in Tampa, but is not usually included in South Florida.

Cuban cuisine is largely based on Spanish cuisine with influence from Taino, African and other Caribbean cuisines. Some Cuban recipes share spices and techniques with Spanish, Taino and African cooking, with some Caribbean influence in spice and flavor. This results in a blend of several different cultural influences. A small but noteworthy Chinese influence can also be accounted for, mainly in the Havana area. There is also some Italian influence. During colonial times, Cuba was an important port for trade, and the Spanish ancestors of Cubans brought with them the culinary traditions of different parts of Spain.

Orlando Bosch Ávila was a Cuban exile militant, who headed the Coordination of United Revolutionary Organizations (CORU), described by the United States Federal Bureau of Investigation as a terrorist organization. Born in Cuba, Bosch attended medical school at the University of Havana, where he befriended Fidel Castro. He worked as a doctor in Santa Clara Province in the 1950s, but moved to Miami in 1960 after he stopped supporting the Cuban Revolution.

Lydia Cabrera was a Cuban independent ethnographer, writer, and literary activist. She was an authority on Santería and other Afro-Cuban religions. During her lifetime she published over one hundred books; little of her work is available in English. Her most important book is El Monte, which was the first major ethnographic study of Afro-Cuban traditions, herbalism and religion. First published in 1954, the book became a "textbook" for those who practice Lukumi and Palo Monte both religions reaching the Caribbean through enslaved Africans. Her papers and research materials were donated to the Cuban Heritage Collection - the largest repository of materials on or about Cuba located outside of Cuba - forming part of the library of the University of Miami. A section in Guillermo Cabrera Infante's book Tres Tigres Tristes is written under Lydia Cabrera's name, in a comical rendition of her literary voice. She was one of the first writers to recognize and sensitively publish on the richness of Afro-Cuban culture and religion. She made valuable contributions in the areas of literature, anthropology, art, ethnomusicology, and ethnology.

Little Havana is a neighborhood of Miami, Florida, United States. Home to many Cuban exiles, as well as many immigrants from Central and South America, Little Havana is named after Havana, the capital and largest city in Cuba.

Ana Mendieta was a Cuban-American performance artist, sculptor, painter, and video artist who is best known for her "earth-body" artwork. She is considered one of the most influential Cuban-American artists of the post–World War II era. Born in Havana, Cuba, Mendieta left for the United States in 1961.

Cuban Americans are Americans who immigrated from or are descended from immigrants from Cuba. As of 2023, Cuban Americans were the fourth largest Hispanic and Latino American group in the United States after Mexican Americans, Stateside Puerto Ricans and Salvadoran Americans.
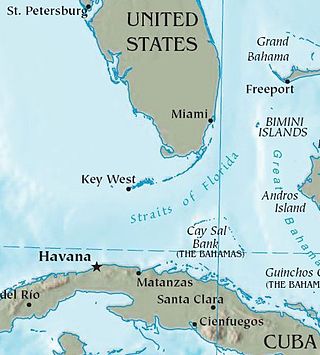
The Cuban exodus is the mass emigration of Cubans from the island of Cuba after the Cuban Revolution of 1959. Throughout the exodus, millions of Cubans from diverse social positions within Cuban society emigrated within various emigration waves, due to political repression and disillusionment with life in Cuba. Between 1959 and 2023, some 2.9 million Cubans emigrated from Cuba.
The Coordination of United Revolutionary Organizations was a militant group responsible for a number of terrorist activities directed at the Cuban government following the Cuban Revolution. The United States government provided them with extensive financial and logistical support throughout their existence. It was founded by a group that included Orlando Bosch and Luis Posada Carriles, both of whom worked with the CIA at various times, and was composed chiefly of Cuban exiles opposed to the Castro government. It was formed in 1976 as an umbrella group for a number of anti-Castro militant groups. Its activities included a number of bombings and assassinations, including the killing of human-rights activist Orlando Letelier in Washington, D.C., and the bombing of Cubana Flight 455 which killed 73 people.

Jose Miguel Battle Sr. was a policeman and Cuban exile who served in the unsuccessful Bay of Pigs Invasion to overthrow the communist Cuban government under Fidel Castro in 1961. He later became the nominal leader and founder of The Corporation, also known as the Cuban Mafia, and he invested in the gambling industry in the United States and Peru. He was eventually convicted of racketeering and sentenced to 20 years in prison.

Christianity has played an important role in Cuba's history. Cuba was discovered by Christopher Columbus a few days after he arrived to the New World in 1492. In 1511, colonization began when the Conquistador Diego Velázquez de Cuéllar established the Catholic Church in Cuba with the early priest Fray Bartolomé de las Casas known commonly as "the Protector of the Indians". Along with Catholicism, Protestantism came during the same time.
Miguel Cubiles is a Cuban-Mexican artist, specializing in paintings, ceramics and engravings.
Emilio Falero is a Cuban Fine Arts painter residing in Florida.
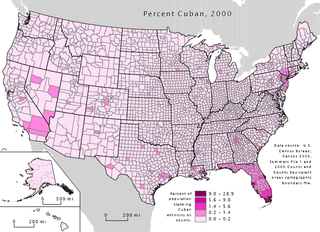
Cuban immigration has greatly affected Miami-Dade County since 1959, creating what is known as "Cuban Miami." However, Miami reflects global trends as well, such as the growing trends of multiculturalism and multiracialism; this reflects the way in which international politics shape local communities.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Miami in Miami-Dade County, Florida, United States.
José María Mijares was a Cuban contemporary visual artist. He began drawing in his adolescent years and entered the San Alejandro Academy of Fine Arts on a scholarship at the age of 16. His greatest influences were the artists of the "Havana School": Carlos Enríquez, René Portocarrero, Cundo Bermúdez, as well as his professors, most notable being modernist painter Fidelio Ponce. He was also a part of the influential group, Los Diez Pintores Concretos, or as they are usually referred to, Los Diez. Although the group had a relatively short life, 1959–1961, and exhibited together only a few times, they remain an important part of Cuba's art history especially in the pre-Castro years and leading up to the revolution. He left Cuba in 1968, resigning his teaching position at the academy when Fidel Castro came into power. Based in Miami, he continued to be a prolific painter and until his death in 2004, at the age of 82.

Baruj Salinas was a Cuban-American contemporary visual artist and architect. He is recognized as a central figure in the establishment of the modern Latin American art market in South Florida.
Miguel Jorge (1928–1984), also known as “Micky” Jorge, was a Cuban artist who was influential in the establishment of South Florida's early Latin American art market in the Greater Miami area from the 1960s through the 1980s.














