
El Salvador, officially the Republic of El Salvador, is a country in Central America. It is bordered on the northeast by Honduras, on the northwest by Guatemala, and on the south by the Pacific Ocean. El Salvador's capital and largest city is San Salvador. The country's population in 2023 was estimated to be 6.5 million.
The Football War, also known as the Hundred Hours' War or 100 Hour War, was a brief military conflict fought between El Salvador and Honduras in 1969. Existing tensions between the two countries coincided with rioting during a 1970 FIFA World Cup qualifier. The war began on 14 July 1969 when the Salvadoran military launched an attack against Honduras. The Organization of American States (OAS) negotiated a cease-fire on the night of 18 July, which took full effect on 20 July. Salvadoran troops were withdrawn in early August. The war had major consequences for both countries and was a major factor in starting the Salvadoran Civil War a decade later.

Óscar Arnulfo Romero y Galdámez was a prelate of the Catholic Church in El Salvador. He served as Auxiliary Bishop of the Archdiocese of San Salvador, the Titular Bishop of Tambeae, as Bishop of Santiago de María, and finally as the fourth Archbishop of San Salvador. As archbishop, Romero spoke out against social injustice and violence amid the escalating conflict between the military government and left-wing insurgents that led to the Salvadoran Civil War. In 1980, Romero was shot by an assassin while celebrating Mass. Though no one was ever convicted for the crime, investigations by the UN-created Truth Commission for El Salvador concluded that Major Roberto D'Aubuisson, a death squad leader and later founder of the right-wing Nationalist Republican Alliance (ARENA) political party, had ordered the killing.
Raymond Bonner is an American lawyer, journalist, author and bookstore owner. He has been a staff writer at The New York Times, The New Yorker and has contributed to The New York Review of Books; received an Emmy for a documentary he produced with Alex Gibney about the CIA's torture program for 9/11 suspects. He now an owner of a bookstore, Bookoccino, in Sydney, Australia.

Joan Didion was an American writer and journalist. She is considered one of the pioneers of New Journalism along with Gay Talese, Hunter S. Thompson, and Tom Wolfe.

The El Mozote massacre took place both in and around the village of El Mozote, in the Morazán Department, El Salvador, on December 11 and 12, 1981, when the Salvadoran Army killed more than 811 civilians during the Salvadoran Civil War. The army had arrived in the village on the 10th, following clashes with guerrillas in the area. The Salvadoran Army's Atlácatl Battalion, under the orders of Domingo Monterrosa was responsible for the massacre.

Roberto D'Aubuisson Arrieta was a Salvadoran military officer, neo-fascist politician, and death squad leader. In 1981, he co-founded and became the first leader of the far-right Nationalist Republican Alliance (ARENA) and served as president of the Legislative Assembly from 1982 to 1983. He was a presidential candidate for 1984 presidential election, losing in the second round to José Napoleón Duarte, the former president of the Revolutionary Government Junta. After ARENA's loss in the 1985 legislative elections, D'Aubuisson stepped down in favor of Alfredo Cristiani and was designated as the party's honorary president for life. D'Aubuisson was named by the United Nations' Truth Commission for El Salvador as having ordered the assassination of Óscar Romero, the archbishop of San Salvador in 1980.

Carlos Eugenio Vides Casanova was the head of the Salvadoran national guard between the years 1979 and 1983 and later served as the nation's Minister of Defense between 1983 and 1989.

The Revolutionary Government Junta was the name of three consecutive joint civilian-military dictatorships that ruled El Salvador between 15 October 1979 and 2 May 1982.

The Salvadoran Civil War was a twelve-year period of civil war in El Salvador that was fought between the government of El Salvador and the Farabundo Martí National Liberation Front (FMLN), a coalition or "umbrella organization" of left-wing groups backed by the Cuban regime of Fidel Castro as well as the Soviet Union. A coup on 15 October 1979 followed by government killings of anti-coup protesters is widely seen as the start of civil war. The war did not formally end until 16 January 1992 with the signing of the Chapultepec Peace Accords in Mexico City.
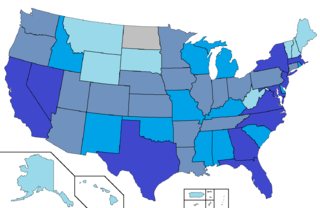
Salvadoran Americans are Americans of full or partial Salvadoran descent. As of 2021, there are 2,473,947 Salvadoran Americans in the United States, the third-largest Hispanic community by nation of ancestry. According to the Census Bureau, in 2021 Salvadorans made up 4.0% of the total Hispanic population in the United States.

Deane Roesch Hinton was an American diplomat and ambassador.

Rufina Amaya was the sole survivor of the El Mozote massacre on December 11 and December 12, 1981, in the Salvadoran department of Morazán during the Salvadoran Civil War.

Choices of the Heart is an American made-for-television drama film based on the lives of the American Roman Catholic missionaries Jean Donovan, Dorothy Kazel, Maura Clarke, and Ita Ford, all of whom were murdered in El Salvador in 1980 during the Salvadoran Civil War. The story primarily focuses on Donovan, played by Melissa Gilbert. The film also depicts the assassination of Salvadoran Archbishop Oscar Romero, which occurred shortly before the women were killed.

The Salvadoran military dictatorship was the period of time in Salvadoran history where the Salvadoran Armed Forces governed the country for almost 48 years from 2 December 1931 until 15 October 1979. The authoritarian military dictatorship limited political rights throughout the country and maintained its governance through rigged and fixed elections.

On December 2, 1980, four Catholic missionaries from the United States working in El Salvador were raped and murdered by five members of the El Salvador National Guard. The murdered missionaries were Maryknoll Sisters Maura Clarke and Ita Ford, Ursuline Dorothy Kazel, and lay missionary Jean Donovan.
The 1979 Salvadoran coup d'état was a military coup d'état that occurred in El Salvador on 15 October 1979. The coup, led by young military officers, bloodlessly overthrew military President Carlos Humberto Romero and sent him into exile. The National Conciliation Party's firm grasp on power was cut, and in its place, the military established the Revolutionary Government Junta of El Salvador (JRG). The junta was composed of two military officers and three civilians.

Death squads in El Salvador were far-right paramilitary groups acting in opposition to Marxist–Leninist guerrilla forces, most notably of the Farabundo Martí National Liberation Front (FMLN), and their allies among the civilian population before, during, and after the Salvadoran Civil War. The death squads committed the vast majority of the murders and massacres during the civil war from 1979 to 1992 and were heavily aligned with the United States-backed government.
Anarchism in El Salvador reached its peak during the labour movement of the 1920s, in which anarcho-syndicalists played a leading role. The movement was subsequently suppressed by the military dictatorship before experiencing a resurgence in the 21st century.

Leonel Eugenio Gómez Vides was a Salvadoran political activist.













