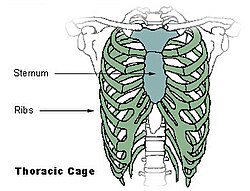
Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic sciences that are applied in medicine.

The neck is the part of the body on many vertebrates that connects the head with the torso. The neck supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that carry sensory and motor information from the brain down to the rest of the body. In addition, the neck is highly flexible and allows the head to turn and flex in all directions. The structures of the human neck are anatomically grouped into four compartments; vertebral, visceral and two vascular compartments. Within these compartments, the neck houses the cervical vertebrae and cervical part of the spinal cord, upper parts of the respiratory and digestive tracts, endocrine glands, nerves, arteries and veins. Muscles of the neck are described separately from the compartments. They bound the neck triangles.

Gray's Anatomy is a reference book of human anatomy written by Henry Gray, illustrated by Henry Vandyke Carter, and first published in London in 1858. It has gone through multiple revised editions and the current edition, the 42nd, remains a standard reference, often considered "the doctors' bible".

The scapula, also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus with the clavicle. Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble.

The occipital bone is a cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput. It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone overlies the occipital lobes of the cerebrum. At the base of the skull in the occipital bone, there is a large oval opening called the foramen magnum, which allows the passage of the spinal cord.

The frontal bone is a bone in the human skull. The bone consists of two portions. These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bony part of the forehead, part of the bony orbital cavity holding the eye, and part of the bony part of the nose respectively. The name comes from the Latin word frons.

The nasal septum separates the left and right airways of the nasal cavity, dividing the two nostrils.
Grey's Anatomy is an American medical drama television series that premiered on March 27, 2005, on ABC as a mid-season replacement. The series focuses on the lives of surgical interns, residents, and attendings as they develop into seasoned doctors while balancing personal and professional relationships. The title is an allusion to Gray's Anatomy, a classic human anatomy textbook first published in 1858 in London and written by Henry Gray. Shonda Rhimes developed the pilot and continued to write for the series until 2015. Krista Vernoff, who previously worked with Rhimes, is now the showrunner. Rhimes was also one of the executive producers alongside Betsy Beers, Mark Gordon, Krista Vernoff, Rob Corn, Mark Wilding, Allan Heinberg, and Ellen Pompeo. Although the series is set in Seattle, Washington, it is filmed primarily in Los Angeles, California, and Vancouver, British Columbia.

The anal canal is the part that connects the rectum to the anus, located below the level of the pelvic diaphragm. It is located within the anal triangle of the perineum, between the right and left ischioanal fossa. As the final functional segment of the bowel, it functions to regulate release of excrement by two muscular sphincter complexes. The anus is the aperture at the terminal portion of the anal canal.

In vertebrate anatomy, hip refers to either an anatomical region or a joint.

The median plane also called a mid-sagittal plane is used to describe the sagittal plane as it bisects the body vertically through the midline marked by the navel, dividing the body exactly in left and right side. The term parasagittal plane is used to refer to any plane parallel to the sagittal and median plane.
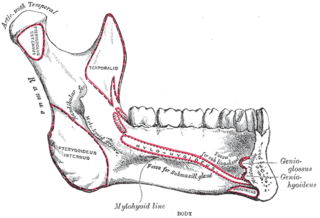
The mylohyoid line is a bony ridge on the internal surface of the mandible. It runs posterosuperiorly. It is the site of origin of the mylohyoid muscle, the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle, and the pterygomandibular raphe.

The nuchal lines are four curved lines on the external surface of the occipital bone:

The inferior rectal artery is an artery that supplies blood to the lower third of the anal canal below the pectinate line.

Near the middle of the squamous part of occipital bone is the external occipital protuberance, the highest point of which is referred to as the inion. The inion is the most prominent projection of the protuberance which is located at the posterioinferior part of the human skull. The nuchal ligament and trapezius muscle attach to it.

The pharynx is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea. It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species. The pharynx carries food and air to the esophagus and larynx respectively. The flap of cartilage called the epiglottis stops food from entering the larynx.
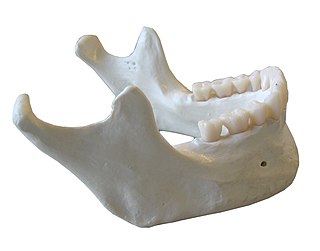
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone of the skull. It is connected to the temporal bones by the temporomandibular joints.

Anatomical terminology is a form of scientific terminology used by anatomists, zoologists, and health professionals such as doctors, physicians, and pharmacists.

In human anatomy, the liver is divided grossly into four parts or lobes: the right lobe, the left lobe, the caudate lobe, and the quadrate lobe. Seen from the front – the diaphragmatic surface - the liver is divided into two lobes: the right lobe and the left lobe. Viewed from the underside – the visceral surface, the other two smaller lobes the caudate lobe, and the quadrate lobe are also visible. The two smaller lobes, the caudate lobe and the quadrate lobe, are known as superficial or accessory lobes, and both are located on the underside of the right lobe.