
Jawor County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, south-western Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. The county covers an area of 581.2 square kilometres (224.4 sq mi). Its administrative seat is the town of Jawor; the only other town in the county is Bolków.

Góra County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, south-western Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. The county covers an area of 738.11 square kilometres (285.0 sq mi). Its administrative seat is the town of Góra; the only other town in the county is Wąsosz.

Legnica County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, south-western Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. The county covers an area of 744.6 square kilometres (287.5 sq mi). Its administrative seat is the city of Legnica, although this city is not part of the county. The only towns in Legnica County are Chojnów and Prochowice.

Lubań County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, south-western Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. The county covers an area of 428.2 square kilometres (165.3 sq mi). Its administrative seat and largest town is Lubań. The county also contains the towns of Olszyna, Leśna and Świeradów-Zdrój.

Lubin County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, south-western Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. The county covers an area of 712 square kilometres (274.9 sq mi). Its administrative seat and largest town is Lubin, and its only other town is Ścinawa.

Środa County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, south-western Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. The county covers an area of 703.7 square kilometres (271.7 sq mi). Its administrative seat and only town is Środa Śląska.

Polkowice County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, south-western Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. The county covers an area of 779.9 square kilometres (301.1 sq mi). Its administrative seat is the town of Polkowice, and it also contains the towns of Chocianów and Przemków.
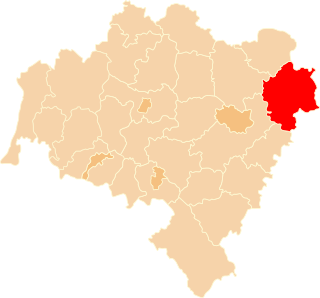
Oleśnica County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, south-western Poland. It was created on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. The county covers an area of 1,049.7 square kilometres (405.3 sq mi). Its administrative seat is the town of Oleśnica, and it also contains the towns of Syców, Twardogóra, Bierutów and Międzybórz.
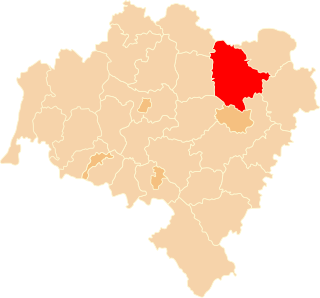
Trzebnica County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, south-western Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. The county covers an area of 1,025.5 square kilometres (395.9 sq mi). Its administrative seat is Trzebnica, and it also contains the towns of Oborniki Śląskie, Żmigród and Prusice.

Złotoryja County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, south-western Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. The county covers an area of 575.45 square kilometres (222.2 sq mi). Its administrative seat is Złotoryja, and it also contains the towns of Wojcieszów and Świerzawa.

Wołów County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, south-western Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. The county covers an area of 675 square kilometres (261 sq mi). Its administrative seat is the town of Wołów, although the county also contains the slightly larger town of Brzeg Dolny.
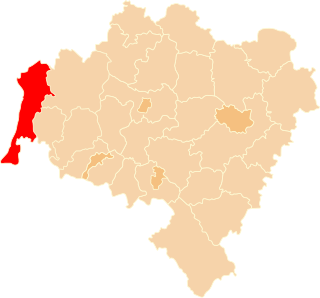
Zgorzelec County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. It is situated in the extreme south-west of Poland, bordering both Germany and the Czech Republic. The county covers an area of 838.1 square kilometres (323.6 sq mi). Its administrative seat is Zgorzelec, on the German border; the other towns in the county are Bogatynia, Pieńsk, Zawidów and Węgliniec.

Wrocław County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, south-western Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. The county covers an area of 1,116 square kilometres (431 sq mi). Its administrative seat is the city of Wrocław, although this city is not part of the county. Wrocław County consists of areas to the east and south of Wrocław, and contains three towns: Sobótka, Kąty Wrocławskie and Siechnice.

Wałbrzych County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, south-western Poland. It was created on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. The county covers an area of 514.2 square kilometres (198.5 sq mi). Its administrative seat is the city of Wałbrzych, which is located outside of the county, and it also contains the towns of Boguszów-Gorce, Głuszyca, Szczawno-Zdrój, Jedlina-Zdrój and Mieroszów.
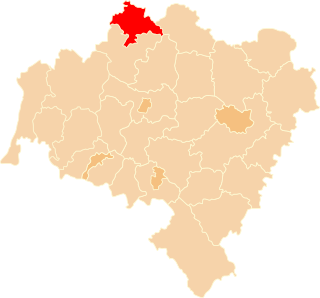
Głogów County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, south-western Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. The county covers an area of 443.06 square kilometres (171.1 sq mi). Its administrative seat and only town is Głogów.

Zambrów County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Podlaskie Voivodeship, north-eastern Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and only town is Zambrów, which lies 64 kilometres (40 mi) west of the regional capital Białystok.

Mońki County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Podlaskie Voivodeship, northeastern Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Mońki, which lies 40 kilometres (25 mi) northwest of the regional capital Białystok. The county also contains the towns of Knyszyn, lying 13 km (8 mi) southeast of Mońki, and Goniądz, 11 km (7 mi) northwest of Mońki.
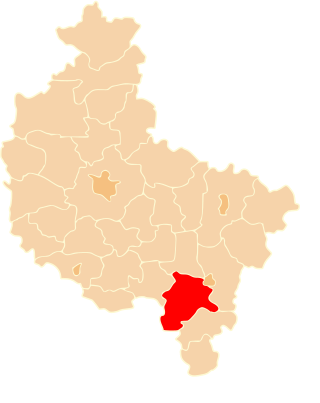
Ostrów County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Greater Poland Voivodeship, west-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Ostrów Wielkopolski, which lies 100 kilometres (62 mi) south-east of the regional capital Poznań. The county contains three other towns: Nowe Skalmierzyce, 22 km (14 mi) east of Ostrów Wielkopolski, Odolanów, 10 km (6 mi) south of Ostrów Wielkopolski, and Raszków, 8 km (5 mi) north of Ostrów Wielkopolski.
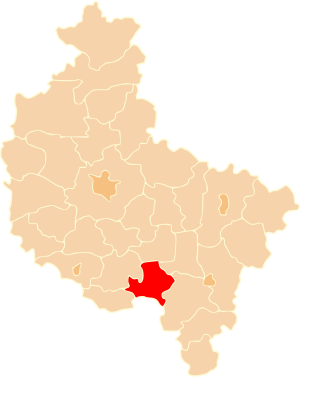
Krotoszyn County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Greater Poland Voivodeship, west-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Krotoszyn, which lies 88 kilometres (55 mi) south-east of the regional capital Poznań. The county contains four other towns: Koźmin Wielkopolski, 16 km (10 mi) north of Krotoszyn, Zduny, 6 km (4 mi) south-west of Krotoszyn, Kobylin, 14 km (9 mi) west of Krotoszyn, and Sulmierzyce, 12 km (7 mi) south-east of Krotoszyn.

Rawicz County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Greater Poland Voivodeship, west-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Rawicz, which lies 88 kilometres (55 mi) south of the regional capital Poznań. The county contains three other towns: Miejska Górka, 9 km (6 mi) north-east of Rawicz, Bojanowo, 13 km (8 mi) north-west of Rawicz, and Jutrosin, 22 km (14 mi) east of Rawicz.
























