This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page . (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page . (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
The origins of military obligation in England pre-date the establishment of the English state in the 10th century, and can be traced to the 'common burdens' of the Anglo-Saxon period, among which was service in the fyrd, or army. There is evidence that such an obligation existed in the Kingdom of Kent by the end of the 7th century, Mercia in the 8th century and Wessex in the 9th century, and the Burghal Hidage of 911–919 indicates that over 27,000 men could have been raised in the defence of 30 West Saxon boroughs. In the late 10th century, areas began to be divided into 'hundreds' as units for the fyrd. The obligation to serve was placed on landholders, and the Domesday Book indicates that individuals were expected to serve for approximately 60 days. [1]
The Norman conquest of England in 1066 brought with it a feudal system which also contained an element of military obligation in the form of the feudal host. This system supplemented rather than replaced the fyrd, which continued to be deployed until at least the beginning of the 12th century. The Assize of Arms of 1181 combined the two systems by dividing the free population into four categories according to wealth and prescribing the weapons each was to maintain. The first category corresponded to the feudal host, the next two corresponded to the old fyrd and the last to a general levy. The Statute of Winchester in 1285 introduced two more non-feudal categories to impose a general military obligation on all able-bodied males, including non-free, between the ages of 15 and 60, and updated the prescribed weaponry in the light of developments in warfare at the time. [2] [3]
Because it was not practical to call out every man, King Edward I introduced a system whereby local gentry were authorised to conduct commissions of array to select those who would actually be called for military service. [4] [5] During the reign of King Edward III, feudal service was recognised as increasingly obsolete, and the feudal host was formally called out in full for the last time in 1327. During the Hundred Years' War, the king raised armies for service in France by indenture, which contracted magnates, under their obligation as subjects rather than feudal tenants, to supply a certain number of men for a specific amount of time in return for a set fee. Those forces allocated for the defence of England, however, were raised on the basis of the general obligation [6]
In 1511, King Henry VIII signalled the elevation of the national obligation as the sole means of raising armies from the citizenry. He ordered the commissioners of array be responsible not just for the raising of levies, but also for ensuring that they were suitably equipped according to the Statute of Winchester. He also restricted landowners to raising forces only from their own tenants or others for whom, by the tenure of office, they were responsible. By these means Henry instituted a quasi-feudal system, whereby he looked to the nobility to raise forces, but expected them to do so within the constraints of the shire levies, and the last use of indenture to raise an army came in 1512. [7]
Italian ambassadors reckoned that England had 150,000 armed men in 1519 and 100,000 in 1544 and 1551 available through their militia, while a French ambassador in 1570 reported that 120,000 were ready to serve. This was reasonably close to the truth as 183,000 militiamen were mustered in 37 counties in 1575, and in the officials returns of 1588 more than 132,000 were expected to be fielded in England and Wales. They were intended to comprise part of the armies raised to combat the Spanish invasion. There were expected to be a total of 92,000 men mustered in the south of England (including 5,300 cavalry). Their poor state of readiness and obsolete nature of the weapons they used (mainly bills and longbows) prompted the creation of the more elite Trained Bands, who numbered 50,000 in 1588 (comprising about a third of the militia). This was only a partial solution however. By 1591 official records show 102,000 men on the rolls, of whom 42,000 are fully trained and furnished, plus 54,000 armed but not sufficiently trained and 6,000 neither armed nor trained. In 1588 the Trained Bands primary weapons were 42% firearms, 26% pikes, 18% longbows, and 16% bills. [8]
A 1522 survey had revealed a significant lapse in the obligation to maintain arms and train in their use, and from 1535 commissioners of muster held tri-annual inspections. [9] In the mid-16th century Lords Lieutenant began to be appointed, a great improvement in local authority, and an increasingly efficient machinery for enforcing the obligations of the citizenry to be ready for war resulted in 1558 the Militia Act, which ended the quasi-feudal system and implemented a more efficient, unified national militia system. [10] [11] In an attempt to remove the statutory limitations and allow the lieutenants to increase their demands on the militia, the act was repealed in 1604. This, however, succeeded only in removing the statutory basis for the militia itself. Although the militia continued to exist, it fell into neglect as attempts to introduce new legislation to regulate it failed. [12]
The beginning of the English Civil War was marked by a struggle between King Charles I and Parliament for control of the militia. [13] The indecisive Battle of Edgehill in 1642, the first pitched battle of the war, revealed the weakness of the amateur military system, and both sides struggled with barely trained, poorly-equipped, ill-disciplined and badly led armies. [14] While the Royalists persisted with the amateur tradition, the Parliamentarians developed the New Model Army, a small but disciplined, well-equipped and trained army led by officers selected according to ability rather than birth. The New Model Army defeated the Royalist army at the Battle of Naseby in 1645, effectively ending the First English Civil War in victory for the Parliamentarians. [15]
Following the execution of King Charles I, the establishment of the Commonwealth of England and the subsequent Protectorate under Oliver Cromwell, the New Model Army became politicised, and by the time of Cromwell's death in 1658, martial law and the Rule of the Major-Generals had renewed the traditional mistrust of standing armies. [16] On the restoration of King Charles II to the throne in 1660, the New Model Army was disbanded. Despite the concerns of Parliament about expense and the threat to the power it had only recently won from the Crown, it still proved necessary to maintain a small standing force in England, for the protection of the new king and to garrison coastal forts. A new army was therefore established in 1660, comprising two regiments born in the civil war; one raised in 1656 as Charles's bodyguard while he was in exile during the Interregnum, the other raised in 1650 as part of the New Model Army. Several conspiracies uncovered towards the end of 1660 convinced Parliament of the need for two more regiments – again, one raised in exile during the Interregnum, the other originally a New Model Army regiment – and the army was officially established by royal warrant on 26 January 1661. [17] [lower-alpha 1]
In the midst of the English Civil War there was some debate as to whether the militia should be a supplement or an alternative to a standing army, and a series of ordinances were passed in attempts to replace the repealed 1558 act. These reflected the ongoing struggle for control of the militia until, in the early 1660s, new legislation established the militia under the control, through the lieutenancy, of the gentry. The legislation made it a counter to the standing army, the main bulwark against disorder and the guarantee of the political settlement. [20]
The army – which, by the time of King James II's accession in 1685, comprised seven regiments of foot and four mounted regiments – was officially part of the royal household and had no basis in law; both king and Parliament were careful to refer to the regiments as 'guards', based on their role as bodyguards to the king, and it was still intended that the militia would provide the country's main force in the event of war. [21] However, it was the army, already made more palatable to Parliament by acts of civilian service in support of the common good, that defeated the Monmouth Rebellion in 1685, the militia having proved too slow to mobilise. [22] Following the rebellion, King James II was able to expand the army with 16 new regiments, paid for by money misappropriated from funds voted by Parliament for the militia. [23] The Glorious Revolution of 1688 brought the Dutch King William III to the throne, and with him came interests in continental Europe. It was the defence of these interests that would lead, by the time of the Battle of Blenheim in 1704, to the establishment of the army as an accepted state body and a military leader in Europe. [24] The status of the army as a state institution under parliamentary control and subject to national law was normalised in 1689 by the Bill of Rights and the annually passed Mutiny Acts. [25]
Failure in the Monmouth Rebellion and controversy over the mis-use of funds had an adverse effect on the militia. Although it continued to be called out, for example in the Second Anglo-Dutch War, in the aftermath of the Battle of Beachy Head and in the face of the Jacobite risings, the militia entered a period of decline. [26] In some areas it received at best only 12 days of annual training, and in others it had not been mustered in a generation. It was regarded as so ineffective that against the Jacobite rising of 1745 it would prove more expedient to raise an ad hoc force of volunteers than to rely on the militia. [27]
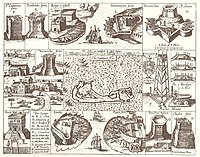
Successful English settlement of North America, where little support could be provided by regular forces, began to take place in 1607, in the face of Spain's determination to prevent England establishing a foothold in territory it claimed for itself. The settlers also had to contend with frequently hostile native populations. It was immediately necessary to raise militia amongst the settlers. The militia in Jamestown saw constant action against the Powhatan Federation and other native polities. In the Virginia Company's other outpost, Bermuda, settled officially in 1612 (unofficially in 1609), the construction of defensive works was placed before all other priorities. A Spanish attack in 1614 was repulsed by two shots fired from the incomplete Castle Islands Fortifications manned by Bermudian Militiamen. In the Nineteenth century, Fortress Bermuda would become Britain's Gibraltar of the West, heavily fortified by a Regular Army garrison to protect the Royal Navy's headquarters and dockyard in the Western Atlantic. In the 17th Century, however, Bermuda's defence was left entirely in the hands of the Militia. In addition to requiring all male civilians to train and serve in the militia of their Parish, the Bermudian Militia included a standing body of trained artillerymen to garrison the numerous fortifications which ringed New London (St. George's). This standing body was created by recruiting volunteers, and by sentencing criminals to serve as punishment. The Bermudian militiamen were called out on numerous occasions of war, and, on one notable occasion, to quell rioting privateers. In 1710, four years after Spanish and French forces seized the Turks Islands from Bermudian salt producers in 1706, they were expelled by Bermudian privateers. Although the Bermudian force operated under a Letter of Marque, its members, as with all military age Bermudian males, were members of the militia. By this time, the 1707 Acts of Union had made Bermudian and other English militiamen British.
Up until the Glorious Revolution in 1688, the Crown and Parliament were in strong disagreement. The English Civil War left a rather unusual military legacy. Both Whigs and Tories distrusted the creation of a large standing army not under civilian control. The former feared that it would be used as an instrument of royal tyranny. The latter had memories of the New Model Army and the anti-monarchical social and political revolution that it brought about. Consequently, both preferred a small standing army under civilian control for defensive deterrence and to prosecute foreign wars, a large navy as the first line of national defence, and a militia composed of their neighbours as additional defence and to preserve domestic order.
Consequently, the English Bill of Rights (1689) declared, amongst other things: "that the raising or keeping a standing army within the kingdom in time of peace, unless it be with consent of Parliament, is against law..." and "that the subjects which are Protestants may have arms for their defense suitable to their conditions and as allowed by law." This implies that they are fitted to serve in the militia, which was intended to serve as a counterweight to the standing army and preserve civil liberties against the use of the army by a tyrannical monarch or government.
The Crown still (in the British constitution) controls the use of the army. This ensures that officers and enlisted men swear an oath to a politically neutral head of state, and not to a politician. While the funding of the standing army subsists on annual financial votes by parliament, the Mutiny Act is also renewed on an annual basis by parliament[ citation needed ]. If it lapses, the legal basis for enforcing discipline disappears, and soldiers lose their legal indemnity for acts committed under orders[ citation needed ].
In 1707, the Acts of Union united the Kingdom of England with the Kingdom of Scotland. The Scottish navy was incorporated into the Royal Navy. The Scottish military (as opposed to naval) forces merged with the English, with pre-existing regular Scottish regiments maintaining their identities, though command of the new British Army was from England. The Militia of England and Wales continued to be enacted separately from the Militia of Scotland (see Militia (Great Britain) and, for the period following 1801, Militia (United Kingdom)).

An army, ground force or land force is a fighting force that fights primarily on land. In the broadest sense, it is the land-based military branch, service branch or armed service of a nation or country. It may also include aviation assets by possessing an army aviation component. Within a national military force, the word army may also mean a field army.

The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. As of 2022, the British Army comprises 80,976 regular full-time personnel, 3,949 Gurkhas, and 52,600 reserve personnel.

A militia is generally an army or some other fighting organization of non-professional soldiers, citizens of a country, or subjects of a state, who may perform military service during a time of need, as opposed to a professional force of regular, full-time military personnel; or, historically, to members of a warrior-nobility class. Generally unable to hold ground against regular forces, militias commonly support regular troops by skirmishing, holding fortifications, or conducting irregular warfare, instead of undertaking offensive campaigns by themselves. Local civilian laws often limit militias to serve only in their home region, and to serve only for a limited time; this further reduces their use in long military campaigns.
A fyrd was a type of early Anglo-Saxon army that was mobilised from freemen or paid men to defend their Shire's lords estate, or from selected representatives to join a royal expedition. Service in the fyrd was usually of short duration and participants were expected to provide their own arms and provisions. The composition of the fyrd evolved over the years, particularly as a reaction to raids and invasions by the Vikings. The system of defence and conscription was reorganised during the reign of Alfred the Great, who set up 33 fortified towns in his kingdom of Wessex. The amount of taxation required to maintain each town was laid down in a document known as the Burghal Hidage. Each lord had his individual holding of land assessed in hides. Based on his land holding, he had to contribute men and arms to maintain and defend the burhs. Non-compliance with this requirement could lead to severe penalties.

The history of the British Army spans over three and a half centuries since its founding in 1660 and involves numerous European wars, colonial wars and world wars. From the late 17th century until the mid-20th century, the United Kingdom was the greatest economic and imperial power in the world, and although this dominance was principally achieved through the strength of the Royal Navy (RN), the British Army played a significant role.
A standing army is a permanent, often professional, army. It is composed of full-time soldiers who may be either career soldiers or conscripts. It differs from army reserves, who are enrolled for the long term, but activated only during wars or natural disasters, and temporary armies, which are raised from the civilian population only during a war or threat of war and disbanded once the war or threat is over. Standing armies tend to be better equipped, better trained, and better prepared for emergencies, defensive deterrence, and particularly, wars. The term dates from approximately 1600 CE, although the phenomenon it describes is much older.

The Massachusetts National Guard is the National Guard component for the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Founded as the Massachusetts Bay Colonial Militia on December 13, 1636, it contains the oldest units in the United States Army. What is today's Massachusetts National Guard evolved through many different forms. Originally founded as a defensive militia for Puritan colonists in the Massachusetts Bay Colony, the militia evolved into a highly organized and armed fighting force. The Massachusetts militia served as a central organ of the New England revolutionary fighting force during the early American Revolution and a major component in the Continental Army under George Washington.
The English Army existed while England was an independent state and was at war with other states, but it was not until the Interregnum and the New Model Army that England acquired a peacetime professional standing army. At the Restoration of the monarchy, Charles II kept a small standing army, formed from elements of the Royalist army in exile and elements of the New Model Army, from which the most senior regular regiments of today's British Army can trace their antecedence. Likewise, Royal Marines can trace their origins back to the formation of the English Army's "Duke of York and Albany's maritime regiment of Foot" at the grounds of the Honourable Artillery Company on 28 October 1664.

The Special Reserve was established on 1 April 1908 with the function of maintaining a reservoir of manpower for the British Army and training replacement drafts in times of war. Its formation was part of the military reforms implemented by Richard Haldane, the Secretary of State for War, which also created the Territorial Force. Haldane originally intended that the Militia would provide the reserve, but opposition from its representatives forced him to abolish it and create the Special Reserve instead. Only 60 per cent of the Militia transferred into the new reserve, and it was consistently under strength, particularly in officers. Reservists enlisted for a six-year term of service, and had to undergo six months of basic training on recruitment and three to four weeks training annually. The Special Reserve was organised into battalions, providing a third for each of the regular army's 64 two-battalion infantry regiments and a fifth and sixth for the five four-battalion infantry regiments. In addition to providing replacements to the regular army, the Special Reserve was deployed on home defence duties guarding the coast and key installations during the First World War. The routine nature of its duties meant that scant attention was paid to it in regimental histories. After the war, the Special Reserve was abolished and the Militia was resurrected in 1921 to take on its former role. No effort was made to restart recruitment, and in 1924 the new Militia's functions were absorbed into the Supplementary Reserve.
The Lancashire Militia was an auxiliary military force in Lancashire in North West England. From their formal organisation as Trained Bands in 1558 and their service in the Williamite War in Ireland and against the Jacobite Risings, the Militia regiments of Lancashire served during times of international tension and all of Britain's major wars. They provided internal security and home defence but sometimes operated further afield, including Ireland and the Mediterranean, relieving regular troops from routine garrison duties, and acting as a source of trained officers and men for the Regular Army. All the infantry battalions went on active service during the Second Boer War and all served as Special Reserve training units in World War I, with one battalion seeing considerable action on the Western Front. After 1921 the militia had only a shadowy existence until its final abolition in 1953.
The East York Militia was a part time home defence force in the East Riding of Yorkshire. The Militia and its predecessors had always been important in Yorkshire, and from its formal creation in 1759 the regiment served in home defence in all Britain's major wars until 1919. It became a battalion of the East Yorkshire Regiment, and its role during World War I was to train thousands of reinforcements for the regiment's battalions serving overseas.
The South Devon Militia was a part-time military unit in the maritime county of Devonshire in the West of England. The Militia had always been important in the county, which was vulnerable to invasion, and from its formal creation in 1758 the regiment served in home defence in all of Britain's major wars, later as a reserve battalion for the Devonshire Regiment. It was disbanded in 1908.
The Devon Militia was a part-time military force in the maritime county of Devonshire in the West of England. From their formal organisation as Trained Bands in 1558 until their final service as a Special Reserve unit of the Devonshire Regiment in World War I, the Militia regiments of Devonshire served in home defence in all of Britain's major wars.
The Surrey Militia was an auxiliary military force in Surrey in the Home counties of England. From their formal organisation as Trained Bands in 1558 until their final service as the Special Reserve, the Militia regiments of the county served in home defence in all of Britain's major wars. They also saw active service during the Second Boer War, and trained thousands of reinforcements during World War I. After a shadowy postwar existence they were formally disbanded in 1953.
The Surrey Trained Bands were a part-time military force in Surrey in the Home counties of England from 1558 until they were reconstituted as the Surrey Militia in 1662. They were periodically embodied for home defence, for example in the army mustered at Tilbury during the Armada Campaign of 1588, and they saw some active service during the English Civil War.
The London Militia were the part-time military forces in the City of London. From their formal organisation as the London Trained Bands in 1559 they were periodically embodied for home defence, for example in the army mustered at Tilbury during the Armada Campaign of 1588. They saw a great deal of active service during the English Civil War, including the First and Second Battles of Newbury and the battles of Cheriton and Cropredy Bridge. Throughout their history they were used to suppress civil disorder and insurrection around the capital. In 1794 the London Trained Bands were reconstituted as part of the national Militia, and in 1881 the Royal London Militia became a battalion of the Royal Fusiliers. Although intended to be a reserve unit, the battalion saw considerable action on the Western Front during World War I. After 1921 the militia had only a shadowy existence until its final abolition in 1953.

The London Trained Bands (LTBs) were a part-time military force in the City of London from 1559 until they were reconstituted as conventional Militia regiments in 1794. They were periodically embodied for home defence, for example in the army mustered at Tilbury during the Armada Campaign of 1588. They saw a great deal of active service during the English Civil War, including the First and Second Battles of Newbury, and the battles of Alton, Cheriton, Cropredy Bridge and Lostwithiel. Throughout their history they were used to suppress civil disorder and insurrection around the capital.
The Staffordshire Militia was an auxiliary military force in Staffordshire in the West Midlands of England. From their formal organisation as Trained Bands in 1572 and their reorganisation in 1662 and 1777, the Militia regiments of Staffordshire served during times of international tension and all of Britain's major wars. They provided internal security and home defence but in the Crimean War were stationed in the Mediterranean relieving regular troops from routine garrison duties. They also acted as a source of trained officers and men for the Regular Army. By the later 19th Century there were four battalions, assigned to the South and North Staffordshire Regiments. All the battalions went on active service during the Second Boer War and all served as Special Reserve training units in World War I, with two battalions seeing considerable action on the Western Front. After 1921 the militia had only a shadowy existence until its final abolition in 1953.
The Sussex Militia was an auxiliary military force in Sussex on the South Coast of England. From their formal organisation as Trained Bands in 1572 they defended the coastline, watched the Spanish Armada and took an active part in the English Civil War. It was the Sussex Militia who captured the Duke of Monmouth after his unsuccessful Rebellion in 1685. After a long hiatus, the Sussex Militia was reformed in 1778 and provided internal security and home defence in all of Britain's major wars thereafter. It eventually became the Royal Sussex Light Infantry Militia (RSLIM) and also formed the Royal Sussex Militia Artillery. After the Cardwell Reforms the RSLIM became a battalion of the Royal Sussex Regiment and saw active service in the Second Boer War. It served as a Special Reserve training unit in World War I. After 1921 the militia had only a shadowy existence until its final abolition in 1953.
The Gloucestershire Militia was a part-time military force in the county of Gloucestershire in the West of England. From their formal organisation as Trained Bands in 1558 until their final service as a Special Reserve unit of the Gloucestershire Regiment in World War I, the Militia regiments of the county served in home defence in all of Britain's major wars.