
The economy of Afghanistan has had significant improvement in the last decade due to the infusion of billions of dollars in international assistance and remittances from Afghan expatriates. The assistance that came from expatriates and outside investors saw this increase when there was more political reliability after the fall of the Taliban regime. The nation's GDP stands at about $70 billion with an exchange rate of $20 billion (2017), and the GDP per capita is about $2,000. It imports over $6 billion worth of goods but exports nearly $1 billion only, mainly fruits and nuts.

Foreign relations of Afghanistan are handled by the nation's Ministry of Foreign Affairs, which is headed by Salahuddin Rabbani. He answers to, and receives guidance from, the President of Afghanistan, Ashraf Ghani.

Hamid Karzai is an Afghan politician who was the President of Afghanistan from 22 December 2001 to 29 September 2014, originally as an interim leader and then as President for almost ten years, from 7 December 2004 to 2014. He comes from a politically active family; Karzai's father, uncle and grandfather were all active in Afghan politics and government. Karzai and his father before him, Abdul Ahad Karzai, were each head of the Popalzai tribe of the Durrani tribal confederation.
The following lists events that happened during 2001 in Afghanistan.

Mohammad Ashraf Ghani Ahmadzai is an Afghan politician and current president of Afghanistan, elected on 21 September 2014. An anthropologist by education, he previously served as finance minister and the chancellor of Kabul University.

Human rights in Afghanistan is a topic of some controversy and conflict. While the Taliban were well known for numerous human rights abuses, several human rights violations continue to take place in the post-Taliban government era. Afghanistan has an interesting strong human rights framework within its constitution.
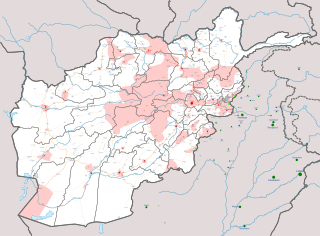
The Taliban insurgency began shortly after the group's fall from power following the 2001 War in Afghanistan. The Taliban forces are fighting against the Afghan government, formerly led by President Hamid Karzai, now led by President Ashraf Ghani, and against the US-led International Security Assistance Force (ISAF). The insurgency has spread to some degree over the Durand Line border to neighboring Pakistan, in particular the Waziristan region and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. The Taliban conduct low-intensity warfare against Afghan National Security Forces and their NATO trainers. Regional countries, particularly Pakistan and Iran, are often accused of funding and supporting the insurgent groups.

Qarabaghdistrict is 56 km to the south-west of Ghazni in eastern Afghanistan. The 1,800 km² area is one of the most populated at 109,000; some reports count more than 218,000. The ethnic composition of the district includes Hazaras and Pashtuns. The landscape varies in different parts of the district - deserts in the southwest, plains in the southeast and mountains in the north. The district is seriously affected by drought, especially farming and animal husbandry. Health and education need serious improvement.
Kidnapping and hostage taking has become a common occurrence in Afghanistan following the U.S. invasion of Afghanistan in 2001. Kidnappers include Taliban and Al-Qaeda fighters and common criminal elements.

Women's rights in Afghanistan have been a subject of international concern since the 1990s. Through different temporary rulers such as the mujahideen and the Taliban in the 1990s, women had very little to no freedom, specifically in terms of civil liberties. Ever since the Taliban regime was removed in late 2001, women's rights have gradually improved under the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan.
The media of Afghanistan includes printing, broadcasting, and digital. It is mainly in Dari and Pashto, the official languages of the nation. According to the Attorney General's Office of Afghanistan, "there are 1,879 active media outlets in Afghanistan which are called as one of the main achievements of the country in the past 18 years."

Bilateral relations between the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan and the Republic of India have traditionally been strong and friendly. The Republic of India was the only South Asian country to recognize the Soviet-backed Democratic Republic of Afghanistan in the 1980s, its relations were diminished during the 1990s Afghan civil war and the Taliban government. India aided the overthrow of the Taliban and became the largest regional provider of humanitarian and reconstruction aid to Afghanistan. Indians are working in various construction projects, as part of India's rebuilding efforts in Afghanistan. Pakistan alleges the Indian intelligence agency R&AW is working in cover to malign Pakistan and train and support insurgents, a claim rejected strongly by India and the United States, the latter historically being a strong ally of Pakistan.

The 2008 Indian embassy bombing in Kabul was a suicide bomb terror attack on the Indian embassy in Kabul, Afghanistan on 7 July 2008 at 8:30 AM local time. The bombing killed 58 people and wounded 141. The suicide car bombing took place near the gates of the embassy during morning hours when officials enter the embassy.
The Haqqani network is an Afghan guerrilla insurgent group using asymmetric warfare to fight against US-led NATO forces and the government of Afghanistan. Maulvi Jalaluddin Haqqani and his son Sirajuddin Haqqani have led the group. It is an offshoot of the Taliban and are thought to be based in the town of Miramshah in Pakistan.

Sikhism in Afghanistan is limited to small populations, primarily in major cities, with the largest numbers of Afghan Sikhs living in Jalalabad, Ghazni, Kabul, and to a lesser extent Kandahar. These Sikhs are Afghan nationals who normally speak native Pashto, but also speak Dari, Hindi or Punjabi. Their total population is around 1,200 families or 8,000 members.

This article covers the history of Afghanistan since the communist military coup on 27 April 1978, known as the Saur Revolution, when the People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan (PDPA) took power. Since that day, an almost continuous series of armed conflicts has dominated and afflicted Afghanistan.
2003 in Afghanistan. A list of notable incidents in Afghanistan during 2003

The Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant – Khorasan Province, or ISIL-KP, is a branch of the militant Islamist group Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL), active in Afghanistan and Pakistan. Some media sources also use the terms ISK, ISISK, IS-KP, or ISIS-K in Ramlal kotr referring to the group. The Khorasan group's area of operations also includes other parts of South Asia, such as India where individuals have pledged allegiance to it.




















