
In the fields of horticulture and botany, the term deciduous (/dɪˈsɪdʒuəs/) means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, after flowering; and to the shedding of ripe fruit.

In forestry and ecology, understory comprises plant life growing beneath the forest canopy without penetrating it to any great extent, but above the forest floor. Only a small percentage of light penetrates the canopy so understory vegetation is generally shade tolerant. The understory typically consists of trees stunted through lack of light, other small trees with low light requirements, saplings, shrubs, vines and undergrowth. Small trees such as holly and dogwood are understory specialists.

Grasslands are areas where the vegetation is dominated by grasses (Poaceae); however, sedge (Cyperaceae) and rush (Juncaceae) families can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes, like clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur naturally on all continents except Antarctica. Grasslands are found in most ecoregions of the Earth. For example, there are five terrestrial ecoregion classifications (subdivisions) of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome (ecosystem), which is one of eight terrestrial ecozones of the Earth's surface.
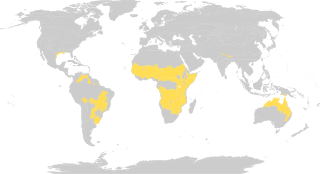
Tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands is a terrestrial habitat type defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature.. The biome is dominated by grass and/or shrubs located in semi-arid to semi-humid climate regions of subtropical and tropical latitudes.

Forsythia is a genus of flowering plants in the olive family Oleaceae. There are about 11 species, mostly native to eastern Asia, but one native to southeastern Europe. Forsythia is also one of the plant's common names, along with Easter tree; the genus is named after William Forsyth.

A shrubbery is a wide border to a garden where shrubs are thickly planted, or a similar larger area with a path winding through it. A singular shrub is also known as a bush.

Arboriculture is the cultivation, management, and study of individual trees, shrubs, vines, and other perennial woody plants. The science of arboriculture studies how these plants grow and respond to cultural practices and to their environment. The practice of arboriculture includes cultural techniques such as selection, planting, training, fertilization, pest and pathogen control, pruning, shaping, and removal.
The cultivation of trees and shrubs especially for ornamental purpose is called as ARBORICULTURE
A person who practices or studies arboriculture can be termed an 'arborist' or an 'arboriculturist'. A 'tree surgeon' is more typically someone who is trained in the physical maintenance and manipulation of trees and therefore more a part of the arboriculture process rather than an arborist. Risk management, legal issues, and aesthetic considerations have come to play prominent roles in the practice of arboriculture. Businesses often need to hire arboriculturists to complete "tree hazard surveys" and generally manage the trees on-site to fulfill occupational safety and health obligations.

The Great Basin Desert is part of the Great Basin between the Sierra Nevada and the Wasatch Range. The desert is a geographical region that largely overlaps the Great Basin shrub steppe defined by the World Wildlife Fund, and the Central Basin and Range ecoregion defined by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and United States Geological Survey. It is a temperate desert with hot, dry summers and snowy winters. The desert spans a large part of the state of Nevada, and extends into western Utah, eastern California, and Idaho. The desert is one of the four biologically defined deserts in North America, in addition to the Mojave, Sonoran, and Chihuahuan Deserts.

A perennial plant or simply perennial is a plant that lives more than two years. Some sources cite perennial plants being plants that live more than three years. The term is often used to differentiate a plant from shorter-lived annuals and biennials. The term is also widely used to distinguish plants with little or no woody growth from trees and shrubs, which are also technically perennials.

A subshrub or dwarf shrub is a short woody plant. Prostrate shrub is a related term. "Subshrub" is often used interchangeably with "bush".

Shrubland, scrubland, scrub, brush, or bush is a plant community characterised by vegetation dominated by shrubs, often also including grasses, herbs, and geophytes. Shrubland may either occur naturally or be the result of human activity. It may be the mature vegetation type in a particular region and remain stable over time, or a transitional community that occurs temporarily as the result of a disturbance, such as fire. A stable state may be maintained by regular natural disturbance such as fire or browsing. Shrubland may be unsuitable for human habitation because of the danger of fire. The term "shrubland" was coined in 1903.

Shrub-steppe is a type of low rainfall natural grassland. While arid, shrub-steppes have sufficient moisture to support a cover of perennial grasses and/or shrubs, a feature which distinguishes them from deserts.

Worcester Shrub Hill railway station is one of two railway stations serving the city of Worcester in Worcestershire, England. It is managed by West Midlands Trains, operating here under the West Midlands Railway brand, and it is also served by Great Western Railway. The platform 2B waiting room of Worcester Shrub Hill is Grade II* listed and reopened in 2015 after a ten-year refurbishment project.

The Field Elm cultivar Ulmus minor 'Viminalis Aurea', probably a "golden" form of Ulmus minor 'Viminalis', was raised before 1866 by Egide Rosseels of Louvain, who was known to have supplied 'Viminalis'.
The elm cultivar Ulmus 'Monstrosa' is believed to have originated in France, where it was listed without description as a form of Field Elm, Ulmus campestris var. monstrosa. Krüssman included it in his manual as an Ulmus glabra cultivar, but the plant's long, slender 2 cm petiole is not a feature of U. glabra, and is even less likely in a shrub form of this tree.
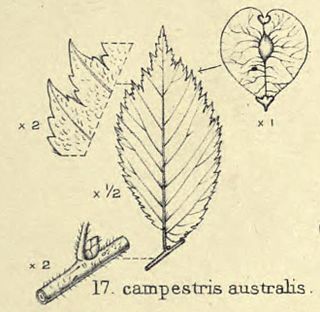
The elm cultivar Ulmus 'Australis' [:'southern'], reputedly endemic to south-eastern France, Switzerland and Italy, is a little-known tree considered by various authorities to have been a variety of Ulmus minor or Ulmus × hollandica.
The hybrid elm cultivar Ulmus × hollandica 'Macrophylla Aurea' was listed by Bean in Kew Hand-List Trees & Shrubs, ed. 3, 273, 1925 as U. montana var. macrophylla aurea, but without description.

Shrub swamps — also called scrub swamps or buttonbush swamps — are a type of freshwater wetland ecosystem occurring in areas too wet to become swamps, but too dry or too shallow to become marshes. They are often considered transitional (“mid-successional”) between wet meadows or fens and conifer or hardwood swamps.

The Northwestern Himalayan alpine shrub and meadows is a montane grasslands and shrublands ecoregion of the elevations of the northwestern Himalaya of China, India, and Pakistan.




















