
The dingiso, also known as bondegezou, is a species of tree-kangaroo endemic to Papua Province central on New Guinea island, in northeastern Indonesia.
The earless water rat is a New Guinea rodent, part of the Hydromys group of the subfamily of Old World rats and mice (Murinae). It is the only species of the genus Crossomys. This species is probably most closely related to Baiyankamys. It is still unclear to which species this group is related. It is one of the most aquatically adapted rodents of the world.

The spectacled flying fox, also known as the spectacled fruit bat, is a megabat that lives in Australia's north-eastern regions of Queensland. It is also found in New Guinea and on the offshore islands including Woodlark Island, Alcester Island, Kiriwina, and Halmahera.

The giant white-tailed rat is an Australian rodent native to tropical rainforest of north Queensland, with subspecies occurring in New Guinea and the Aru Islands. It is one of the largest rodents in Australia, reaching up to 1 kg in weight. It is grey-brown above, cream to white below, and has a long, naked tail of which the distal section is white.
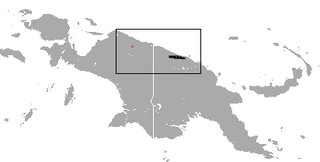
The golden-mantled tree-kangaroo is a species of tree-kangaroo endemic to the Northern New Guinea montane rain forests ecoregion of northern New Guinea island.
The angulate pipistrelle, also known as the New Guinea pipistrelle, is a species of vesper bat found in Papua New Guinea and the Solomon Islands.

The little bent-wing bat or little long-fingered bat is a species of vesper bat in the family Miniopteridae. It is found in Australia, Indonesia, the Philippines, and Vanuatu.
Poncelet's giant rat or Poncelet's naked-tailed rat is a species of rodent in the family Muridae. It is found in Papua New Guinea and Solomon Islands.
The Florida naked-tailed rat is a poorly known and possible extinct species of rodent in the family Muridae. It was confined to the Nggela Islands in the Solomon Islands. The originally mentioned type locality Ugi Island is an erratum.

The grizzled tree-kangaroo is a small arboreal species of marsupial in the family Macropodidae. It is found in foothill forests of northern and western New Guinea and is indigenous to some of the offshore islands.
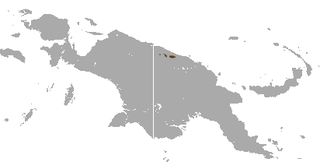
The tenkile, also known as Scott's tree-kangaroo, is a species of tree-kangaroo in the family Macropodidae. It is endemic to a very small area of the Torricelli Mountains of Papua New Guinea. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical dry forests. It is threatened by habitat loss and by hunting. The tenkile is listed as endangered due to hunting and logging activities in Papua New Guinea. The tenkile is hunted for its meat, and is the main protein source for the residents of Papua New Guinea. The population of Papua New Guinea has increased in recent years due to improvements in healthcare; therefore increasing need in tenkile meat which means that more tenkiles are being hunted. Additionally, tenkiles are poached for their fur and are captured and sold as a part of the illegal pet trade. Domesticated dogs also hunt tenkiles. Deforestation in Papua New Guinea affects all tree-Kangaroos, however industrial logging that occurs in the Torricelli Mountain Range decreases the species' already restricted habitat. The Torricelli Mountain Range faces additional deforestation due to the timber industry, and the production of coffee, rice and wheat.

The Woodlark cuscus is a species of marsupial in the family Phalangeridae endemic to Papua New Guinea, specifically on Madau and Woodlark Island, a part of the Milne Bay Province of Papua New Guinea. It happens to be the largest mammal living on Woodlark Island but it is also found on the neighboring island of Alcester, 70 kilometers south of Woodlark Island.

The northern common cuscus, also known as the grey cuscus, is a species of marsupial in the family Phalangeridae native to northern New Guinea and adjacent smaller islands, but is now also found in the Bismarck Archipelago, southeast and central Moluccas, the Solomons, and Timor, where it is believed to have been introduced in prehistoric times from New Guinea. It was formerly considered conspecific with the allopatric P. intercastellanus and P. mimicus.

The dusky leaf-nosed bat is a bat from the genus Hipposideros whose habitat extends from India and Sri Lanka to the Philippines, New Guinea and Northern Australia. This species is counted in the H. bicolor species group and was formerly classified within that species.

The great flying fox, also known as the greater flying fox or Bismarck flying fox, is a species of megabat in the genus Pteropus, found throughout lowland areas of New Guinea and in the Bismarck Archipelago. Conflicting evidence suggests that its closest relative is either the spectacled flying fox or, jointly, the Pelew and insular flying foxes. Two subspecies are recognized. At up to 1.6 kg (3.5 lb) in weight, it is among the heaviest bats in the world and the largest bat in Melanesia. It is a gregarious animal which roosts with hundreds or thousands of individuals. In part due to its wide variation in color, it has many taxonomic synonyms, including Pteropus degener, Pteropus papuanus, and Pteropus sepikensis. It may forage during the day or night in search of fruit, including figs or fruits from the family Sapotaceae. It is considered a least-concern species by the IUCN, though its numbers have been negatively impacted by what appeared to be a disease, as well as by hunting for bushmeat that occurs across its range.

The Bismarck masked flying fox is a species of flying fox in the family Pteropodidae found in Papua New Guinea and named after the Bismarck Archipelago. It was once considered a subspecies of Pteropus temminckii before being reassessed in 2001. This species has two subspecies, P. c. capistratus and P. c. ennisae. The IUCN classified it as Near Threatened in 2009, noting that the rate of decline is almost high enough to reclassify the species as Vulnerable.

The big-eared flying fox is a species of bat in the family Pteropodidae, larger bats who subsist largely on fruits. The species is distributed across a range in Indonesia, Papua New Guinea and islands nearing the Cape York peninsula at the northeast of Australia, at elevations less than 500 metres and often in coastal mangroves.
The eastern striped bandicoot is a species of marsupial in the family Peramelidae. It is found in eastern Papua New Guinea in the Enga Province. It is endemic to mountain forested habitats ranging from 1,000 – 3,600 m in elevation. The eastern striped bandicoot is a terrestrial omnivore.

The Halmahera naked-backed fruit bat is a common and widespread species of megabat in the family Pteropodidae. It is endemic to Indonesia. It is assessed as least-concern by the IUCN as it has a wide range and seems to have no significant threats.
The long-nosed paramelomys is a species of rodent of the family Muridae endemic to New Guinea. It is found in the lowlands of the south of the country.















