
Namadgi National Park is a protected area in the south-west of the Australian Capital Territory (ACT), bordering Kosciuszko National Park in New South Wales. It lies approximately 40 kilometres (25 mi) southwest of Canberra, and occupies approximately 46 percent of the ACT's land area.

Echidnas, sometimes known as spiny anteaters, are quill-covered monotremes belonging to the family Tachyglossidae, living in Australia and New Guinea. The four extant species of echidnas and the platypus are the only living mammals that lay eggs and the only surviving members of the order Monotremata. The diet of some species consists of ants and termites, but they are not closely related to the American true anteaters or to hedgehogs. Their young are called puggles.
The Kosciuszko National Park is a 6,900-square-kilometre (2,700 sq mi) national park and contains mainland Australia's highest peak, Mount Kosciuszko, for which it is named, and Cabramurra, the highest town in Australia. Its borders contain a mix of rugged mountains and wilderness, characterised by an alpine climate, which makes it popular with recreational skiers and bushwalkers.

Mount Kosciuszko is mainland Australia's tallest mountain, at 2,228 metres (7,310 ft) above sea level. It is located on the Main Range of the Snowy Mountains in Kosciuszko National Park, part of the Australian Alps National Parks and Reserves, in New South Wales, Australia, and is located west of Crackenback and close to Jindabyne, near the border with Victoria. Mount Kosciuszko is ranked 35th by topographic isolation.

A crane fly is any member of the dipteran superfamily Tipuloidea, which contains the living families Cylindrotomidae, Limoniidae, Pediciidae and Tipulidae, as well as several extinct families. "Winter crane flies", members of the family Trichoceridae, are sufficiently different from the typical crane flies of Tipuloidea to be excluded from the superfamily Tipuloidea, and are placed as their sister group within Tipulomorpha.

The drongos are a family, Dicruridae, of passerine birds of the Old World tropics. The 31 species in the family are placed in a single genus, Dicrurus.

The Australian Alps are a mountain range in southeast Australia. The range comprises an interim Australian bioregion, and is the highest mountain range in Australia. The range straddles the borders of eastern Victoria, southeastern New South Wales, and the Australian Capital Territory. It contains Australia's only peaks exceeding 2,000 m (6,600 ft) in elevation, and is the only bioregion on the Australian mainland in which deep snow falls annually. The range comprises an area of 1,232,981 ha.

Charlotte Pass is a snow resort and village in the Snowy Mountains of New South Wales, Australia. The pass is in the Kosciuszko National Park where the Kosciuszko Road crosses Kangaroo Ridge. Charlotte Pass is the closest village to Mount Kosciuszko, the tallest mountain in Australia.

The roundtail chub is a cyprinid fish in the genus Gila, of southwestern North America. It is native to the Colorado River drainage basin, including the Gila River and other tributaries, and in several other rivers. It is part of the "robusta complex", which includes the Gila robusta robusta, G.r. grahami, and G.r. seminuda.
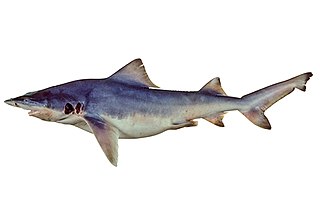
The northern river shark or New Guinea river shark is a species of requiem shark, in the family Carcharhinidae, found in scattered tidal rivers and associated coastal waters in northern Australia and in Papua New Guinea. This species inhabits areas with poor visibility, soft bottoms, and large tides, with immature sharks ranging into fresh and brackish water. It is similar to other river sharks in having a stocky grey body with a high back, tiny eyes, and broad fins. It measures up to 2.5 m (8.2 ft) long.

The smoky mouse is a species of rodent in the family Muridae native to southeastern Australia. It was first described in 1934 and its species name is Latin for "smoky". As its name suggests, it is a grey-furred mouse, darker grey above and paler smoky grey below. Mice from the Grampians are larger and a darker more slate-grey above. It has a black eye-ring and dark grey muzzle. The feet are light pink, and the ears a grey-pink. The tail is longer than the mouse's body, and is pink with a brownish stripe along the top. Mice from east of Melbourne average around 35 grams and have 107 mm long bodies with 116 mm long tails, while those from the Grampians are around 65 grams and have 122 mm long bodies with 132 mm long tails.

Eucalyptus robusta, commonly known as swamp mahogany or swamp messmate, is a tree native to eastern Australia. Growing in swampy or waterlogged soils, it is up to 30 m (100 ft) high with thick spongy reddish-brown bark and dark green broad leaves, which help form a dense canopy. The white to cream flowers appear in autumn and winter. The leaves are commonly eaten by insects and are a food item for the koala. It is an important autumn-winter flowering species in eastern Australia and has been planted extensively in many countries around the world. Its timber is used for firewood and in general construction.

Grevillea victoriae, also known as royal grevillea or mountain grevillea, is a species of flowering plant in the family Proteaceae and is endemic to mountainous regions of south-eastern continental Australia. It is an erect to spreading shrub with elliptic to lance-shaped leaves, and pendulous clusters of red to orange flowers.

Podolepis robusta, commonly known as alpine podolepis, mountain lettuce or cattleman's lettuce, is a perennial herb from the Australian Alps in the family Asteraceae.
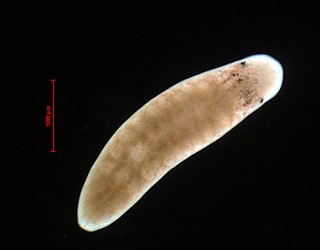
Camerata robusta is a species of triclad flatworm found in the shores of Italy. It is the only known species in the genus Camerata. Camerata refers to the chambers present in this genus' penis. The species name robusta refers to the strong muscles present in the copulatory apparatus.

The fauna of Bangladesh includes about 1,600 species of vertebrate fauna and about 1,000 species of invertebrate fauna based on incomplete records. The vertebrate fauna consists of roughly 22 species of amphibians, 708 species of fish, 126 species of reptiles, 628 species of birds and 113 species of mammals. The invertebrate fauna includes about 30 species of aphids, 20 species of bees, 178 species of beetles, 135 species of flies, 400 species of spiders, 150 species of lepidopterans 52 species of decapods, 30 species of copepods, 2 species of starfish, and some species of sand dollars, sea cucumbers, and sea urchins.

The white-cheeked macaque is a species of macaque found only in Mêdog County in southeastern Tibet and Arunachal Pradesh in northeastern India. The white-cheeked macaque lives in forest habitats, from tropical forests to primary and secondary evergreen broad-leaved forests and mixed broadleaf-conifer forests. The species was first described by Chinese primatologists Cheng Li, Chao Zhao, and Peng-Fei Fan, in the American Journal of Primatology in 2015. It is one of twenty-three extant species in the genus Macaca, and the most recent to be formally described to science. While the species' exact conservation status has not yet been determined, it is likely threatened by poaching, deforestation, and increased human development of its habitat, much like the other primates which inhabit the area.
Phallocephale is a monospecific genus of ovoviviparous velvet worm containing the single species Phallocephale tallagandensis. Males are distinguished by the presence of an eversible knoblike structure on the head, whereas females instead have a depression on their head. This species has 15 pairs of legs in both sexes. The type locality of this species is Tallaganda National Park, New South Wales, Australia. This species exhibits lecithotrophic ovoviviparity; that is, mothers in this species retain yolky eggs in their uteri.

The southern corroboree frog is a species of Australian ground frog native to southeastern Australia.
















