The Kuomintang (KMT), also referred to as the Guomindang (GMD), the Nationalist Party of China (NPC) or the Chinese Nationalist Party (CNP), is a political party in the Republic of China, initially based on the Chinese mainland and then in Taiwan since 1949. The KMT is a centre-right to right-wing party and the largest in the Pan-Blue Coalition, one of the two main political groups in Taiwan. Its primary rival is the Democratic Progressive Party (DPP), the largest party in the Pan-Green Coalition. As of 2024, the KMT is the largest single party in the Legislative Yuan. The current chairman is Eric Chu.
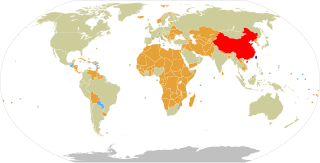
Foreign relations of the Republic of China (ROC), more commonly known as Taiwan, are accomplished by efforts of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of China, a cabinet-level ministry of the Government of the Republic of China. As of January 2024, the ROC has formal diplomatic relations with 11 of the 193 United Nations member states and with the Holy See, which governs the Vatican City State. In addition to these relations, the ROC also maintains unofficial relations with 59 UN member states, one self-declared state (Somaliland), three territories (Guam, Hong Kong, and Macau), and the European Union via its representative offices and consulates. In 2021, the Government of the Republic of China had the 33rd largest diplomatic network in the world with 110 offices.
The Taiwan independence movement is a political movement which advocates the formal declaration of an independent and sovereign Taiwanese state, as opposed to Chinese unification or the status quo in Cross-Strait relations.
Chinese unification, also known as Cross-Strait unification or Chinese reunification, is the potential unification of territories currently controlled, or claimed, by the People's Republic of China and the Republic of China ("Taiwan") under one political entity, possibly the formation of a political union between the two republics. Together with full Taiwan independence, unification is one of the main proposals to address questions on the political status of Taiwan, which is a central focus of Cross-Strait relations.
One China is a phrase describing the relationship between the People's Republic of China (PRC) based on Mainland China, and the Republic of China (ROC) based on the Taiwan Area. "One China" asserts that there is only one de jure Chinese nation despite the de facto division between the two rival governments in the aftermath of the Chinese Civil War. The term may refer, in alphabetical order, to one of the following:
The history of the Republic of China began in 1912 with the end of the Qing dynasty, when the Xinhai Revolution and the formation of the Republic of China put an end to 2,000 years of imperial rule. The Republic experienced many trials and tribulations after its founding which included being dominated by elements as disparate as warlord generals and foreign powers.
As a result of the surrender and occupation of Japan at the end of World War II, the islands of Taiwan and Penghu were placed under the governance of the Republic of China (ROC), ruled by the Kuomintang (KMT), on 25 October 1945. Following the February 28 massacre in 1947, martial law was declared in 1949 by the Governor of Taiwan, Chen Cheng, and the ROC Ministry of National Defense. Following the end of the Chinese Civil War in 1949, the ROC government retreated from the mainland as the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) proclaimed the establishment of the People's Republic of China. The KMT retreated to Taiwan and declared Taipei the temporary capital of the ROC. For many years, the ROC and PRC each continued to claim in the diplomatic arena to be the sole legitimate government of "China". In 1971, the United Nations expelled the ROC and replaced it with the PRC.

Chiang Pin-kung was a Taiwanese politician. He led the Ministry of Economic Affairs from 1993 to 1996, when he was named Minister of the Council for Economic Planning and Development, where he served until 2000. Chiang was subsequently elected to consecutive terms on the Legislative Yuan from 2002 to 2008. During his first term as a legislator, Chiang was Vice President of the Legislative Yuan. He was Chairman of the Straits Exchange Foundation from 2008 to 2012.

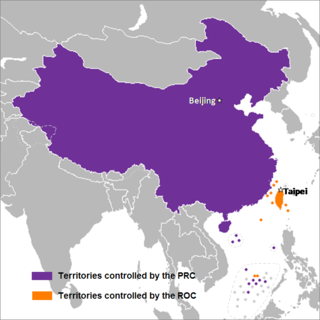
Cross-strait relations are the political and economic relations between mainland China and Taiwan across the Taiwan Strait. Due to the existing controversy over the status of Taiwan, they are also not defined as diplomatic relations by both sides.

Propaganda in the Republic of China has been an important tool since its inception with the 1911 Revolution for legitimizing the Nationalist government that retreated from mainland China to Taiwan in 1949. Anti-communism and opposition to the Chinese Communist Party have historically been central to propaganda in the Republic of China.

The concept of Two Chinas refers to the political divide between the People's Republic of China (PRC) and the Republic of China (ROC). The PRC was established in 1949 by the Chinese Communist Party, while the ROC was founded in 1912 and retreated to Taiwan after losing the Chinese Civil War.
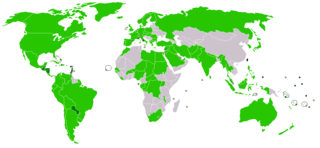
Numerous states have ceased their diplomatic recognition of the Republic of China during the last 70 years, since the founding of the People's Republic of China. Under the One China policy, the ROC is recognized by 11 UN member states and Holy See with 59 UN member states and Somaliland maintaining unofficial cultural and economic relations.

India and Republic of China (ROC) had formal diplomatic relations from 1942 to 1949. After severing diplomatic relations, the bilateral relations have improved since the 1990s, despite both countries not maintaining official diplomatic relations. India only recognises the People's Republic of China (PRC) since 1949. However, India's economic and commercial links as well as people-to-people contacts with Taiwan have expanded in recent years.

The Kuomintang (KMT) is a Chinese political party that ruled mainland China from 1927 to 1949 prior to its relocation to Taiwan as a result of the Chinese Civil War. The name of the party translates as "China's National People's Party" and was historically referred to as the Chinese Nationalists. The party was initially founded on 23 August 1912, by Sun Yat-sen but dissolved in November 1913. It reformed on October 10, 1919, again led by Sun Yat-sen, and became the ruling party in China. After Sun's death, the party was dominated from 1927 to 1975 by Chiang Kai-shek. After the KMT lost the civil war with the Chinese Communist Party in 1949, the party retreated to Taiwan and remains a major political party of the Republic of China based in Taiwan.

Chang Li-sheng was a Chinese politician and diplomat who served as the Secretary General of the Kuomintang from 1954 to 1959. L.S. Chang as he was commonly known, played a key role in Republic of China (ROC)'s political, economic, financial, and foreign affairs as well as in Kuomintang affairs from the 1920s until his death in Taiwan in 1971. Throughout his political life over four decades, Chang served in numerous important posts within both the KMT and the ROC's local and central governments. He was a rare example of Chinese political virtues, noted for his integrity and honesty. He is remembered for numerous achievements and deeds, including his role in assisting Chen Cheng (1897–1965), former Taiwan provincial governor, Premier, and Vice President, to launch Taiwan's local autonomy, economic and land reforms.

Fredrick F. Chien, or Fred Chien, Chien Foo, is a retired Taiwanese diplomat and politician who served as the President of the Republic of China Control Yuan from 1999 to 2005. After graduating from Yale University, he assumed a series of governmental positions include Director-General of the Government Information Office from 1972 to 1975, Republic of China Representative to the United States from 1982 to 1988, Chairman of the Council for Economic Planning and Development from 1988 to 1990, and Minister of Foreign Affairs from 1990 to 1996. He was also the Speaker of the National Assembly between 1996 and 1999.

The Republic of China (ROC) began as a sovereign state in mainland China on 1 January 1912 following the 1911 Revolution, which overthrew the Manchu-led Qing dynasty and ended China's imperial history. From 1927, the Kuomintang (KMT) ruled the country as a one-party state and made Nanjing the national capital. In 1949, the KMT-led government was defeated in the Chinese Civil War and lost control of the mainland to the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). The CCP established the People's Republic of China (PRC) while the ROC was forced to retreat to Taiwan and retains control over the "Taiwan Area"; the political status of Taiwan remains in dispute to this day.

Singapore–Taiwan relations are the international relations between Singapore and Taiwan. Taiwan has a representative office in Singapore. Singapore operates the Singapore Trade Office in Taipei in Taiwan, both of whom are members of the World Trade Organization (WTO). The Presidential Envoy of ROC and Prime Minister of Singapore regularly meet, in the form similar to private state-to-state gesture diplomacy at APEC.

Andrew Hsia is a Taiwanese politician who is a vice chairman of the Kuomintang. He was minister of the Mainland Affairs Council from February 2015 to May 2016, and was chairman of the Association of Foreign Relations (AFR) from 2017 to 2022. Since 2023, he continues to serve on the AFR Board as managing supervisor.

Larry Wang or Wang Yu-yuan is a Taiwanese senior diplomat of the Republic of China (Taiwan). He is a native of Wujin County, Jiangsu Province. He is proficient in English and Spanish.