Guaviare is a department of Colombia. It is in the southern central region of the country. Its capital is San José del Guaviare. Guaviare was created on July 4, 1991 by the new Political Constitution of Colombia. Up until that point, it was a national territory that operated as a Commissariat, segregated from territory of the then Commissariat of Vaupés on December 23, 1977.

The National Liberation Army is a Marxist–Leninist guerrilla group involved in the continuing Colombian conflict, which has existed in Colombia since 1964. The ELN advocate a composite communist ideology of Marxism-Leninism and liberation theology. In 2013, it was estimated that the ELN forces consisted of between 1,380 and 3,000 guerrillas. According to former ELN national directorate member Felipe Torres, one fifth of ELN supporters have taken up arms. The ELN has been classified as a terrorist organization by the governments of Colombia, United States, Canada the European Union and Venezuela's National Assembly.

The Colombian conflict began on May 27, 1964, and is a low-intensity asymmetric war between the government of Colombia, far-right paramilitary groups, crime syndicates, and far-left guerrilla groups such as the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC), the National Liberation Army (ELN) and the Popular Liberation Army (EPL), fighting each other to increase their influence in Colombian territory. Some of the most important international contributors to the Colombian conflict include multinational corporations, the United States, Cuba, and the drug trafficking industry.

Mitú is the capital town of the department of Vaupés in Colombia. It is a small town located in South eastern Colombia in the Amazon Basin. Founded in 1936, Mitú lies next to the Vaupés River at 180 meters above sea level. It is where the core of the services are provided to the Vaupés Department.
The Bojayá massacre was a massacre that occurred on May 2, 2002 in the town of Bellavista, Bojayá Municipality, Chocó Department, Colombia. Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC) guerrillas attacked the town in an attempt to take control of the Atrato River region from United Self-Defense Forces of Colombia (AUC) paramilitaries. During the fighting, a cylinder bomb launched by the FARC with a mortar at the AUC paramilitaries positioned by the walls of a church, went through the roof of the church instead, landing on the altar inside. Of the approximately 300 inhabitants of the town who had taken refuge in the church, 119 died in the explosion.
The Eastern Bloc of the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia, from September 2010 known as Bloque Comandante Jorge Briceño, in honour of the slain guerrilla leader, was considered to be the strongest military faction of the guerrilla group. It was divided into groups of 50–400 combatants in each group, which patrolled and controlled different areas of Colombia's Eastern and Central-Eastern territory, as well as helped to carry out the killings, taxation, and arrests necessary to advance the organization's financial and political goals.

Fonseca is a municipality located in the Colombian Department of La Guajira. The town celebrates the Festival del Retorno in honor of St Augustine with religious celebrations, vallenato music events and others.

Cumaribo is a town and municipality located in the Department of Vichada, Republic of Colombia. Cumaribo was founded by Jose Nicolino Mattar in 1959.
The Northwestern Bloc of the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia, also known as the Iván Ríos Bloc has historically been a strong influence in the Medellín and Antioquia regions, and still is today. It has been among the blocs most seriously targeted by former president Álvaro Uribe's defense plan and the Colombian Army's offensive. Due to this, the bloc has been forced to retreat to more remote areas of the countryside and has lost the dominance it once had in the area. The specific divisions of the group are arguable. Because of the current conflict existing in the country, much of the information recovered is conflicting. Some of the believed divisions or "fronts", as they are commonly called, are shown below. Many of these fronts sometimes work together towards a certain mission, while others are further divided into "columns" and "companies" with a smaller number of members. For more general information see FARC-EP Chain of Command.

Jhon Frank Pinchao Blanco is a Colombian policeman with the rank of Second Lieutenant who was kidnapped by the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC) guerrilla group after Farc's attack on the town of Mitú, Vaupés Department on November 1, 1998. He escaped in 2007.

The Valle del Cauca Deputies hostage crisis refers to the kidnapping of 12 Deputies of the Valle del Cauca Department, Colombia, on April 12, 2002 by members of the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC) to pressure a prisoner exchange between them and the government and to negotiate the demilitarization of the municipalities of Florida and Pradera to initiate peace dialogues.

This is a timeline of events related to the Colombian armed conflict.

The Colombian elections of 2007 refers to the democratic elections of October 28, 2007 in the Republic of Colombia. The elections were organized as established by the Colombian Constitution of 1991 by the National Electoral Council to elect Department governors with its respective Department Assemblies, Mayors with their respective City Councils and the Local Administrative Juntas (JAL).
Jorge Enrique Rodríguez Mendieta known by his nom de guerre Iván Vargas is a Colombian guerrilla leader member of the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC-EP), former commander of the 24th Front of the Middle Magdalena Bloc of the FARC-EP. Vargas was arrested in late 2004 in the city of Bucaramanga by Colombian authorities and extradited to the United States on 3 November 2007 on charges of narcotrafficking.

The Humanitarian Exchange or Humanitarian Accord referred to a possible accord to exchange hostages for prisoners between the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC) guerrilla group and the Government of Colombia.
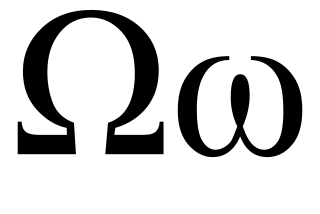
Joint Task Force OMEGA is a joint task force involving the Military of Colombia in support of Plan Patriota assembled with the main purpose of capturing the leaders of the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC).
Operation JM was a military operation by the Military of Colombia Joint Task Force OMEGA intended to capture or kill the leaders of the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia guerrilla (FARC), as part of the Plan Patriota. The operations began in April 2004 and after some 30 operations concluded without the main objective being accomplished in December 2006. However, the Colombian military achieved numerous military advances in a region that had been dominated by the guerrillas.
Mauricio Jaramillo is the nom de guerre of Jaime Alberto Parra, known as El Médico or Wilson Valderrama Cano a former high-ranking guerrilla commander of the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC), also known as El Médico. Jaramillo became a member of the FARC Secretariat in March 2008, replacing Iván Ríos.
Operation Jaque, named after the first letter of the month of the operation, July, and referencing check in chess, was a Colombian military operation that resulted in the successful rescue of 15 hostages, including former Colombian presidential candidate Íngrid Betancourt. The hostages had been held by the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC). The operation took place on July 2, 2008, along the Apaporis River in the department of Guaviare.