Bombesin is a 14-amino acid peptide originally isolated from the skin of the European fire-bellied toad by Vittorio Erspamer et al. and named after its source. It has two known homologs in mammals called neuromedin B and gastrin-releasing peptide. It stimulates gastrin release from G cells. It activates three different G-protein-coupled receptors known as BBR1, -2, and -3. It also activates these receptors in the brain. Together with cholecystokinin, it is the second major source of negative feedback signals that stop eating behaviour.

Virgil Craig Jordan,, is a scientist with American and British citizenship specializing in drugs for breast cancer treatment and prevention. Currently, he is Professor of Breast Medical Oncology, and Professor of Molecular and Cellular Oncology at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas. Previously, he was Scientific Director and Vice Chairman of Oncology at the Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center of Georgetown University. Jordan was the first to discover the breast cancer prevention properties of tamoxifen and the scientific principles for adjuvant therapy with antihormones. More recently his work has branched out into the prevention of multiple diseases in women with the discovery of the drug group, selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERMs). Currently, he plans to develop a new Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) for post-menopausal women that prevents breast cancer and does not increase the risk of breast cancer.

G protein-coupled receptor 35 also known as GPR35 is a G protein-coupled receptor which in humans is encoded by the GPR35 gene. Heightened expression of GPR35 is found in immune and gastrointestinal tissues, including the crypts of Lieberkühn.
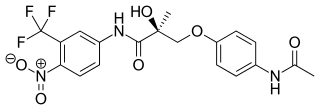
Andarine is an investigational selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) developed by GTX, Inc for treatment of conditions such as muscle wasting, osteoporosis and benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH), using the nonsteroidal antiandrogen bicalutamide as a lead compound.
The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering pharmacology. It has been published since 1909 by the American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics (ASPET). The journal publishes mainly original research articles, and accepts papers covering all aspects of the interactions of chemicals with biological systems.
The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics (ASPET) is a scientific society founded in late 1908 by John Jacob Abel of Johns Hopkins University, with the aim of promoting the growth of pharmacological research. Many society members are researchers in basic and clinical pharmacology who help develop disease-fighting medications and therapeutics. ASPET is one of the constituent societies of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB). The society's headquarters are in Rockville, MD. The current president is Michael F. Jarvis.

Drug Metabolism and Disposition is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering the fields of pharmacology and toxicology. It was established in 1973 and is published monthly by the American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. The journal publishes articles on in vitro and in vivo studies of the metabolism, transport, and disposition of drugs and environmental chemicals, including the expression of drug-metabolizing enzymes and their regulation. As of 2022, the editor-in-chief is XinXin Ding.

Hopeaphenol is a stilbenoid. It is a resveratrol tetramer. It has been first isolated from Dipterocarpaceae like Shorea ovalis. It has also been isolated from wines from North Africa.
Michael J. Kuhar, is an American neuroscientist, author, and Candler Professor of Neuropharmacology at The Yerkes National Primate Research Center of Emory University. He is a Georgia Research Alliance eminent scholar, and a senior fellow in the Center for Ethics at Emory. He was previously a professor at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and branchchief at the National Institute on Drug Abuse.
Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal which covers research on the nature, action, efficacy, and evaluation of therapeutics. The editor-in-chief is Piet van der Graaf. The journal was established in 1960 and is published by Wiley-Blackwell. It is an official journal of the American Society for Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics.
The John J. Abel Award is an annual award presented by the American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics (ASPET). The award is given for outstanding research in the field of pharmacology and/or experimental therapeutics; which comes with a $5000 prize, An engraved plaque, and all travel expenses paid to attend the ASPET Annual Meeting at Experimental Biology. The Award is named after American biochemist and pharmacologist, John Jacob Abel.

Salomon Zender Langer is an Argentinian pharmacologist whose family had fled from Poland to Argentina in the early 1930s and were thus saved from the Holocaust during the Second World War.
Nancy Rutledge Zahniser was an American pharmacologist, best known for her work involving the mechanism of dopaminergic pathways and chemical modifications of them. Although born in Ann Arbor, Michigan, Zahniser grew up in Chillicothe, Ohio and subsequently enrolled at the College of Wooster, where she obtained a degree in chemistry. After completing her degree, Zahniser spent some time in India where she met her first husband Mark Zahniser; she later returned to the United States to attend the University of Pittsburgh School of Pharmacy, where she earned her PhD in pharmacology in 1977. Zahniser went on to complete her post-doctoral training at the University of Colorado Health Sciences Center's Department of Pharmacology and then became a part of the faculty there. In 2007, she became associate dean for research education. She played a role in advancing the careers of many post-doctoral students in her lab. In addition to her work as a professor, Zahniser was also a member of several boards, committees, review panels, and professional societies related to pharmacology, neuroscience, and addiction. She led several national research meetings from 1995-2002.
Marion Sewer (1972-2016) was a pharmacologist and professor at the University of California, San Diego's Skaggs School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences known for her research on steroid hormone biogenesis and her commitment to increasing diversity in science. Much of her research centered around cytochrome P450, a family of enzymes involved in the conversion of cholesterol into steroid hormones. She died unexpectedly at the age of 43 from a pulmonary embolism on January 28, 2016, while traveling through the Detroit airport.

Namandjé N. Bumpus is an American pharmacologist and the Chief Scientist of the Food and Drug Administration. She was previously director of the department of pharmacology and molecular sciences at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, where she holds the E.K. Marshall and Thomas H. Maren professorship in pharmacology. Bumpus is known for her research on the metabolism of antiviral drugs used to treat HIV-1 and how genetic variations in drug-processing enzymes may impact these drugs' efficacy. Bumpus received a Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers in 2016.
Joan Heller Brown is an American pharmacologist. She is Distinguished Professor and Chair of the Department of Pharmacology at UC San Diego School of Medicine. She is known for fundamental contributions to the understanding of G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) — molecules that span cell membranes, where they transmit messages between cells and their environments — and how GPCRs regulate cell growth and survival, in healthy and various disease states. Many therapeutic drugs work by influencing GPCRs, thus Heller Brown's discoveries have been crucial to their development.
Paul Anthony Insel is an American physician and pharmacologist. He has been the chief editor of four academic journals and is an elected fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science, American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, and American Physiological Society. His research is primarily focused on G proteins.
Lee Limbird is a pharmacologist, Dean of the School of Natural Science, Mathematics and Business & Professor in the Department of Life and Physical Sciences at Fisk University, Nashville, Tennessee.
Eva King Killam was a research pharmacologist who studied the activity of drugs on the brain and behavior, developing animal models for epilepsy and opiate dependence.
John Stephen Lazo is an American pharmacologist noted for his work discovering the fundamental mechanisms of action of small molecule therapeutics and the factors that confer drug resistance. He is a professor emeritus of pharmacology at University of Virginia.








