
Niger–Congo is a hypothetical language family spoken over the majority of sub-Saharan Africa. It unites the Mande languages, the Atlantic-Congo languages, and possibly several smaller groups of languages that are difficult to classify. If valid, Niger-Congo would be the world's largest in terms of member languages, the third-largest in terms of speakers, and Africa's largest in terms of geographical area. It is generally considered to be the world's largest language family in terms of the number of distinct languages, just ahead of Austronesian, although this is complicated by the ambiguity about what constitutes a distinct language; the number of named Niger–Congo languages listed by Ethnologue is 1,540.

The Nilo-Saharan languages are a proposed family of African languages spoken by some 50–60 million people, mainly in the upper parts of the Chari and Nile rivers, including historic Nubia, north of where the two tributaries of the Nile meet. The languages extend through 17 nations in the northern half of Africa: from Algeria to Benin in the west; from Libya to the Democratic Republic of the Congo in the centre; and from Egypt to Tanzania in the east.

Benue–Congo is a major branch of the Volta-Congo languages which covers most of Sub-Saharan Africa.
Mpra, or Mpre, is an extinct language spoken in the village of Butei in central Ghana, located between the towns of Techiman and Tamale near the confluence of the Black and White Voltas. Mpra has been difficult to classify due to its divergent vocabulary. It is known only from a 70-word list given in a 1931 article. Blench (2007) considers it to be a possible language isolate. A poorly attested language spoken in the nearby village of Tuluwe, Mpur, may also turn out to be yet another language isolate. Both Butie and Tuluwe are located near the village of Mpaha.

Southern Bantoid is a branch of the Bantoid language family. It consists of the Bantu languages along with several small branches and isolates of eastern Nigeria and west-central Cameroon. Since the Bantu languages are spoken across most of Sub-Saharan Africa, Southern Bantoid comprises 643 languages as counted by Ethnologue, though many of these are mutually intelligible.

The approximately 450 Oceanic languages are a branch of the Austronesian languages. The area occupied by speakers of these languages includes Polynesia, as well as much of Melanesia and Micronesia. Though covering a vast area, Oceanic languages are spoken by only two million people. The largest individual Oceanic languages are Eastern Fijian with over 600,000 speakers, and Samoan with an estimated 400,000 speakers. The Gilbertese (Kiribati), Tongan, Tahitian, Māori and Tolai languages each have over 100,000 speakers. The common ancestor which is reconstructed for this group of languages is called Proto-Oceanic.
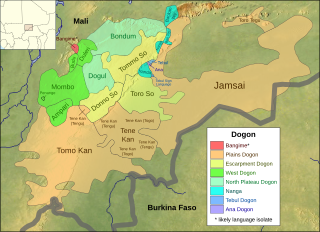
The Dogon languages are a small closely-related language family that is spoken by the Dogon people of Mali and may belong to the proposed Niger–Congo family. There are about 600,000 speakers of its dozen languages. They are tonal languages, and most, like Dogul, have two tones, but some, like Donno So, have three. Their basic word order is subject–object–verb.

The Tivoid languages are a branch of the Southern Bantoid languages spoken in parts of Nigeria and Cameroon. The subfamily takes its name after Tiv, the most spoken language in the group.

There are over 525 native languages spoken in Nigeria. The Nigerian official language is English, the language of former colonial British Nigeria. As reported in 2003, Nigerian Pidgin was spoken as a second language by 60 million people in Nigeria.
Semi-Bantu or Semibantu is a used for specific inhabitants of the Western grassfields of Cameroon, who speak languages that have certain characteristics to the Bantu language family, but they're excluded from them. The people themselves are considered ethnically and linguistically divergent from other Bantu peoples of central and southern Africa.

The Beboid languages are any of several groups of languages spoken principally in southwest Cameroon, although two languages are spoken over the border in Nigeria. They are probably not most closely related to each other. The Eastern Beboid languages may be most closely related to the Tivoid and Momo groups, though some of the geographical Western Beboid grouping may be closer to Ekoid and Bantu.

The Ekoid languages are a dialect cluster of Southern Bantoid languages spoken principally in southeastern Nigeria and in adjacent regions of Cameroon. They have long been associated with the Bantu languages, without their status being precisely defined. Crabb (1969) remains the major monograph on these languages, although regrettably, Part II, which was to contain grammatical analyses, was never published. Crabb also reviews the literature on Ekoid up to the date of publication.
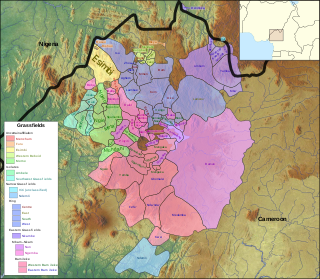
The Grassfields languages are a branch of the Southern Bantoid languages spoken in the Western High Plateau of Cameroon and some parts of Taraba state, Nigeria. Better known Grassfields languages include the Eastern Grassfields languages Bamun, Yamba and the Ring language, Kom, Nso, Oku, Bali, Bafut. Almost all of these languages are closely related, sharing approximately half of their vocabulary.
The Nun languages are a group of Eastern Grassfields languages spoken by the Bamum (Mum) and related peoples of the Western High Plateau of Cameroon.
The Southwest Grassfields, traditionally called Western Momo when considered part of the Momo group or when Momo is included in Grassfields, are a small branch of the Southern Bantoid languages spoken in the Western grassfields of Cameroon.
Yiwom (Ywom), also known as Gerka or Gerkawa by the Hausa, is a Chadic (Afro-Asiatic) language spoken in Plateau State, Nigeria.
Menka is a Grassfields language of Cameroon. Other names include Mamwoh and Wando Bando. It is spoken by an estimated 5,200 people.
Amasi is a Southern Bantoid language of Cameroon.

The Ron, Ronic or Ron–Fyer languages, group A.4 of the West Chadic branch of the Afro-Asiatic language family, are spoken in Plateau State, north-central Nigeria.
Ndzerem is a Grassfields Bantu language spoken in Cameroon.












