Related Research Articles
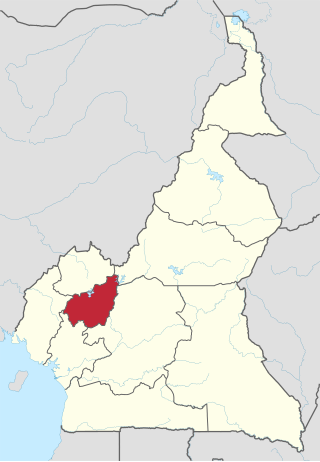
The West Region is 14,000 km2 of territory located in the central-western portion of the Republic of Cameroon. It borders the Northwest Region to the northwest, the Adamawa Region to the northeast, the Centre Region to the southeast, the Littoral Region to the southwest, and the Southwest Region to the west. The West Region is the smallest of Cameroon's ten regions in area, yet it has the highest population density.

The Bamileke are a Central African people who inhabit the Western High Plateau of Cameroon. They primarily speak Yemba, a Southern Bantoid language within the Bamileke language group.
Bangangté is a town and commune in Cameroon. It is the capital of the Ndé division of West Region. The town is primarily inhabited by the people of the Bamileke (Bamiléké) tribe.

Bafoussam is the capital and largest city of the West Region of Cameroon, in the Bamboutos Mountains. It is the 3rd most important (financially) city in Cameroon, after Yaoundé and Douala. The communauté urbaine of Bafoussam, is a decentralized territorial collectivity. Originally called Urban Commune of Bafoussam, the communauté urbaine of Bafoussam, was born after the Presidential Decree N ° 2008/022 of January 17, 2008 and composed of three communes, namely: the Commune of Bafoussam I, the Commune of Bafoussam II (Baleng) and the Commune of Bafoussam III (Bamougoum).
Bend-skin is a kind of urban Cameroonian popular music. Kouchouam Mbada is the best known group associated with the genre. Several other artists have over the years contributed to the growth and popularity of bend skin. It is related to mangambeu, and is played using only drums and maracas, with a vocalist who both sings and raps. It is often sung in Medumba which is the language of the Bangangte people and in many other Bamileke dialects.
Fe'fe' or Fe'efe'e, also known as Nufi or Bafang, is a Bamileke language spoken in Cameroon, around the town of Bafang. It was one of the four languages selected for option at the Collège Libermann at Douala.
The Bamileke languages are a group of Eastern Grassfields languages spoken by the Bamileke people in the Western High Plateau of Cameroon.
The Ngiemboon (N'Jhamboon) language, Ngyɛmbɔɔŋ, is one of a dozen Bamileke languages spoken in Cameroon. Its speakers are located primarily within the department of Bamboutos in the West Region of Cameroon.
The Eastern Grassfields languages, spoken in the Western High Plateau of Cameroon, are a branch of the Grassfields languages including Bamun, Yamba and Bamileke.

The Ngemba languages are a group of Eastern Grassfields languages of the Western High Plateau of Cameroon.
Ngwe is a Bamileke language spoken predominantly in Lebialem, Cameroon. As of 2001, Ngwe had 73,200 speakers, which was an increase from the numbers of previous censuses. Its closest relatives are Yemba and Ngiemboon.

Baham is the seat of the Department of Hauts-Plateaux, in the Western Province of Cameroon. It also constitutes a traditional Bamileke chiefdom.

Ghɔmálá’, or Bamileke-Banjun (Bamiléké-Bandjoun), is a major Bamileke language of Cameroon.
Yɛmba or Yemba, also Yémba or Bamiléké Dschang, is a major Bamileke language of Cameroon. It was spoken by 300,000 or so people in the West Region ca. 1990.
Medumba is a Bamileke language of Cameroon. The people who speak it originate from the Nde division of the West Region of the country, with their main settlements in Bangangté, Bakong, Bangoulap, Bahouoc, Bagnoun and Tonga. It is a major Bamileke language, and is located in an area where sacred kingship played a pivotal role in government, justice, and diplomacy. The modern history of the Bamileke area, which was a German colony placed under French trusteeship by the League of Nations in 1919, is closely associated with the nationalist movement of the Union des Populations du Cameroun (UPC), which developed primarily in the coastal hinterland (Bassa) and the western highlands (Bamileke). From 1956 to the late 1960s, this area of Cameroon experienced a period of unrest; this episode continues to shape Bamileke political culture, and has an impact on language identity and the linguistic landscape.
Ngomba, or Ngomba Bamileke, is a Bamileke language of Cameroon.
Mengaka (Məgaka), or Mengaka Bamileke, is a Bamileke language of Cameroon. It was written in an indigenous script called Bagam.
Ndaʼndaʼ is a Bamileke language of Cameroon. Dialects are Ungameha and Undimeha ; Batoufam is a subdialect of the latter.
Kwaʼ (Bakwa) is a minor Bamileke language of Cameroon.
Kingunge Ngombale–Mwiru was a veteran Tanzanian politician, who died on 2 February 2018.
References
- ↑ Ngombale at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)