Related Research Articles
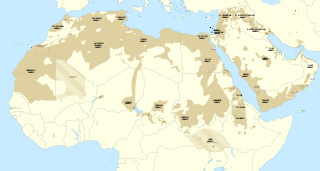
The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They include Arabic, Amharic, Hebrew, and numerous other ancient and modern languages. They are spoken by more than 330 million people across much of West Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, Malta, and in large immigrant and expatriate communities in North America, Europe, and Australasia. The terminology was first used in the 1780s by members of the Göttingen school of history, who derived the name from Shem, one of the three sons of Noah in the Book of Genesis.

Asia is home to hundreds of languages comprising several families and some unrelated isolates. The most spoken language families on the continent include Austroasiatic, Austronesian, Japonic, Dravidian, Indo-European, Afroasiatic, Turkic, Sino-Tibetan and Kra–Dai. Many languages of Asia, such as Kurdish, Sanskrit, Arabic or Tamil, have a long history as a written language.

An extinct language is a language that no longer has any first-language or second-language speakers, especially if the language also has no living descendants. In contrast, a dead language is a language that no longer has any first-language speakers, but does have second-language speakers, such as Latin. A dormant language is a dead language that still serves as a symbol of ethnic identity to an ethnic group; these languages are often undergoing a process of revitalisation. Languages that have first-language speakers are known as modern or living languages to contrast them with dead languages, especially in educational contexts.
Bikya is a potentially extinct Southern Bantoid language spoken in Cameroon. It is one of the three, or four, Furu languages. In 1986 four surviving speakers were identified, although only one spoke the language fluently.

Southern Bantoid is a branch of the Bantoid language family. It consists of the Bantu languages along with several small branches and isolates of eastern Nigeria and west-central Cameroon. Since the Bantu languages are spoken across most of Sub-Saharan Africa, Southern Bantoid comprises 643 languages as counted by Ethnologue, though many of these are mutually intelligible.

Barbacoan is a language family spoken in Colombia and Ecuador.

Furus also known as Phuroos or Furoos is a village in Ratnagiri district, Maharashtra state in Western India. The 2011 Census of India recorded a total of 3255 residents in the village with total area 1062.35 hectares. It is predominantly populated by Konkani Muslims along with Hindu and Buddhist. Furus is believed to be named by Persians who came here to trade in horses. The main language spoken in Furus is Kokni, a blend of Bankoti, Sangameshwari and Marathi infused with words of Arabic, Urdu and Persian origin.

Furu Furu Park is a collection of minigames for the Wii. It was developed and published by Taito and was originally planned for a release in Japan for the Wii launch, but was pushed back to April 19, 2007. The minigames are inspired by classic Taito arcade games. Majesco Entertainment published the title in the US on January 16, 2008. There are 2 single-player modes and 3 multi-player modes. It has 30 minigames to play.

The Beboid languages are any of several groups of languages spoken principally in southwest Cameroon, although two languages are spoken over the border in Nigeria. They are probably not most closely related to each other. The Eastern Beboid languages may be most closely related to the Tivoid and Momo groups, though some of the geographical Western Beboid grouping may be closer to Ekoid and Bantu.
Furu River may refer to:
Busuu is an unclassified Southern Bantoid language of Cameroon. According to Ethnologue it is extinct. As of 2005 there were 3 speakers of the language. Busuu is an endangered language.
The Kara languages are Tar Gula and possibly related Central Sudanic languages of the Central African Republic. The name Kara is used for numerous other peoples of the region, and so is often ambiguous.
Furu may refer to:
The Furu languages are a proposed group of poorly attested extinct or nearly extinct and otherwise unclassified Southern Bantoid languages of Cameroon. Suggested Furu languages are:
Furu is a Central Sudanic language of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Glottolog has it as one of the Kara languages, in line with recent literature, while Blench (2012) follows older lit in listing it as a Kresh language.
Kresh is a small language group of South Sudan. It is generally considered to be a branch of the Central Sudanic languages. Boyeldieu (2010) judges that this has yet to be demonstrated satisfactorily, but Starostin (2016) finds convincing evidence, and that its closest relative within that family appears to be Birri.

Kum Kum is a Japanese animated television series, consisting of 26 episodes. The plot and characters were created by Yoshikazu Yasuhiko, and it was directed by Rintaro and first broadcast on TBS between 3 October 1975 and 26 March 1976. The name was changed to Kum Kum after the sixth episode.
Afudu may refer to:
Jamal al-Din al-Ghaznawi, was a Sunni Hanafi jurist, theologian, and Kalam scholar of the Maturidi school.