Related Research Articles
Duala is a dialect cluster spoken by the Duala and Mungo peoples of Cameroon. Douala belongs to the Bantu language family, in a subgroup called Sawabantu. Maho (2009) treats Douala as a cluster of five languages: Douala proper, Bodiman, Oli, Pongo and Mongo. He also notes a Douala-based pidgin named Jo.

The Bakweri are an ethnic group of the Republic of Cameroon. They are closely related to Cameroon's coastal peoples, particularly the Duala and Isubu.

Kamerun was an African colony of the German Empire from 1884 to 1916 in the region of today's Republic of Cameroon. Kamerun also included northern parts of Gabon and the Congo with western parts of the Central African Republic, southwestern parts of Chad and far eastern parts of Nigeria.
Duala or Douala can refer to:

The Duala are a Bantu ethnic group of Cameroon. They primarily inhabit the littoral and southwest region of Cameroon and form a portion of the Sawabantu or "coastal people" of Cameroon. The Dualas readily welcomed German and French colonial policies. The number of German-speaking Africans increased in four West African German colonies prior to 1914. The Duala leadership in 1884 placed the tribe under German rule. Most converted to Protestantism and were schooled along German lines. Colonial officials and businessmen preferred them as inexpensive clerks to German government offices and firms in Africa. They have historically played a highly influential role in Cameroon due to their long contact with Europeans, high rate of education, and wealth gained over centuries as slave traders and landowners. Duala (surname)
The Mungo (Moungo) are an ethnic group of the Republic of Cameroon. Along with the other coastal peoples, they belong to the Sawa ethnic groups. The Mungo have historically been dominated by the Duala people, and the two groups share similar cultures, histories, and claims of origin.

The Isubu are an ethnic group who inhabit part of the coast of Cameroon. Along with other coastal peoples, they belong to Cameroon's Sawa ethnic groups. They were one of the earliest Cameroonian peoples to make contact with Europeans, and over two centuries, they became influential traders and middlemen. Under the kings William I of Bimbia and Young King William, the Isubu formed a state called Bimbia.
Malimba may refer to:
A jengu is a water spirit in the traditional beliefs of the Sawa ethnic groups of Cameroon, particularly the Duala, Bakweri, Malimba, Batanga, Bakoko,Oroko People and related Sawa peoples. Among the Bakweri, the name is liengu. Miengu are similar to Mami Wata spirits Bakoko the name is Bisima.

Martin-Paul Samba, born Mebenga m'Ebono, was a Bulu military officer during the Imperial German colonial period of Cameroon. M'Ebono became a favourite of the German colonials during his upbringing in Kribi, a coastal settlement in southern Cameroon. He was sent to Germany in 1891 to enter the German Military Academy; he was baptised Martin-Paul Samba while abroad. Upon graduation, Samba returned to Cameroon and accompanied German military expeditions across the colony.

The Bakole are an ethnic group of the Republic of Cameroon. They belong to the Sawa, or Cameroonian coastal peoples. The Bakole speak a language of the same name.
The Mulimba are an ethnic group of the Republic of Cameroon. They belong to the Sawa peoples, those of the Cameroonian coast.
Ewale a Mbedi was the eponymous ancestor of the Duala people of Cameroon. According to the oral histories of the Duala and related Sawa peoples of the Cameroon coast, Ewale hailed from a place called Piti. He and his followers migrated southwest to the coast and settled at the present-day location of Douala. The area was inhabited by the Bassa and/or Bakoko, who were driven inland by the new arrivals. Meanwhile, Ewale and his followers set up trade with European merchant ships.
Mbedi a Mbongo is the common ancestor of many of the Sawa coastal ethnic groups of Cameroon according to their oral traditions. Stories say that he lived at a place called Piti, northeast of present-day Douala. From there, his sons migrated south toward the coast in what are known as the Mbedine events. These movements may be mythical in many cases, but anthropologists and historians accept the plausibility of a migration of some Sawa ancestors to the coast during the 16th century.

Rudolf Duala Manga Bell was a Duala king and resistance leader in the German colony of Kamerun (Cameroon). After being educated in both Kamerun and Europe, he succeeded his father Manga Ndumbe Bell on 2 September 1908, styling himself after European rulers, and generally supporting the colonial German authorities. He was quite wealthy and educated, although his father left him a substantial debt.
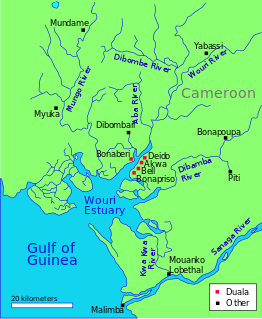
The Wouri estuary, or Cameroon estuary is a large tidal estuary in Cameroon where several rivers come together, emptying into the Bight of Biafra. Douala, the largest city in Cameroon, is at the mouth of the Wouri River where it enters the estuary. The estuary contains extensive mangrove forests, which are being damaged by pollution and population pressures.
Sawabantu languages are a group of Bantu languages comprising most of zones A.20 and A.30 of Guthrie's classification, and most likely also part of zone A.10. According to Nurse & Philippson (2003), the A.20 and A.30 languages apart from Bubi form a valid node. The most important of these languages is Duala, which is a vehicular language.
Tanga, or Noho, is a Bantu language of Cameroon and Equatorial Guinea. Limba speakers report some degree of mutual intelligibility and call it "Old Malimba".
The Oroko are an ethnic group in Cameroon. They belong to the coastal Bantu group, widely known as Sawa, and primarily occupy the Ndian and Meme divisions of the Southwest Region of Cameroon. The people predominantly speak Oroko, English, and Cameroon Pidgin English. The Oroko are related to several ethnic groups in Cameroon's coastal areas, with whom they share a common traditional origin, and similar histories and cultures. These include the Bakweri (Kwe), Bakole, Duala, Ewodi, the Bodiman, the Pongo, the Bamboko, the Isubu, the Limba, the Mungo, and the Wovea.
References
- ↑ Limba at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Malimba". Glottolog 3.0 . Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- ↑ Jouni Filip Maho, 2009. New Updated Guthrie List Online
- ↑ M. Lamberty - A rapid appraisal survey of Malimba in Cameroon
| This Bantu language-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |