Related Research Articles

Makhuwa is the primary Bantu language of northern Mozambique. It is spoken by four million Makua people, who live north of the Zambezi River, particularly in Nampula Province, which is virtually entirely ethnically Makua. It is the most widely spoken indigenous language of Mozambique.
Haya is a Bantu language spoken by the Haya people of Tanzania, in the south and southwest coast of Lake Victoria. In 1991, the population of Haya speakers was estimated at 1,200,000 people. Its closest relative is the Nyambo language and it is also closely related to the languages of southwest Uganda such as Nkore-Kiga, Rutooro and Runyoro which all form a group called Rutara.
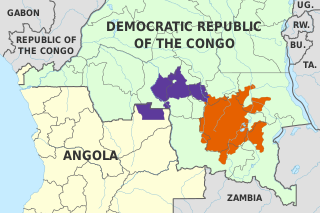
Luba-Katanga, also known as Luba-Shaba and Kiluba, is a Bantu language of Central Africa. It is spoken mostly in the south-east area of the Democratic Republic of the Congo by the Luba people.
Mongo, also called Nkundo or Mongo-Nkundu, is a Bantu language spoken by several of the Mongo peoples in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Mongo speakers reside in the north-west of the country over a large area inside the curve of the Congo River. Mongo is a tonal language.
Tswa (Xitswa) is a South-Eastern Bantu language in Southern Mozambique. Its closest relatives are Ronga and Tsonga, the three forming the Tswa–Ronga family of languages.
Makonde, or Kimakonde, is the language spoken by the Makonde, an ethnic group in southeast Tanzania and northern Mozambique. Makonde is a central Bantu language closely related to Yao. The Matambwe (Matembwe) and Mabiha (Maviha) dialects are divergent, and may not be Makonde.
The Mwani language, also known by its native name Kimwani, is a Bantu language spoken on the coast of the Cabo Delgado Province of Mozambique, including the Quirimbas Islands. Although it shares high lexical similarity (60%) with Swahili, it is not intelligible with it. It is spoken by around 167,150 people. Speakers also use Portuguese, Swahili and Makhuwa language. Kiwibo, the dialect of the Island of Ibo is the prestige dialect. Kimwani is also called Mwani and Ibo. According to Anthony P. Grant Kimwani of northern Mozambique appears to be the result of imperfect shift towards Swahili several centuries ago by speakers of Makonde, and Arends et al. suggest it might turn out to be a Makonde–Swahili mixed language.
Kgalagadi is a Bantu language spoken in Botswana, along the South African border. It is spoken by about 40,000 people. In the language, it is known as Shekgalagari.
Mbugwe or Mbuwe (Kimbugwe) is a Bantu language spoken by the Mbugwe people of Lake Manyara in the Manyara Region of Central Tanzania. Mbugwe is estimated to be spoken by some 34,000 people.
Kuria is a Bantu language spoken by the Kuria people of Northern Tanzania, with some speakers also residing in Kenya.
The Luban languages are a group of Bantu languages spoken by the Lubas in the south of DRC Congo, established by Christine Ahmed (1995). They constitute half of Guthrie's Zone L. The languages, or clusters, along with their Guthrie identifications, are:
Luyana (Luyaana), also known as Luyi, is a Bantu language spoken in Zambia and perhaps in small numbers in neighboring countries. It appears to be an divergent lineage of Bantu. It is spoken by the Luyana people, a subgroup of the Lozi people.
Mituku is a Bantu language of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The Mokpá dialect is distinct.
Holoholo is a Bantu language of DR Congo and formerly in Tanzania spoken by the Holoholo people on either side of Lake Tanganyika. Classification is uncertain, but it may belong with the Takama group.
Lwalu, also known as Lwalwa, is a Bantu language of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Its classification is uncertain: Nurse (2003), following Ahmed (1995), assigns all of Guthrie's L.20 languages to Luban, including Lwalu.
Kaalong (Kàlòng) also known as Dimbong (Mbong), is an almost extinct Bantu language from the Center Province of Southern Cameroon.
Binji is a Bantu language of eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo. Maho (2009) states that it is close to Songe, which is otherwise isolated within the Luban languages established by Ahmed (1995).
Luna is a Bantu language of eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo. Assigned by Guthrie to a group called Songe (L.20), it is presumably one of the Luban languages established by Ahmed (1995), like most of the other Songe languages, though it was not specifically addressed. Ruhlen (1987) agrees in placing it with the Luban languages.
Aushi, known by native speakers as Ikyaushi, is a Bantu language primarily spoken in the Lwapula Province of Zambia and the (Haut-)Katanga Province of the Democratic Republic of Congo. Although many scholars argue that it is a dialect of the closely related Bemba, native speakers insist that it is a distinct language. Nonetheless, speakers of both linguistic varieties enjoy extensive mutual intelligibility, particularly in the Lwapula Province.
Suba-Simbiti is a Bantu language of Tanzania. Suba-Simbiti is spoken by six groups in the Tarime region of Tanzania. This include Hacha, Kine, Sweta, Simbiti and Kiroba. The total number of speakers is in the region of 110,000.
References
- ↑ Songe at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ↑ Jouni Filip Maho, 2009. New Updated Guthrie List Online
- ↑ Stappers, Leo (1964). Morfologie van het Songye. Leuven: Katholieke Universiteit.