Related Research Articles
Bikya is a potentially extinct Southern Bantoid language spoken in Cameroon. It is one of the three, or four, Furu languages. In 1986 four surviving speakers were identified, although only one spoke the language fluently.

Southern Bantoid is a branch of the Bantoid language family. It consists of the Bantu languages along with several small branches and isolates of eastern Nigeria and west-central Cameroon. Since the Bantu languages are spoken across most of Sub-Saharan Africa, Southern Bantoid comprises 643 languages as counted by Ethnologue, though many of these are mutually intelligible.
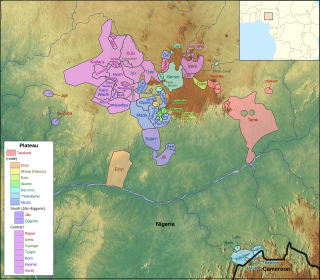
The forty or so Plateau languages are a tentative group of Benue–Congo languages spoken by 15 million people on the Jos Plateau, Southern Kaduna, Nasarawa State and in adjacent areas in central Nigeria.

The Beboid languages are any of several groups of languages spoken principally in southwest Cameroon, although two languages are spoken over the border in Nigeria. They are probably not most closely related to each other. The Eastern Beboid languages may be most closely related to the Tivoid and Momo groups, though some of the geographical Western Beboid grouping may be closer to Ekoid and Bantu.
Chakato is a West Chadic language spoken in Plateau State, Nigeria. It was identified by Roger Blench in 2016. It is spoken by about 500 people in one village, Dokan Tofa, which is located on the Jos-Shendam road in Plateau State. Blench (2017) suggests that Chakato may be related to spurious records of the Jorto language. Chakato speakers claim that their language is closely related to Goemai.
Daza or Dazawa is listed by Blench (2006) as a Chadic language within the Bole group. It is allegedly spoken in a few villages of Darazo LGA, Bauchi State, Nigeria. Glottolog (2017) lists the language as "unattested". Newman (2019) lists Daza as a possible synonym of Bole.
The Kara languages are Tar Gula and possibly related Central Sudanic languages of the Central African Republic. The name Kara is used for numerous other peoples of the region, and so is often ambiguous.

The Jukunoid languages are a branch of the Benue-Congo languages spoken by the Jukun and related peoples of Nigeria and Cameroon. They are distributed mostly throughout Taraba State, Nigeria and surrounding regions.
The Furu languages are a proposed group of poorly attested extinct or nearly extinct and otherwise unclassified Southern Bantoid languages of Cameroon. Suggested Furu languages are:
The East Kainji languages are spoken in a compact area of the Jos Plateau in Nigeria, near Jos. There are more than 20 of them, most of which are poorly studied.
Kresh is a small language group of South Sudan. It is generally considered to be a branch of the Central Sudanic languages. Boyeldieu (2010) judges that this has yet to be demonstrated satisfactorily, but Starostin (2016) finds convincing evidence, and that its closest relative within that family appears to be Birri.
The Kulu language, Ikulu, also known as Ankulu or Ikolu, is a Plateau language of Nigeria. It is spoken by the Bakulu, found in the Zangon Kataf, Kachia and Kauru Local Government Areas of Kaduna State.
Jju is the native language of the Bajju people of Kaduna State in central Nigeria. As of 1988, there were approximately 300,000 speakers. According to Blench (2008), Jju—with more speakers—appears to be a form of Tyap.
The Yukubenic languages are a branch of either the Jukunoid family or the Plateau family spoken in southeastern Nigeria. Glottolog places Yukubenic in the Plateau family. Ethnologue, however, places Yukubenic in the Jukunoid family, based on Shimizu (1980), and Blench also follows this classification.
Nincut (Aboro) is a Plateau language of Kaduna State, Nigeria belonging to the Beromic branch. Blench estimates 5,000 speakers in 2003. It is spoken 7 km north of Fadan Karshe in Kaduna State. Nincut is not recorded in Ethnologue or Glottolog.
Nigbo is an extinct Plateau language of Nigeria. It was spoken near Agameti on the Fadan Karshi-Wamba road near Sanga LGA, Kaduna State. The language, listed in Blench (2012) and (2019), is not reported in Ethnologue or Glottolog. It is presumably an Alumic language based on its proximity to Akpondu, a language closely related to Alumu and Tesu.
Kulung (Wurkum) is a minor West Chadic language of Karim Lamido LGA, Taraba State, Nigeria that was recently discovered by Roger Blench. The language is not reported in Ethnologue or Glottolog. Blench (2019) gives a rough estimate of about 2,000 speakers.
Kagare (Kwagere) is a Kainji language of Nigeria belonging to the Kamuku language complex. There is partial intelligibility with Cinda, Regi and Səgəmuk (Zubazuba). Kagare is reported by Blench, but is not in Ethnologue or Glottolog.
Rubaruba (tuRubaruba) is a Kainji language of Nigeria belonging to the Kamuku language complex. Rubaruba is reported by Blench (2012), but is not covered in Ethnologue or Glottolog.
Ajuwa (Ajegha) is a Plateau language of Kaduna State, Nigeria. It is spoken in Kalla, Afogo, Iburu, Idon, and Makyali towns. Ajuwa was reported by Roger Blench (2019), but is not reported in Ethnologue or Glottolog. Blench classifies it as Northwestern.