Related Research Articles
Most languages of Europe belong to the Indo-European language family. Out of a total European population of 744 million as of 2018, some 94% are native speakers of an Indo-European language; within Indo-European, the three largest phyla are Romance, Germanic, and Slavic with more than 200 million speakers each, between them accounting for close to 90% of Europeans. Smaller phyla of Indo-European found in Europe include Hellenic, Baltic, Albanian, Celtic and Indo-Aryan.
Ethnologue: Languages of the World is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It was first issued in 1951, and is now published annually by SIL International, a U.S.-based, worldwide, Christian non-profit organization. SIL's main purpose is to study, develop and document languages for religious purposes and to promote literacy.
Luhya is a Bantu language of western Kenya.

Kalinga is a dialect continuum of Kalinga Province in the Philippines, spoken by the Kalinga people, alongside Ilocano. The Banao Itneg variety is not one of the neighboring Itneg languages.
Ngiri is a Bantu language closely related to Lingala.
Central Tibetan, also known as Dbus, Ü or Ü-Tsang, is the most widely spoken Tibetic language and the basis of Standard Tibetan.
Yaka, also spelled Iaca and Iyaka, is a Bantu language spoken in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Angola. There are two dialects, Yaka proper, which comprises 99% of speakers, and Ngoongo. The alleged varieties Pelende and Lonzo are political rather than ethnolinguistic entities.
Mijikenda is a Bantu dialect cluster spoken along the coast of East Africa, mostly in Kenya, where there are 1.9 million speakers but also in Tanzania, where there are 100,000 speakers. The name Mijikenda means "the nine settlements" or "the nine communities" and refers to the multiple language communities that make up the group. An older, derogatory term for the group is Nyika which refers to the "dry and bushy country" along the coast.
West Teke is a Bantu language spoken in the Republic of Congo and Gabon.

Lega is a Bantu language, or dialect cluster, of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. There are two major varieties, Shabunda Lega and Mwenga Lega; Mwenga Lega, with about 10% of speakers, finds Shabunda difficult to understand. Kanu has been assigned a separate ISO code but is a dialect of Shabunda, and no more divergent than other dialects.
The Ki language, Tuki, is a Southern Bantoid language of Cameroon.
Kayan is a dialect cluster spoken by the Kayan people of Borneo. It is a cluster of closely related dialects with limited mutual intelligibility, and is itself part of the Kayan-Murik group of Austronesian languages.
Agusan is a Manobo language of northeastern Mindanao in the Philippines.
Kinabatangan is a language of Sabah.
Lamaholot, also known as Solor or Solorese, is a Central Malayo-Polynesian dialect cluster of Flores, Indonesia. The varieties may not be all mutually intelligible; Keraf (1978) reports that there are 18 languages under the name.
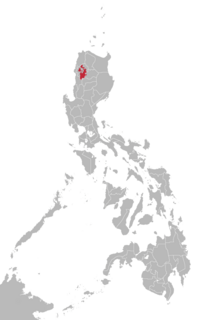
Itneg is a South-Central Cordilleran dialect continuum found in the island of Luzon, Philippines. This language and Ilocano are spoken by the Itneg people in Abra.
Kimaragang (Marigang), Tobilung, and Rungus are varieties of a single Austronesian language of Sabah, Malaysia. The three varieties share moderate mutual intelligibility. Children are not learning it well in some areas.
Atta is an Austronesian dialect cluster spoken by the Aeta (Agta) Negritos of the northern Philippines.
Masela (Marsela) is the language of Marsela Island in southern Maluku, Indonesia. Regional varieties are distinct; Ethnologue counts it as three languages.
References
- ↑ Ndunga at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)