Related Research Articles

Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, is a country in Northeast Africa. It borders the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Egypt to the north, Eritrea to the northeast, Ethiopia to the southeast, Libya to the northwest, South Sudan to the south, and the Red Sea. It has a population of 45.7 million people as of 2022 and occupies 1,886,068 square kilometres, making it Africa's third-largest country by area and the third-largest by area in the Arab League. It was the largest country by area in Africa and the Arab League until the secession of South Sudan in 2011; since then both titles have been held by Algeria. Its capital city is Khartoum, and its most populous city is Omdurman.

The demographics of Sudan include the Sudanese people and their characteristics, Sudan, including population density, ethnicity, education level, health, economic status, religious affiliations, and other aspects of the population.
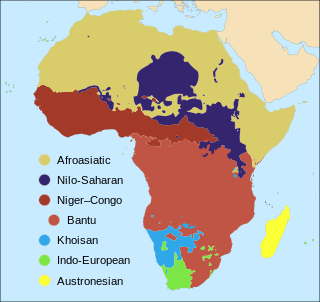
The number of languages natively spoken in Africa is variously estimated at between 1,250 and 2,100, and by some counts at over 3,000. Nigeria alone has over 500 languages, one of the greatest concentrations of linguistic diversity in the world. The languages of Africa belong to many distinct language families, among which the largest are:
Nubians are a Nilo-Saharan ethnic group indigenous to the region which is now Northern Sudan and Southern Egypt. They originate from the early inhabitants of the central Nile valley, believed to be one of the earliest cradles of civilization. In the southern valley of Egypt, Nubians differ culturally and ethnically from Egyptians, although they intermarried with members of other ethnic groups, especially Arabs. They speak Nubian languages as a mother tongue, part of the Northern Eastern Sudanic languages, and Arabic as a second language.

Sudanese Arabic, also referred to as the Sudanese dialect, Colloquial Sudanese or locally as Common Sudanese refers to the various related varieties of Arabic spoken in Sudan as well as parts of Egypt, Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Chad. In 2021 there were 1,840,000 Sudanese Arabic speakers in Egypt Sudanese Arabic has also influenced a number of Arabic-based pidgins and creoles, including Juba Arabic, widely used in South Sudan, as well as Ki-Nubi, spoken by the Nubi communities of Kenya and Uganda.

The Nilotic languages are a group of related languages spoken across a wide area between South Sudan and Tanzania by the Nilotic peoples. In 2004 a South Sudanese Deng CHOL developed a ne writing system (Scripts) for Nilotic languages, the new alphabets are modification of meroetic writing system an old writing system practiced in ancient kingdom of Kush in modern days, the new Dinka alphabet presented for use in 2020.
Dinka is a Nilotic dialect cluster spoken by the Dinka people, the major ethnic group of South Sudan. There are several main varieties, such as Padang, Rek, Agaar, Ciec, Apaak, Aliep, Bor, Hol, Twic East and Twic Mayardit, which are distinct enough to require separate literary standards. Jaang, Jieng or Muonyjieng is used as a general term to cover all Dinka languages. Recently Akutmɛ̈t Latueŋ Thuɔŋjäŋ has proposed a unified written grammar of Dinka.

Juba Arabic, also known since 2011 as South Sudanese Arabic, is a lingua franca spoken mainly in Equatoria Province in South Sudan, and derives its name from the South Sudanese capital, Juba. It is also spoken among communities of people from South Sudan living in towns in Sudan. The pidgin developed in the 19th century, among descendants of Sudanese soldiers, many of whom were recruited from southern Sudan. Residents of other large towns in South Sudan, notably Malakal and Wau, do not generally speak Juba Arabic, tending towards the use of Arabic closer to Sudanese Arabic, in addition to local languages. Reportedly, it is the most spoken language in South Sudan despite government attempts to discourage its use due to its association with past Arab rule.

Domari is an endangered Indo-Aryan language, spoken by Dom people scattered across the Middle East and North Africa. The language is reported to be spoken as far north as Azerbaijan and as far south as central Sudan, in Turkey, Iran, Iraq, Palestine, Israel, Jordan, Egypt, Sudan, Libya, Tunisia, Algeria, Morocco, Syria and Lebanon. Based on the systematicity of sound changes, it is known with a fair degree of certainty that the names Domari and Romani derive from the Indo-Aryan word ḍom. Although they are both Central Indo-Aryan languages, Domari and Romani do not derive from the same immediate ancestor. The Arabs referred to them as Nawar as they were a nomadic people that originally immigrated to the Middle East from the Indian subcontinent.

Sudan is a multilingual country dominated by Sudanese Arabic. In the 2005 constitution of the Republic of Sudan, the official languages of Sudan are Literary Arabic and English.

Chadian Arabic, also known as Shuwa Arabic, Baggara Arabic, Western Sudanic Arabic, or West Sudanic Arabic (WSA), is a variety of Arabic and the first language of 1.6 million people, both town dwellers and nomadic cattle herders. The majority of its speakers live in southern Chad. Its range is an east-to-west oval in the Sahel. Nearly all of this territory is within Chad or Sudan. It is also spoken elsewhere in the vicinity of Lake Chad in the countries of Cameroon, Nigeria, Niger. Finally, it is spoken in slivers of the Central African Republic, and Libya. In addition, this language serves as a lingua franca in much of the region. In most of its range, it is one of several local languages and often not among the major ones.
The Sere languages are a proposed family of Ubangian languages spoken in South Sudan and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Several are endangered or extinct. The most populous Sere language is Ndogo of South Sudan, with about 30,000 speakers.

South Sudan, officially the Republic of South Sudan, is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia, Sudan, the Central African Republic, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda, and Kenya. Its population was estimated at 11,088,796 in 2023. Juba is the capital and largest city.

The culture of South Sudan encompasses the religions, languages, ethnic groups, foods, and other traditions of peoples of the modern state of South Sudan, as well as of the inhabitants of the historical regions of southern Sudan.

South Sudan is home to around 60 indigenous ethnic groups and 80 linguistic partitions among a 2021 population of around 11 million. Historically, most ethnic groups were lacking in formal Western political institutions, with land held by the community and elders acting as problem solvers and adjudicators. Today, most ethnic groups still embrace a cattle culture in which livestock is the main measure of wealth and used for bride wealth.

South Sudan is a multilingual country, with over 60 indigenous languages spoken. The official language of the country is English which was introduced in the region during the colonial era.
The mass media in South Sudan is underdeveloped compared to many other countries, including fellow East African states like Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda. Poor transportation infrastructure and entrenched poverty in the country inhibit both the circulation of newspapers, particularly in states located far from the capital of Juba, and the ability of media outlets to maintain regular coverage of the entire country.

Raga County is a county in the Western Bahr el Ghazal, South Sudan. It is the largest county in the nation. In Arabic, Raga County can be known as "Raja".
Liffi was a military station in Sudan, named after a nearby hill, and the surrounding region. It was the location of several clashes between Egyptian forces and Mahdists in the early 1880s. In 1894 the Belgians temporarily established a base there.
References
- ↑ Togoyo at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)

- ↑ Santandrea, S. (1953). "A PRELIMINARY ACCOUNT OF THE INDRI, TOGOYO, FEROGE, MANGAYA AND WORO". Sudan Notes and Records. 34 (2): 230–264. ISSN 0375-2984.
- ↑ Language Death. De Gruyter Mouton. 2012-10-25. p. 396. doi:10.1515/9783110870602. ISBN 978-3-11-087060-2.