Related Research Articles
Kuy, also known as Kui, Suay or Kuay, is a Katuic language, part of the larger Austroasiatic family spoken by the Kuy people of Southeast Asia.

Wakashan is a family of languages spoken in British Columbia around and on Vancouver Island, and in the northwestern corner of the Olympic Peninsula of Washington state, on the south side of the Strait of Juan de Fuca.
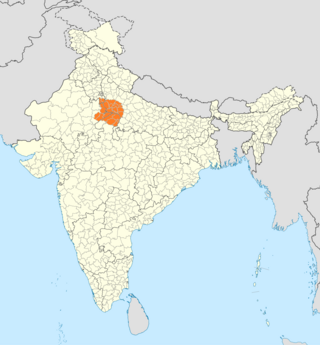
The Braj language, commonly called Braj Bhasha, also known as Vraj Bhasha or Brij Bhasha or Braj Boli, is a language within the Indo-Aryan language family spoken in the Braj region. Along with Awadhi, it was one of the two predominant literary languages of North-Central India before being replaced by Hindi in the 19th century.
The Ida'an language is a Malayo-Polynesian language spoken by the Ida'an people on the east coast of Sabah, Malaysia.
Nupe is a Volta–Niger language of the Nupoid branch primarily spoken by the Nupe people of the North Central region of Nigeria. Its geographical distribution stretches and maintains pre-eminence in Niger State as well as Kwara, Kogi, Nasarawa and the Federal Capital Territory. Nupe is closely related to Kakanda in structure and vocabulary. There are at least two markedly different dialects of Nupe: Nupe central and Nupe Tako.
The Gong language is an endangered Tibeto-Burman language of Western Thailand, spoken in isolated pockets in Uthai Thani and Suphanburi provinces.
Duwet, also known as Guwot or Waing, is an aberrant member of the Busu subgroup of Lower Markham languages in Morobe Province, Papua New Guinea. Duwet is spoken by about 400 people and appears to have been heavily influenced by its neighboring Nabak language of the Papuan Trans–New Guinea languages. It is spoken in the three villages of Lambaip, Lawasumbileng, and Ninggiet.
The Simeulue language is spoken by the Simeulue people of Simeulue off the western coast of Sumatra, Indonesia.

The Kwasio language, also known as Ngumba / Mvumbo, Bujeba, and Gyele / Kola, is a language of Cameroon, spoken in the south along the coast and at the border with Equatorial Guinea by some 70,000 members of the Ngumba, Kwasio, Gyele and Mabi peoples. Many authors view Kwasio and the Gyele/Kola language as distinct. In the Ethnologue, the languages therefore receive different codes: Kwasio has the ISO 639-3 code nmg, while Gyele has the code gyi. The Kwasio, Ngumba, and Mabi are village farmers; the Gyele are nomadic Pygmy hunter-gatherers living in the rain forest.

Terengganu Malay is a Malayic language spoken in the Malaysian state of Terengganu all the way southward to coastal Pahang and northeast Johor. It is the native language of Terengganu Malays and highly localised Chinese Peranakan community as well as a second language among the smaller Indian minority. The language has developed a distinct phonetic, syntactic and lexical distinctions which makes it mutually unintelligible for speakers from outside the east coast of Peninsular Malaysia especially those who speak Standard Malay/Malaysian. Terengganu Malay still shares close linguistic ties with neighbouring Kelantan-Pattani and Pahang of which it forms under the umbrella term of "East Coast Peninsular Malayic languages". These similarities have often confused many people outside the region, who usually interchange Terengganu Malay with Kelantan Malay, even though there are major phonological and vocabulary differences between the two.
Chamba Leko is one of two languages spoken by the Chamba people, the other being Chamba Daka. It is a member of the Leko branch of Savanna languages, and is spoken across the northern Nigerian–Cameroonian border.
Hruso, also known as Aka (Angka), is a language of Arunachal Pradesh India. Long assumed to be a Sino-Tibetan language, it may actually be a language isolate. It is spoken by 3,000 people in 21 villages in Thrizino Circle, West Kameng District. The Hruso people inhabit areas of South East Kameng and are concentrated in the Bichom River Valley, and speak English, Hindi, and Miji in addition to Hruso.
The Kamuku languages are a branch of the Kainji languages spoken by the Kamuku people of Niger State, western Nigeria, mostly in Mariga and Rafi LGAs.
Tombulu, also known as Minahasan language, is an Austronesian language of northern Sulawesi in Indonesia. It is a Minahasan language, a sub-group of the Philippine languages.
Maklew is a language of the proposed Trans-Fly – Bulaka River family in West Papua. It is known to be spoken in Welbuti village, Merauke Regency. It is thought to be closely related to the Yelmek Language.
Lawa is a Mon–Khmer language of Thailand. There are two distinct varieties or dialects of Lawa, considered to be separate languages; their names in the Ethnologue are Eastern Lawa and Western Lawa. They are spoken in Lawa villages in the provinces of Mae Hong Son and Chiang Mai in Northern Thailand.
Ambel (Amber), also known as Waigeo after the island where it is primarily spoken, is a heavily Papuan-influenced Austronesian language spoken on the island of Waigeo in the Raja Ampat archipelago near the northwestern tip of West Papua, Indonesia. It is spoken by approximately 1,600 people. It is endangered, as the population is shifting to Papuan Malay and few people born after the year 2000 have any knowledge of the language.
Thor, also known as Tawr, Laamtuk Thet, or Ruavan Thet, is a Kuki-Chin language spoken in two villages of Hakha Township, Chin State, Myanmar.
Sanie is a Loloish language of Yunnan, China. It is similar to Samataw. There were 17,320 ethnic Sanie in 1998, but only about 8,000 spoke the Sanie language fluently. The Sanie are also known as the White Yi (白彝).
Bannoni, also known as Tsunari, is an Austronesian language of Papua New Guinea. It has approximately 1,000 native speakers. The Banoni people refer to their language as Tsunari, but acknowledge the name Banoni and accept it as well. Tsunari technically translates to 'their truth'.
References
- ↑ Geme at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)

- ↑ Moñino, Yves (1988). Lexique comparatif des langues oubanguiennes. Paris: Geuthner.