Related Research Articles
Fang is a Central African language spoken by around 1 million people, most of them in Equatorial Guinea, and northern Gabon, where it is the dominant Bantu language; Fang is also spoken in southern Cameroon, the Republic of the Congo, and small fractions of the islands of São Tomé and Príncipe. It is related to the Bulu and Ewondo languages of southern Cameroon.

Cameroon is home to at least 250 languages, with some accounts reporting around 600. These include 55 Afro-Asiatic languages, two Nilo-Saharan languages, four Ubangian languages, and 169 Niger–Congo languages. This latter group comprises one Senegambian language (Fulfulde), 28 Adamawa languages, and 142 Benue–Congo languages . French and English are official languages, a heritage of Cameroon's colonial past as a colony of both France and the United Kingdom from 1916 to 1961. Eight out of the ten regions of Cameroon are primarily francophone and two are anglophone. The official percentage of French and English speakers by the Presidency of Cameroon is estimated to be 70% and 30% respectively.
Tupuri is a language mostly spoken in the Mayo-Kebbi Est Region of southern Chad and in small parts of northern Cameroon. It is an Mbum language spoken by the Tupuri people with approximately 300,000 speakers.
Afade (Afaɗə) is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in eastern Nigeria and northwestern Cameroon.
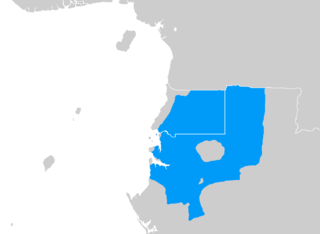
North Mofu is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in northern Cameroon. Dialects are Douroun and Wazan.
Wuzlam, also called Uldeme (Ouldémé), is an Afro-Asiatic language of the Chadic branch. It is spoken in northern Cameroon.

Bata (Gbwata) is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in Nigeria in Adamawa State in the Numan, Song, Fufore and Jimeta gire Yola maiha Demsa lamorde LGAs, and in Cameroon in North Province along the border with Nigeria. Dialects are Demsa, Garoua, Jirai, Kobotachi, Malabu, Ndeewe, Ribaw, Wadi, and Zumu (Jimo). It is often considered the same language as Bacama.
Daba is a Chadic dialect cluster spoken in Cameroon in Far North Province and in one village in neighboring Nigeria. Blench (2006) considers Mazagway to be a dialect.
The Mina language, also known by the names Hina and Besleri, is a Chadic language spoken in Northern Cameroon by 10,000 people. Speakers of Mina are generally bilingual, with Fulfulde (Fula) being the second language. Fulfulde is often joined by French as a third language in educated speakers.
Kol is a Niger–Congo language of the Bantu family, associated with the Bikélé ethnic group. It is spoken in the East Province of Cameroon, in the vicinity of Messaména. Alternate names for Kol language include Bikele-Bikay, Bikele-Bikeng, Bikélé, and Bekol.
Bankon is a Bantu language spoken in the Moungo department of the Littoral Province of southwestern Cameroon. It has a lexical similarity of 86% with Rombi which is spoken in the nearby Meme department of Southwest Province.

The Kwasio language, also known as Ngumba / Mvumbo, Bujeba, and Gyele / Kola, is a language of Cameroon, spoken in the south along the coast and at the border with Equatorial Guinea by some 70,000 members of the Ngumba, Kwasio, Gyele and Mabi peoples. Many authors view Kwasio and the Gyele/Kola language as distinct. In the Ethnologue, the languages therefore receive different codes: Kwasio has the ISO 639-3 code nmg, while Gyele has the code gyi. The Kwasio, Ngumba, and Mabi are village farmers; the Gyele are nomadic Pygmy hunter-gatherers living in the rain forest.
Baka is a dialect cluster of Ubangian languages spoken by the Baka Pygmies of Cameroon and Gabon. The people are ethnically close related to the Aka, collectively known as the Mbenga (Bambenga).However, the languages are not related, apart from some vocabulary dealing with the forest economy, which suggests the Aka may have shifted to Bantu, with an estimated 15000 people have shifted.
Nzime (Koonzime) is a Bantu language of Cameroon, spoken by the Nzime and Dwe'e (Bajwe'e) people. Maho (2009) lists these as two languages.
The Gwèri or Vere language Were also known as Kobo or Mom Jango, is a member of the Duru branch of Savanna languages. It is spoken across the northern Nigerian–Cameroonian border.
Pol is a Bantu language of Cameroon. Pol proper is spoken in central Cameroon; the Pomo and Kweso dialects are spoken in Congo and the CAR near the Cameroonian border.

The Pévé language, sometimes referred to as Lamé, is a member of the Masa branch of the Chadic family that is spoken in parts of Cameroon and the Republic of Chad.
Mpumpong (Mpongmpong) is a Bantu language of Cameroon. Maho (2009) considers Mpiemo to be a dialect.
Duli is an extinct Adamawa language of northern Cameroon.
Mono is a moribund Mbum language spoken by older adults in northern Cameroon.
References
- 1 2 Bangandu at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
Nombe at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required) - ↑ Hammarström (2015) Ethnologue 16/17/18th editions: a comprehensive review: online appendices
- ↑ Language Status
- 1 2 Binam Bikoi, Charles, ed. (2012). Atlas linguistique du Cameroun (ALCAM)[Linguistic Atlas of Cameroon]. Atlas linguistique de l'Afrique centrale (ALAC) (in French). Vol. 1: Inventaire des langues. Yaoundé: CERDOTOLA. ISBN 9789956796069.
- ↑ J.W. Berry, S.H Irvine, E.G. Hunt, Indigenous Cognition: Functioning in Cultural Context, 1988
- ↑ Victor Barnouw, American Anthropologist, Basic Problems in Cross-Cultural Psychology: Selected Papers from the Third International Conference of the International Association for Cross-Cultural Psychology pg 405-406, 1978