Related Research Articles
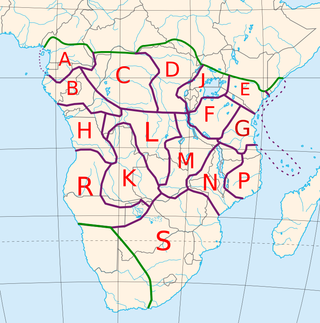
The 250 or so "Narrow Bantu languages" are conventionally divided up into geographic zones first proposed by Malcolm Guthrie (1967–1971). These were assigned letters A–S and divided into decades ; individual languages were assigned unit numbers, and dialects further subdivided. This coding system has become the standard for identifying Bantu languages; it was the only practical way to distinguish many ambiguously named languages before the introduction of ISO 639-3 coding, and it continues to be widely used. Only Guthrie's Zone S is (sometimes) considered to be a genealogical group. Since Guthrie's time a Zone J has been set up as another possible genealogical group bordering the Great Lakes.

The Mongo people are an ethnic group who live in the equatorial forest of Central Africa. They are the second largest ethnic group in the Democratic Republic of Congo, highly influential in its north region. A diverse collection of sub-ethnic groups, they are mostly residents of a region north of the Kasai and the Sankuru Rivers, south of the main Congo River bend and many other provinces. Their highest presence is in the province of Équateur and the northern parts of the Bandundu Province.
The Mpama are an ethnic group that today live in eastern Congo and western Democratic Republic of Congo, mainly along the Congo River. Because of their similarity to the Lia, Ntomba and Sengele, they are considered part of the Mongo ethnic group. They are river residents and lived traditionally from fishing, agriculture and trade in the Congo.
References
- ↑ Sengele at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ↑ Jouni Filip Maho, 2009. New Updated Guthrie List Online
| Official language | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| National languages | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Indigenous languages (by province) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Sign languages | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Note: The Guthrie classification is geographic and its groupings do not imply a relationship between the languages within them. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||