Related Research Articles

The Ovambo language is a dialect cluster spoken by the Ovambo people in southern Angola and northern Namibia, of which the written standards are Kwanyama and Ndonga.
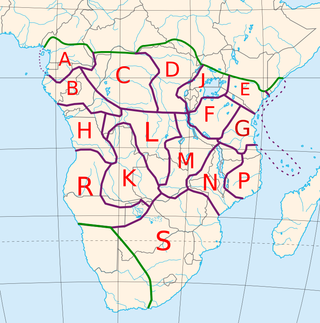
The 250 or so "Narrow Bantu languages" are conventionally divided up into geographic zones first proposed by Malcolm Guthrie (1967–1971). These were assigned letters A–S and divided into decades ; individual languages were assigned unit numbers, and dialects further subdivided. This coding system has become the standard for identifying Bantu languages; it was the only practical way to distinguish many ambiguously named languages before the introduction of ISO 639-3 coding, and it continues to be widely used. Only Guthrie's Zone S is (sometimes) considered to be a genealogical group. Since Guthrie's time a Zone J has been set up as another possible genealogical group bordering the Great Lakes.
Mbukushu or Thimbukushu is a Bantu language spoken by 45,000 people along the Okavango River in Namibia, where it is a national language, and in Botswana, Angola and Zambia.
Kwangali, or RuKwangali, is a Bantu language spoken by 85,000 people along the Kavango River in Namibia, where it is a national language, and in Angola. It is one of several Bantu languages of the Kavango which have click consonants; these are the dental clicks c and gc, along with prenasalization and aspiration.
The Northeast Bantu languages are a group of Bantu languages spoken in East Africa. In Guthrie's geographic classification, they fall within Bantu zones E50 plus E46 (Sonjo), E60 plus E74a (Taita), F21–22, J, G60, plus Northeast Coast Bantu. Some of these languages share a phonological innovation called Dahl's law that is unlikely to be borrowed as a productive process, though individual words reflecting Dahl's law have been borrowed into neighboring languages.
Bila, or Forest Bira, is a Bantu language spoken in the Mambasa Territory of the Democratic Republic of Congo. It is also spoken by the Mbuti Pygmies who live in that area. Pygmy groups to the west include the Kango and Sua (Batchua). Other Mbuti speak Central Sudanic languages. The Kango and Sua speak distinct dialects, but not enough to impair mutual intelligibility with their farming Bila patrons.
Yans (Yanzi) is a Bantu language spoken in the Democratic Republic of the Congo by the Bayanzi.
Lala-Bisa is a Bantu language of Zambia that is closely related to Bemba.
The Komo–Bira languages are part of the Bantu languages coded Zone D.20–30 in Guthrie's classification, specifically D.21, D.22, D.23, D.31, D.32. According to Nurse & Philippson (2003), they form a valid node; the rest of D.20 include the Lega–Holoholo languages, while the rest of the D.30 languages are not related to each other, apart from a close Budu–Ndaka group.
Tongwe (Sitongwe) and Bende (Sibende) constitute a clade of Bantu languages coded Zone F.10 in Guthrie's classification. According to Nurse & Philippson (2003), they form a valid node. Indeed, at 90% lexical similarity they may be dialects of a single language.
Kuba is a Bantu language of Kasai, Democratic Republic of Congo.
Lwalu, also known as Lwalwa, is a Bantu language of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Its classification is uncertain: Nurse (2003), following Ahmed (1995), assigns all of Guthrie's L.20 languages to Luban, including Lwalu.
Ngoni is a Bantu language of Zambia, Tanzania, and Mozambique. There is a 'hard break' across the Tanzanian–Mozambican border, with marginal mutual intelligibility. It is one of several languages of the Ngoni people, who descend from the Nguni people of southern Africa, and the language is a member of the Nguni subgroup, with the variety spoken in Malawi sometimes referred to as a dialect of Zulu. Other languages spoken by the Ngoni may also be referred to as "Chingoni"; many Ngoni in Malawi, for instance, speak Chewa, and other Ngoni speak Tumbuka or Nsenga.
Bango, is a Bantu language spoken in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Ethnologue suggests it may be a dialect of Budza, but Nurse & Philippson (2003) list it as one of the Bwa languages.
Binji is a Bantu language of eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo. Maho (2009) states that it is close to Songe, which is otherwise isolated within the Luban languages established by Ahmed (1995).
Mashi (Kamaxi), or Kwandu, is a Bantu language of Zambia and Angola. It was assigned by Guthrie to Bantu group K.30, which Pfouts (2003) established as part of the Kavango–Southwest branch of Bantu. Though not specifically addressed, Mashi may be in that family as well.
Ndombe (Dombe) is a Bantu language of Angola. It was assigned by Guthrie to Bantu group R.10, which apart from Umbundu Pfouts (2003) established as part of the Kavango–Southwest branch of Bantu. Though not specifically addressed, Ndombe may be in that branch as well.
Kebwe (Mikebwe) is a Bantu language of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It was related to Hemba by Ahmed (1995).
Suku is a Bantu language of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Vidunda (Chividunda) is a Bantu language spoken along the north bank of the Ruaha River in Tanzania. It belongs to the Ruvu branch of Northeast Coast Bantu.
References
- ↑ Holoholo at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- 1 2 Jouni Filip Maho, 2009. New Updated Guthrie List Online
- Nurse, Derek; Philippson, Gérard, eds. (2003). The Bantu languages. London: Routledge. ISBN 9780700711345.