Related Research Articles

The Bantu languages are a language family of about 600 languages that are spoken by the Bantu peoples of Central, Southern, Eastern and Southeast Africa. They form the largest branch of the Southern Bantoid languages.

Niger–Congo is a hypothetical language family spoken over the majority of sub-Saharan Africa. It unites the Mande languages, the Atlantic-Congo languages, and possibly several smaller groups of languages that are difficult to classify. If valid, Niger-Congo would be the world's largest in terms of member languages, the third-largest in terms of speakers, and Africa's largest in terms of geographical area. It is generally considered to be the world's largest language family in terms of the number of distinct languages, just ahead of Austronesian, although this is complicated by the ambiguity about what constitutes a distinct language; the number of named Niger–Congo languages listed by Ethnologue is 1,540.
Kaonde (kiiKaonde) is a Bantu language spoken primarily in Zambia but also in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Kaonde and its dialects are spoken and understood by perhaps 350,000 people or more. It is estimated that approximately 2.3% of Zambians are native Kaonde speakers. Kaonde speakers overwhelmingly live in the Northwestern and parts of Central regions of Zambia.
Kisuba, also known as Olusuba, is a Bantu language spoken by the Suba people of Kenya. The language features an extensive noun-classification system using prefixes that address gender and number. Suba clans are located on the eastern shore and islands of Lake Victoria in Kenya and Tanzania. They have formed alliances with neighboring clans, such as the Luo people, via intermarriages, and as a result a majority of Suba people are bilingual in Dholuo. The Suba religion has an ancient polytheistic history that includes writings of diverse, ancestral spirits. A recent revival of the Suba language and its culture has influenced the increasing number of native speakers each year.

Bantoid is a major branch of the Benue–Congo language family. It consists of the Northern Bantoid languages and the Southern Bantoid languages, a division which also includes the Bantu languages that constitute the overwhelming majority and after which Bantoid is named.
Tonga (Chitonga), also known as Zambezi, is a Bantu language primarily spoken by the Tonga people (Batonga) who live mainly in the Southern province, Lusaka province, Central Province and Western province of Zambia, and in northern Zimbabwe, with a few in Mozambique. The language is also spoken by the Iwe, Toka and Leya people, and perhaps by the Kafwe Twa, as well as many bilingual Zambians and Zimbabweans. In Zambia Tonga is taught in schools as first language in the whole of Southern Province, Lusaka and Central Provinces.

The Turu are an ethnic and linguistic group based in the Singida Region of north-central Tanzania who speak Bantu language Kinyaturu. In 1993, the Turu population was estimated to number 556,000. The current population of the Turu is now over 1,000,000. They speak the Turu language.
Gweno is a Bantu language spoken in the North Pare Mountains in the Kilimanjaro Region of Tanzania. The people known as the Gweno are a Chaga ethnic and linguistic group. Since the Chaga people are Bantu speakers, the adopted language contains dialects similar to that of the Kenyan language Kamba. Gweno shares about 54% to 56% of its vocabulary with other Chaga dialects and 46% with Taita dialects. However, a large percentage of its vocabulary is not seen in the other dialects. Also at the start of the 11th century, the Chaga people descended and migrated from the Bantu group in which they migrated to the foothills of mount Kilimanjaro. The Gweno language is today spoken mostly by older adults, with younger generations having shifted to Asu and Swahili. Ethnologue considers Gweno to be moribund; the language is not being passed down because children have not been exposed to Gweno since the 1970s. The generational shift from Gweno to either Asu or Swahili has certainly created shifts in dialect, however Gweno speakers do not see this as a threat.
Iau or Turu is a Lakes Plain language of West Papua, Indonesia, spoken by about 2,100 people, native speakers of this language are the Turu people (Iau). Most speakers are monolingual, and their number is growing. Other peoples in the western Lakes Plain area speak basic Iau. Iau is heavily tonal, with 11 tones on nouns and 19 simple and compound tones on verbs.
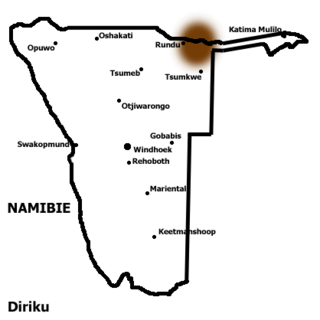
Gciriku or Dciriku, is a Bantu language spoken by 305,000 people along the Okavango River in Namibia, Botswana and Angola. 24,000 people speak Gciriku in Angola, according to Ethnologue. It was first known in the west via the Vagciriku, who had migrated from the main Vamanyo area and spoke Rugciriku, a dialect of Rumanyo. The name Gciriku remains common in the literature, but within Namibia the name Rumanyo has been revived. The Mbogedu dialect is extinct; Maho (2009) lists it as a distinct language, and notes that the names 'Manyo' and 'Rumanyo' are inappropriate for it.
Rangi or Langi is a Bantu language of spoken by the Rangi people of Kondoa District in the Dodoma Region of Central Tanzania. Whilst the language is known as Rangi in English and Kirangi in the dominant Swahili spoken throughout the African Great Lakes, the self-referent term is Kilaangi.
The Zigula or Zigua language, Chizigua, is a Bantu language of Tanzania and Somalia, where the Mushunguli dialect is spoken.
Luyana (Luyaana), also known as Luyi, is a Bantu language spoken in Zambia and perhaps in small numbers in neighboring countries. It appears to be an divergent lineage of Bantu. It is spoken by the Luyana people, a subgroup of the Lozi people.

Tanzania is a multilingual country. There are many languages spoken in the country, but no one language is spoken natively by a majority or a large plurality of the population. Swahili and English, the latter of which was inherited from colonial rule, are widely spoken as lingua francas. They serve as working languages in the country, with Swahili being the official national language. There are more speakers of Swahili than of English in Tanzania.
Ruund (Ruwund), also known as Northern Lunda or Uruund, is a Bantu language of the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Angola. It is highly unusual among Bantu languages for allowing consonantal codas and for its reduced vowel system, in which short /e/ and /o/ have become [i] and [a] respectively, leaving only 3 short vowels.

Jita is a Bantu language of Tanzania, spoken on the southeastern shore of Lake Victoria/Nyanza and on the island of Ukerewe.
The Bantu peoples, or Bantu, are an ethnolinguistic grouping of approximately 400 distinct ethnic groups who speak Bantu languages, consisting of some 600 languages with varied mutual intelligibility. The languages are native to 24 countries spread over a vast area from Central Africa to Southeast Africa and into Southern Africa. There are several hundred Bantu languages. Depending on the definition of "language" or "dialect", it is estimated that there are between 440 and 680 distinct languages. The total number of speakers is in the hundreds of millions, ranging at roughly 350 million in the mid-2010s. About 60 million speakers (2015), divided into some 200 ethnic or tribal groups, are found in the Democratic Republic of the Congo alone.
Limi is a locale in Nepal.
Turu may refer to:
Nzadi is a Bantu language spoken in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, "from Kwamuntu to Ilebo along the north side of the Kasai River in Bandundu Province." The number of speakers of Nzadi is not known, but is estimated to be in the thousands. The Nzadi language has three dialects, Ngiemba, Lensibun, and Ndzé Ntaa.
References
- ↑ Turu at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ↑ Jouni Filip Maho, 2009. New Updated Guthrie List Online