Related Research Articles
Central Kilimanjaro, or Central Chaga, is a Bantu language of Tanzania spoken by the Chaga people.
Yeyi is a Bantu language spoken by many of the approximately 50,000 Yeyi people along the Okavango River in Namibia and Botswana. Yeyi, influenced by Juu languages, is one of several Bantu languages along the Okavango with clicks. Indeed, it has the largest known inventory of clicks of any Bantu language, with dental, alveolar, palatal, and lateral articulations. Though most of its older speakers prefer Yeyi in normal conversation, it is being gradually phased out in Botswana by a popular move towards Tswana, with Yeyi only being learned by children in a few villages. Yeyi speakers in the Caprivi Strip of north-eastern Namibia, however, retain Yeyi in villages, but may also speak the regional lingua franca, Lozi.
Mbukushu or Thimbukushu is a Bantu language spoken by 45,000 people along the Kavango East Region in Namibia, where it is a national language, and in Botswana, Angola and Zambia.
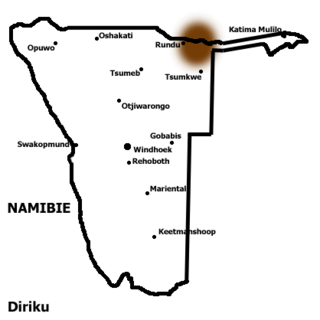
Gciriku, or Dciriku, is a Bantu language spoken by 305,000 people along the Kavango River in Namibia, Botswana and Angola. 24,000 people speak Gciriku in Angola, according to Ethnologue. It was first known in the west via the Vagciriku, who had migrated from the main Vamanyo area and spoke Rugciriku, a dialect of Rumanyo. The name Gciriku remains common in the literature, but within Namibia the name Rumanyo has been revived. The Mbogedu dialect is extinct; Maho (2009) lists it as a distinct language, and notes that the names 'Manyo' and 'Rumanyo' are inappropriate for it.
The lhukonzo (Konzo) language, variously rendered Lukonzo, Olukonzo, and konzo, is a Bantu language spoken by the Konzo people of Uganda and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It has a 77% lexical similarity with Nande. There are many dialects, including Sanza (Ekisanza).
Chokwe is a Bantu language spoken by the Chokwe people of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Angola and Zambia. It is recognised as a national language of Angola, where half a million people were estimated to have spoken it in 1991; another half a million speakers lived in the Congo in 1990, and some 20,000 in Zambia in 2010. It is used as a lingua franca in eastern Angola.
The Kavango – Southwest Bantu languages are a group of Bantu languages established by Anita Pfouts (2003). The Southwest Bantu languages constitute most of Guthrie's Zone R. The languages, or clusters, along with their Guthrie identifications, are:

'Lega is a Bantu language, or dialect cluster, of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. There are two major varieties, Shabunda Lega, Mwenga Lega; Mwenga Lega, with about 10% of speakers, finds Shabunda difficult to understand.
The Tsogo languages are a clade of Bantu languages coded Zone B.30 in Guthrie's classification. According to Nurse & Philippson (2003), the languages form a valid node. They are:
The Sira languages are a clade of Bantu languages coded Zone B.40 in Guthrie's classification. According to Nurse & Philippson (2003), together with a couple languages from H10, they form a valid node. They are:
The Mboshi languages are a clade of Bantu languages coded Zone C.20 in Guthrie's classification. According to Nurse & Philippson (2003), apart from Kyba (Kuba), the languages form a valid node. They are:
The Tetela languages are a clade of Bantu languages coded Zone C.70 in Guthrie's classification. According to Nurse & Philippson (2003), together with C.81 Dengese and C.89, the Shuwa "dialect" of Bushoong, the languages form a valid node. They are:
Tongwe (Sitongwe) and Bende (Sibende) constitute a clade of Bantu languages coded Zone F.10 in Guthrie's classification. According to Nurse & Philippson (2003), they form a valid node. Indeed, at 90% lexical similarity they may be dialects of a single language.
The Pende or Holu languages are a clade of Bantu languages coded Zone L.10 in Guthrie's classification. According to Nurse & Philippson (2003), they form a valid node together with a couple languages from Zone H:
Makaa (Maka), or South Makaa, is a Bantu language of Cameroon. It is not intelligible with the other language spoken by the Makaa people, North Makaa.
Kuba is a Bantu language of Kasai, Democratic Republic of Congo.
Holoholo is a Bantu language of DR Congo and formerly in Tanzania spoken by the Holoholo people on either side of Lake Tanganyika. Classification is uncertain, but it may belong with the Takama group.
Bango, is a Bantu language spoken in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Ethnologue suggests it may be a dialect of Budza, but Nurse & Philippson (2003) list it as one of the Bwa languages.
Suku is a Bantu language of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Proto-Bantu is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Bantu languages, a subgroup of the Southern Bantoid languages. It is thought to have originally been spoken in West/Central Africa in the area of what is now Cameroon. About 6,000 years ago, it split off from Proto-Southern Bantoid when the Bantu expansion began to the south and east. Two theories have been put forward about the way the languages expanded: one is that the Bantu-speaking people moved first to the Congo region and then a branch split off and moved to East Africa; the other is that the two groups split from the beginning, one moving to the Congo region, and the other to East Africa.
References
- ↑ "Kwangali". Ethnologue. Retrieved 15 August 2018.
- ↑ Jouni Filip Maho, 2009. New Updated Guthrie List Online
- ↑ Dammann (1957)
- ↑ Sommer, Gabi (2003). Western Savanna. Nurse, Derek and Philippson, Gérard (eds.), The Bantu languages: London & New York: Routledge. pp. 566–580.
- Dammann, Ernst (1957). Studien zum Kwangali: Grammatik, Texte, Glossar. Hamburg: Cram, de Gruyter
- Derek Nurse & Gérard Philippson, The Bantu languages, 2003:569.
Books
- Rukwangali/English for Children, Éditions du Cygne, 2013, ISBN 978-2-84924-310-7
- Biblical passages in Kwangali