Related Research Articles
SothoSesotho, also known as Southern Sotho or Sesotho sa Borwa is a Southern Bantu language of the Sotho–Tswana ("S.30") group, spoken in Lesotho, and South Africa where it is an official language;
Shona is a Bantu language of the Shona people of Zimbabwe. The term is variously used to collectively describe all the Central Shonic varieties or specifically Standard Shona, a variety codified in the mid-20th century. Using the broader term, the language is spoken by over 14,000,000 people.
Tongan is an Austronesian language of the Polynesian branch native to the island nation of Tonga. It has around 187,000 speakers. It uses the word order verb–subject–object.
Tonga may refer to five different languages:

Tsonga or Xitsonga as an endonym, is a Bantu language spoken by the Tsonga people of southern Africa. It is mutually intelligible with Tswa and Ronga and the name "Tsonga" is often used as a cover term for all three, also sometimes referred to as Tswa-Ronga. The Xitsonga language has been standardised for both academic and home use. Tsonga is an official language of South Africa, and under the name "Shangani" it is recognised as an official language in the Constitution of Zimbabwe. All Tswa-Ronga languages are recognised in Mozambique. It is not official in Eswatini.

The Lapita culture is the name given to a Neolithic Austronesian people and their material culture, who settled Island Melanesia via a seaborne migration at around 1600 to 500 BCE. They are believed to have originated from the northern Philippines, either directly, via the Mariana Islands, or both. They were notable for their distinctive geometric designs on dentate-stamped pottery, which closely resemble the pottery recovered from the Nagsabaran archaeological site in northern Luzon. The Lapita intermarried with the Papuan populations to various degrees, and are the direct ancestors of the Austronesian peoples of Polynesia, eastern Micronesia, and Island Melanesia.
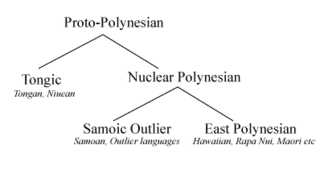
Nuclear Polynesian refers to those languages comprising the Samoic and the Eastern Polynesian branches of the Polynesian group of Austronesian languages.
Tonga is a Pacific Island nation whose people are known as Tongans.
Cook Islands Māori is an Eastern Polynesian language that is the official language of the Cook Islands. Cook Islands Māori is closely related to New Zealand Māori, but is a distinct language in its own right. Cook Islands Māori is simply called Māori when there is no need to disambiguate it from New Zealand Māori, but it is also known as Māori Kūki ʻĀirani or, controversially, Rarotongan. Many Cook Islanders also call it Te reo Ipukarea, literally "the language of the Ancestral Homeland".
Tonga (Chitonga), also known as Zambezi, is a Bantu language primarily spoken by the Tonga people (Batonga) who live mainly in the Southern province, Lusaka province, Central Province and Western province of Zambia, and in northern Zimbabwe, with a few in Mozambique. The language is also spoken by the Iwe, Toka and Leya people, and perhaps by the Kafwe Twa, as well as many bilingual Zambians and Zimbabweans. In Zambia Tonga is taught in schools as first language in the whole of Southern Province, Lusaka and Central Provinces.

Niuafoʻou, or Niuafoʻouan, is the language spoken on Tonga's northernmost island, Niuafoʻou.

Zambia has several major indigenous languages, all members of the Bantu family, as well as Khwedam, Zambian Sign Language, several immigrant languages and the pidgins Settla and Fanagalo. English is the official language and the major language of business and education.
The Northern Aslian languages are a group of Aslian languages spoken by about 5,000 people in inland areas of Peninsular Malaysia, with a few pockets in southern Thailand. The most distinctive language in the group is the outlier Cheq Wong, which is spoken south of the Central Aslian language Semai. The other languages apart from Tonga can be split into two divisions:
Charles Gitonga is a retired athlete from Kenya who specialized in the 400 metres. He is best known for winning the gold medal at the 1994 Commonwealth Games in Victoria.

The Tonga people of Zambia and Zimbabwe are a Bantu ethnic group of southern Zambia and neighbouring northern Zimbabwe, and to a lesser extent, in Mozambique. They are related to the Batoka who are part of the Tokaleya people in the same area, but not to the Tonga people of Malawi. In southern Zambia they are patrons of the Kafue Twa. They differ culturally and linguistically from the Tsonga people of South Africa and southern Mozambique.

Many languages are spoken, or historically have been spoken, in Zimbabwe. Since the adoption of its 2013 Constitution, Zimbabwe has 16 official languages, namely Chewa, Chibarwe, English, Kalanga, Koisan, Nambya, Ndau, Ndebele, Shona, The country's main languages are Shona, spoken by over 82% of the population, and Ndebele, spoken by roughly 15%. English is the country's lingua franca, used in government and business and as the main medium of instruction in schools. English is the first language of most white Zimbabweans, and is the second language of a majority of black Zimbabweans. Historically, a minority of white Zimbabweans spoke Afrikaans, Greek, Italian, Polish, and Portuguese, among other languages, while Gujarati and Hindi could be found amongst the country's Indian population. Deaf Zimbabweans commonly use one of several varieties of Zimbabwean Sign Language, with some using American Sign Language. Zimbabwean language data is based on estimates, as Zimbabwe has never conducted a census that enumerated people by language.
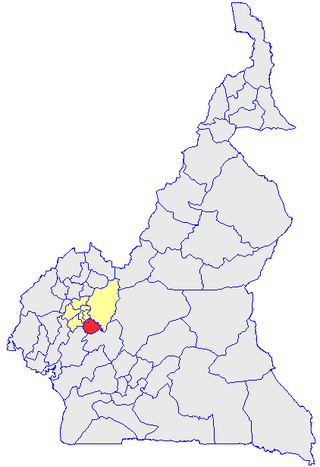
Ndé is one of the 58 divisions in Cameroon. It is located in the West region of the country, about 150km from Douala, the economic capital, and about 265 km from Yaoundé, the political capital. Its estimated population is 304,800. The term Nde is the name of a nearby river. Bangangte has been the headquarter of the Ndé division since June 14, 1961. Medumba is the most common language spoken in the region. Its kingdoms include: Bangangte, Bangoulap, Balengou, Bazou, Bakong, Bamena, Tonga (Badounga), Bahouoc, Bangang-Fokam, Bawock, Bangoua, Batchingou, Bamaha and Bagnoun. The main religious belief is Christianity, with the two main denominations being Catholics and Protestant. Its climate ranges between 14- 22 Celsius at night and between 24-30 Celsius. Some anthropological research has been done by Pradelles de Latour.

Tonga is a Bantu language spoken mainly in the Nkhata Bay District of Malawi. The number of speakers is estimated to be 170,000. According to the Mdawuku wa Atonga (MWATO) there are also significant numbers of speakers living elsewhere in Malawi and in neighbouring countries.
Ten'edn, also known as Mos in Thailand and Tonga-Mos or just Tonga in some literature, is an aboriginal Mon–Khmer language spoken by the Maniq tribe of Thailand and Malaysia.
Sikaiana is a Polynesian language, spoken by about 730 people on Sikaiana in the Solomon Islands.
References
- ↑ Tonga at Ethnologue (26th ed., 2023)

- ↑ Jouni Filip Maho, 2009. New Updated Guthrie List Online