Related Research Articles

The Bantu languages are a language family of about 600 languages that are spoken by the Bantu peoples of Central, Southern, Eastern and Southeast Africa. They form the largest branch of the Southern Bantoid languages.

Niger–Congo is a hypothetical language family spoken over the majority of sub-Saharan Africa. It unites the Mande languages, the Atlantic–Congo languages, and possibly several smaller groups of languages that are difficult to classify. If valid, Niger–Congo would be the world's largest in terms of member languages, the third-largest in terms of speakers, and Africa's largest in terms of geographical area. Austronesian has almost as many member languages, although this is complicated by the ambiguity about what constitutes a distinct language; the number of named Niger–Congo languages listed by Ethnologue is 1,540.
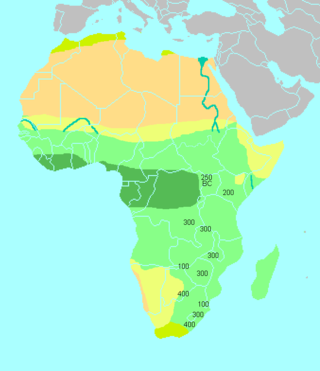
The Bantu expansion was a major series of migrations of the original Proto-Bantu-speaking group, which spread from an original nucleus around West-Central Africa. In the process, the Proto-Bantu-speaking settlers displaced, eliminated or absorbed pre-existing hunter-gatherer and pastoralist groups that they encountered.

Southern Bantoid is a branch of the Bantoid language family. It consists of the Bantu languages along with several small branches and isolates of eastern Nigeria and west-central Cameroon. Since the Bantu languages are spoken across most of Sub-Saharan Africa, Southern Bantoid comprises 643 languages as counted by Ethnologue, though many of these are mutually intelligible.

Bantoid is a major branch of the Benue–Congo language family. It consists of the Northern Bantoid languages and the Southern Bantoid languages, a division which also includes the Bantu languages that constitute the overwhelming majority and after which Bantoid is named.
Gweno is a Bantu language spoken in the North Pare Mountains in the Kilimanjaro Region of Tanzania. The people known as the Gweno are a Chaga ethnic and linguistic group. Since the Chaga people are Bantu speakers, the adopted language contains dialects similar to that of the Kenyan language Kamba. Gweno shares about 54% to 56% of its vocabulary with other Chaga dialects and 46% with Taita dialects. However, a large percentage of its vocabulary is not seen in the other dialects. Also at the start of the 11th century, the Chaga people descended and migrated from the Bantu group in which they migrated to the foothills of mount Kilimanjaro. The Gweno language is today spoken mostly by older adults, with younger generations having shifted to Asu and Swahili. Ethnologue considers Gweno to be moribund; the language is not being passed down because children have not been exposed to Gweno since the 1970s. The generational shift from Gweno to either Asu or Swahili has certainly created shifts in dialect, however Gweno speakers do not see this as a threat.
Myene is a cluster of closely related Bantu varieties spoken in Gabon by about 46,000 people. It is perhaps the most divergent of the Narrow Bantu languages, though Nurse & Philippson (2003) place it in with the Tsogo languages (B.30). The more distinctive varieties are Mpongwe (Pongoué), Galwa (Galloa), and Nkomi.
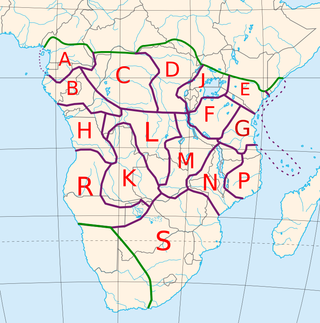
The 250 or so "Narrow Bantu languages" are conventionally divided up into geographic zones first proposed by Malcolm Guthrie (1967–1971). These were assigned letters A–S and divided into decades ; individual languages were assigned unit numbers, and dialects further subdivided. This coding system has become the standard for identifying Bantu languages; it was a practical way to distinguish many ambiguously named languages before the introduction of ISO 639-3 coding, and it continues to be widely used. Only Guthrie's Zone S is (sometimes) considered to be a genealogical group. Since Guthrie's time a Zone J has been set up as another possible genealogical group bordering the Great Lakes.
Tswa (Xitswa) is a South-Eastern Bantu language in Southern Mozambique. Its closest relatives are Ronga and Tsonga, the three forming the Tswa–Ronga family of languages.
Yao is a Bantu language in Africa with approximately two million speakers in Malawi, and half a million each in Tanzania and Mozambique. There are also some speakers in Zambia. In Malawi, the main dialect is Mangochi, mostly spoken around Lake Malawi. In Mozambique, the main dialects are Makale and Massaninga. The language has also gone by several other names in English, including chiYao or ciYao, Achawa, Adsawa, Adsoa, Ajawa, Ayawa, Ayo, Ayao, Djao, Haiao, Hiao, Hyao, Jao, Veiao, and waJao.
Bantu may refer to:
Lej or LEJ may refer to:
Mbugwe or Mbuwe (Kimbugwe) is a Bantu language spoken by the Mbugwe people of Lake Manyara in the Manyara Region of Central Tanzania. Mbugwe is estimated to be spoken by some 34,000 people.
The Nen language, Tunen (Banen), is a Bantu language of Cameroon. Maho (2009) considers Aling'a to be a distinct language. Unlike all other Bantu languages, Nen has an SOV word order rather than the standard Bantu SVO word order.
Taita is a Bantu language spoken in the Taita Hills of Kenya. It is closely related to the Chaga languages of Kenya and Tanzania. The Saghala variety is distinct enough to be considered a language separate from the Daw'ida and Kasigau dialects.

Jita is a Bantu language of Tanzania, spoken on the southeastern shore of Lake Victoria/Nyanza and on the island of Ukerewe.
The Nyali languages are a clade of Bantu languages coded Zone D.33 in Guthrie's classification. They are:
Lebonya is a proposed intermediate group of Bantu languages coded Zone D in Guthrie's classification. There are three branches:

The Bantu peoples are an indigenous ethnolinguistic grouping of approximately 400 distinct native African ethnic groups who speak Bantu languages. The languages are native to countries spread over a vast area from West Africa, to Central Africa, Southeast Africa and into Southern Africa. Bantu people also inhabit southern areas of Northeast African states.
Mahongwe is an undocumented and threatened Bantu language spoken in Gabon. The Mahongwe language is a language spoken by the Mahongwe people, belonging to the Bantu ethnic group, who mainly reside in the central Gabon region. It is one of several Bantoid languages spoken in the Central African region.
References
- ↑ Lengola at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ↑ Jouni Filip Maho, 2009. New Updated Guthrie List Online
- 1 2 3 Stappers, Leo (1971). "Esquisse de la langue lengola". African Linguistica. 5: 255–303.