Related Research Articles
Zizilivakan, also known as Fali of Jilbu and Ulan Mazhilvən, is a Chadic language spoken in Cameroon in Far North Province and neighboring Nigeria. It is one of several in the area that go by the name Fali.
Massa is a Chadic language spoken in southern Chad and northern Cameroon by the Masa people. It has approximately 200,000 speakers.
Afade (Afaɗə) is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in eastern Nigeria and northwestern Cameroon.
Lagwan (Logone) is a Chadic language spoken in northern Cameroon and southwestern Chad. Dialects include Logone-Birni and Logone-Gana.
Malgbe is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in northern Cameroon and southwestern Chad. Dialects are Douguia, Dro, Malgbe, Mara, and Walia.
Maslam is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in northern Cameroon, with a few in southwestern Chad. Dialects are Maslam and Sao. Maslam is in rapid decline.
Mpadə is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in northern Cameroon and southwestern Chad. Dialects are Bodo, Biamo, Digam, Mpade (Makari), Shoe (Shewe), and Woulki.
Mser (Msər), or Kousseri (Kuseri), is a moribund Afro-Asiatic language spoken in northern Cameroon and southwestern Chad. Dialects are Gawi, Houlouf, Kabe, Kalo, Mser (Kuseri).
Hya is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in northern Cameroon and neighboring regions of Nigeria.
Baldemu, or Mbazlam, is a nearly extinct Afro-Asiatic language spoken in northern Cameroon. Baldamu is spoken in Bogo commune, Diamaré department, Far North Region by only 5 speakers as of 2012. Speakers have been shifting to Fulfulde.
Cuvok is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in northern Cameroon.
Mafa is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in northern Cameroon and Northern Nigeria by the Mafa people.
Mofu-Gudur, or South Mofu, is a Chadic language spoken in northern Cameroon. Dialects are Dimeo, Gudur, Massagal, Mokong, Njeleng, and Zidim.
Daba is a Chadic dialect cluster spoken in Cameroon in Far North Province and in one village in neighboring Nigeria. Blench (2006) considers Mazagway to be a dialect.
Mazagway is a Chadic language spoken in Cameroon, in North Province and Far North Province. Blench (2006) classifies it as a dialect of Daba.
Dangaléat is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in central Chad. Speakers make up the majority of the population of Migami Canton in Mongo, Chad.
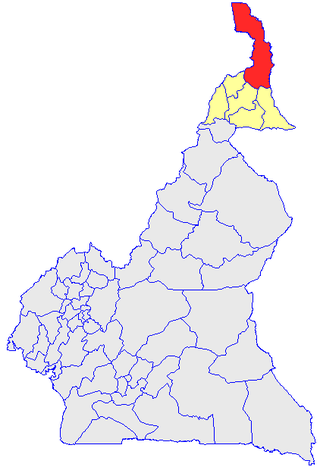
Logone-et-Chari is a department of Extreme-Nord Province in Cameroon. The department covers an area of 12,133 km2 and at the 2005 Census had a total population of 486,997. The capital of the department is at Kousséri. Most inhabitants of this department speak Chadian Arabic.
Musgu is a cluster of closely related language varieties of the Biu–Mandara subgroup of the Chadic languages spoken in Cameroon and Chad. The endonym is Mulwi. Blench (2006) classifies the three varieties as separate languages. Speakers of the extinct related language Muskum have switched to one of these.
Pol is a Bantu language of Cameroon. Pol proper is spoken in central Cameroon; the Pomo and Kweso dialects are spoken in Congo and the CAR near the Cameroonian border.
Majera (Mazera) is a minor Afro-Asiatic language of Chad and Cameroon.
References
- ↑ Jina at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ↑ Binam Bikoi, Charles, ed. (2012). Atlas linguistique du Cameroun (ALCAM)[Linguistic Atlas of Cameroon]. Atlas linguistique de l'Afrique centrale (ALAC) (in French). Vol. 1: Inventaire des langues. Yaoundé: CERDOTOLA. ISBN 9789956796069.
- ↑ Tourneux, Henry (October 2001). Le système consonantique des langues dites "kotoko". 1st Biennial International Colloquium on the Chadic Language Family (in French). Leipzig. pp. 115–135.
- ↑ Tourneux, Henry (August 2000). Le système vocalique dans le groupe "kotoko". 3ème Congrès mondial de linguistique africaine (in French). Lomé. pp. 69–77.