Related Research Articles
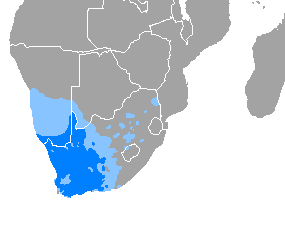
Afrikaans is a West Germanic language, spoken in South Africa, Namibia and Botswana, Zambia and Zimbabwe. It evolved from the Dutch vernacular of South Holland spoken by the predominantly Dutch settlers and enslaved population of the Dutch Cape Colony, where it gradually began to develop distinguishing characteristics in the 17th and 18th centuries.
Aramaic is a Northwest Semitic language that originated in the ancient region of Syria and quickly spread to Mesopotamia, the southern Levant, southeastern Anatolia, Eastern Arabia and the Sinai Peninsula, where it has been continually written and spoken in different varieties for over three thousand years.

Low Saxon, also known as West Low German are a group of Low German dialects spoken in parts of the Netherlands, northwestern Germany and southern Denmark. It is one of two dialect groups, the other being East Low German.

Friedrich Wilhelm Christian Karl Ferdinand von Humboldt was a German philosopher, linguist, government functionary, diplomat, and founder of the Humboldt University of Berlin. In 1949, the university was named after him and his younger brother, Alexander von Humboldt, a naturalist.

Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period. Despite his short life, his rapid pace of composition resulted in more than 800 works representing virtually every Western classical genre of his time. Many of these compositions are acknowledged as pinnacles of the symphonic, concertante, chamber, operatic, and choral repertoire. Mozart is widely regarded as one of the greatest composers in the history of Western music, with his music admired for its "melodic beauty, its formal elegance and its richness of harmony and texture".

The Egyptian language, or Ancient Egyptian is an extinct branch of the Afro-Asiatic languages that was spoken in ancient Egypt. It is known today from a large corpus of surviving texts, which were made accessible to the modern world following the decipherment of the ancient Egyptian scripts in the early 19th century.

Carl Heinrich Maria Orff was a German composer and music educator, who composed the cantata Carmina Burana (1937). The concepts of his Schulwerk were influential for children's music education.
Standard High German (SHG), less precisely Standard German or High German, is the umbrella term for the standardized varieties of the German language, which are used in formal contexts and for communication between different dialect areas. German is a pluricentric Dachsprache with currently three codified specific national varieties: German Standard German, Austrian Standard German and Swiss Standard German.

Arvanitika, also known as Arvanitic, is the variety of Albanian traditionally spoken by the Arvanites, a population group in Greece. Arvanitika was brought to southern Greece during the late Middle Ages by Albanian settlers who moved south from their homeland in present-day Albania in several waves. The dialect preserves elements of medieval Albanian, while also being significantly influenced by the Greek language. Arvanitika is today endangered, as its speakers have been shifting to the use of Greek and most younger members of the community no longer speak it.

The voiced alveolar approximant is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents the alveolar and postalveolar approximants is ⟨ɹ⟩, a lowercase letter r rotated 180 degrees. The equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is r\.
The voiced bilabial nasal is a type of consonantal sound which has been observed to occur in about 96% of spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨m⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is m. The bilabial nasal occurs in English, and it is the sound represented by "m" in map and rum. Very few languages are known to lack this sound. A small number of languages have been observed to lack independent nasal phonemes altogether, such as Quileute, Makah, and Central Rotokas.
The Yeni language is an extinct language of Cameroon, formerly spoken around Djeni Mountain in the Nyalang area. All that remains of the language, apparently, is a song remembered by some Sandani speakers. However, according to Bruce Connell, comparison of the song's words to neighboring languages suggests that "it was closely related to [the Mambiloid languages] Cambap, Njerep, and Kasabe."

Toto is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken on the border of India and Bhutan, by the tribal Toto people in Totopara, West Bengal along the border with Bhutan. It is also spoken in Subhapara, Dhunchipara, and Panchayatpara hillocks on India-Bhutan border in Jalpaiguri district, West Bengal (Ethnologue).

Abbas Zaryab or 'Abbās Zaryāb was a historian, translator, literature Professor and Iranologist. He was the author of several books, including a life of Muhammad, and articles in The Persian Encyclopedia, Western peer reviewed Journals as well as Iranica.
Inku is an Indo-Aryan language spoken, at least historically, throughout Afghanistan by four of the country's itinerant communities: the Jalali, the Pikraj, the Shadibaz and the Vangawala. Itinerant communities in Afghanistan, whether Inku-speaking or not, are locally known as "Jats", a term which is not a self-designation of the groups but rather a collective, often pejorative name given by outsiders. The reference work Ethnologue has an entry for what could be this language, but under the name Jakati, but that entry is at least partly erroneous.
The Illyrian language was an Indo-European language or group of languages spoken by the Illyrians in Southeast Europe during antiquity. The language is unattested with the exception of personal names and placenames. Just enough information can be drawn from these to allow the conclusion that it belonged to the Indo-European language family.

Dutch is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, spoken by about 25 million people as a first language and 5 million as a second language and is the third most spoken Germanic language. In Europe, Dutch is the native language of most of the population of the Netherlands and Flanders. Dutch was one of the official languages of South Africa until 1925, when it was replaced by Afrikaans, a separate but partially mutually intelligible daughter language of Dutch. Afrikaans, depending on the definition used, may be considered a sister language, spoken, to some degree, by at least 16 million people, mainly in South Africa and Namibia, and evolving from Cape Dutch dialects.
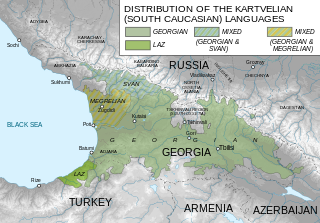
The Kartvelian languages are a language family indigenous to the South Caucasus and spoken primarily in Georgia. There are approximately 5 million Georgian language speakers worldwide, with large groups in Russia, Iran, the United States, the European Union, Israel, and northeastern Turkey. The Kartvelian family has no known relation to any other language family, making it one of the world's primary language families.
Kayeli is an extinct Austronesian language once used by the Kayeli people of the Indonesian island Buru. Two dialects were recognized, namely Leliali (Liliali) and Lumaete.
References
- ↑ Crystal, David (1999-11-20). "Millennium briefing: the death of language". Prospectmagazine.co.uk. Retrieved 2013-09-02.