
The Marchantiophyta are a division of non-vascular land plants commonly referred to as hepatics or liverworts. Like mosses and hornworts, they have a gametophyte-dominant life cycle, in which cells of the plant carry only a single set of genetic information.

Hornworts are a group of bryophytes constituting the division Anthocerotophyta. The common name refers to the elongated horn-like structure, which is the sporophyte. As in mosses and liverworts, the flattened, green plant body of a hornwort is the gametophyte plant.

Marchantiales is an order of thallose liverworts that includes species like Marchantia polymorpha, a widespread plant often found beside rivers, and Lunularia cruciata, a common and often troublesome weed in moist, temperate gardens and greenhouses.

Marchantia is a genus in the family Marchantiaceae of the order Marchantiales, a group of liverworts.

Lunularia cruciata, the crescent-cup liverwort, is a liverwort of the order Marchantiales, and the only species in the genus Lunularia and family Lunulariaceae. The name, from Latin luna, moon, refers to the moon-shaped gemmacups.

Metzgeriales is an order of liverworts. The group is sometimes called the simple thalloid liverworts: "thalloid" because the members lack structures resembling stems or leaves, and "simple" because their tissues are thin and relatively undifferentiated. All species in the order have a small gametophyte stage and a smaller, relatively short-lived, spore-bearing stage. Although these plants are almost entirely restricted to regions with high humidity or readily available moisture, the group as a whole is widely distributed, and occurs on every continent except Antarctica.

Sphaerocarpales is an order of plants within the liverworts. Approximately twenty species are in this order which is sub-divided into four families: Monocarpaceae, Sphaerocarpaceae and Riellaceae, as well as the extinct family Naiaditaceae. The inclusion of the Naiaditaceae is uncertain, and the family has sometimes been assigned to the Calobryales.

Cavicularia densa is the only species in the liverwort genus Cavicularia. The species was first described in 1897 by Franz Stephani, and is endemic to Japan, where it grows on fine moist soil.

Haplomitriopsida is a newly recognized class of liverworts comprising fifteen species in three genera. Recent cladistic analyses of nuclear, mitochondrial, and plastid gene sequences place this monophyletic group as the basal sister group to all other liverworts. The group thus provides a unique insight into the early evolution of liverworts in particular and of land plants in general.

Blasiales is an order of liverworts with a single living family and two species. The order has traditionally been classified among the Metzgeriales, but molecular cladistics suggests a placement at the base of the Marchantiopsida.
Cyanobionts are cyanobacteria that live in symbiosis with a wide range of organisms such as terrestrial or aquatic plants; as well as, algal and fungal species. They can reside within extracellular or intracellular structures of the host. In order for a cyanobacterium to successfully form a symbiotic relationship, it must be able to exchange signals with the host, overcome defense mounted by the host, be capable of hormogonia formation, chemotaxis, heterocyst formation, as well as possess adequate resilience to reside in host tissue which may present extreme conditions, such as low oxygen levels, and/or acidic mucilage. The most well-known plant-associated cyanobionts belong to the genus Nostoc. With the ability to differentiate into several cell types that have various functions, members of the genus Nostoc have the morphological plasticity, flexibility and adaptability to adjust to a wide range of environmental conditions, contributing to its high capacity to form symbiotic relationships with other organisms. Several cyanobionts involved with fungi and marine organisms also belong to the genera Richelia, Calothrix, Synechocystis, Aphanocapsa and Anabaena, as well as the species Oscillatoria spongeliae. Although there are many documented symbioses between cyanobacteria and marine organisms, little is known about the nature of many of these symbioses. The possibility of discovering more novel symbiotic relationships is apparent from preliminary microscopic observations.

Hymenophyton is a genus of the order Pallaviciniales (liverworts) containing one to three species. The genus was formerly described as monotypic, as each member possesses a close morphological resemblance, but phytochemical and molecular evidence now supports an infrageneric classification two separate species. The name Hymenophyton leptopodum, regarded as a synonym of Hymenophyton flabellatum, has been resurrected. A population found in Chile is regarded as a separate clade, and the reinstatement of Hymenophyton pedicellatum has been proposed.

Ptilidium is a genus of liverwort, and is the only genus in family Ptilidiaceae. It includes only three species: Ptilidium californicum, Ptilidium ciliare, and Ptilidium pulcherrimum. The genus is distributed throughout the arctic and subarctic, with disjunct populations in New Zealand and Tierra del Fuego. Molecular analysis suggests that the genus has few close relatives and diverged from other leafy liverworts early in their evolution.

Sphaerocarpos texanus, the Texas balloonwort, is a species of liverwort in the Sphaerocarpaceae family, found in the Americas, northern Africa and Europe.
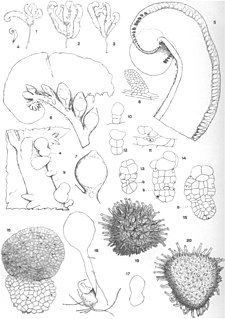
Riella is a genus in the liverwort family Riellaceae, and includes about eighteen species. Plants in the genus are small and grow submerged in shallow temporary pools. Although the genus is widely distributed in the Northern Hemisphere, locating populations is often difficult. Its occurrence is sporadic and local, and the tiny plants are ephemeral. The ornamented spores remain viable for several years, allowing the plants to survive annual drying of their habitat. The plants are easily grown in laboratory cultures.

Cephaloziaceae is a family of liverworts.

Neohodgsonia is a genus of liverworts containing the single species Neohodgsonia mirabilis. Neohodgsonia is the only genus in the family Neohodgsoniaceae, which is the only family in the order Neohodgsoniales.

Ricciocarpos natans is the only species in the genus Ricciocarpos, a genus of liverworts in the family Ricciaceae. It was formerly listed in 1759 as a species of Riccia by Linnaeus, but then assigned to a new genus of its own in 1829 by August Carl Joseph Corda.

Cryptomitrium tenerum is a species of liverwort native to North America. It is the only representative of its genus on the continent.

Veronica jovellanoides, commonly known as Riverhead speedwell, is a threatened flowering plant in the family Plantaginaceae. Endemic to New Zealand, only three plants are known in the wild, all in the Ernest Morgan Reserve, a 20 ha forest northwest of Auckland. Its discovery is accredited to a retired plant nursery owner, Geoff Davidson, who organised the land's protection a few decades prior, and found it by chance on a walk in November 2007.


















