
Buenos Aires, officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires, is the capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata, on South America's southeastern coast. "Buenos Aires" can be translated as "fair winds" or "good airs", but the former was the meaning intended by the founders in the 16th century, by the use of the original name "Real de Nuestra Señora Santa María del Buen Ayre", named after the Madonna of Bonaria in Sardinia, Italy. Buenos Aires is classified as an alpha global city, according to the Globalization and World Cities Research Network (GaWC) 2020 ranking.

Mar del Plata is a city on the coast of the Atlantic Ocean, in Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. It is the seat of General Pueyrredón district. Mar del Plata is the second largest city in Buenos Aires Province. The name "Mar del Plata" is a shortening of "Mar del Rio de la Plata," and has the meaning of "sea of the Rio de la Plata basin" or "adjoining sea to the (River) Plate region". Mar del Plata is one of the major fishing ports and the biggest seaside beach resort in Argentina. With a population of 614,350 as per the 2010 census [INDEC], it is the 5th largest city in Argentina.

Quilmes is a city on the coast of the Rio de la Plata, in the province of Buenos Aires, Argentina, on the south east of the Greater Buenos Aires. The city was founded in 1666 and it is the seat of the eponymous county. With a population of 230,810, it is located 17 km (11 mi) south of the capital of Argentina, the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires.

The Autódromo de Buenos Aires Oscar y Juan Gálvez is a 45,000 capacity motor racing circuit in Buenos Aires, Argentina built in 1952 under president Juan Perón, named Autódromo 17 de Octubre after the date of Loyalty Day until Perón's overthrow. It was later renamed after Argentinian racing driver brothers, Juan Gálvez (1916–1963) and Oscar Alfredo Gálvez (1913–1989).

Ferrocarriles Argentinos was a state-owned company that managed the entire Argentine railway system for nearly 45 years. It was formed in 1948 when all the private railway companies were nationalised during Juan Perón's first presidential term, and transformed into the Empresa de Ferrocarriles del Estado Argentino.

A piquetero is a member of a group that has blocked a street with the purpose of demonstrating and calling attention over a particular issue or demand. The word is a neologism in the Spanish of Argentina, coming from piquete, that is, its specific meaning as a standing or walking demonstration of protest in a significant spot.

Colectivo is the name given in Argentina, Colombia, Chile and Paraguay to a type of public transportation vehicle, especially those of Argentina's capital city, Buenos Aires. The name comes from vehículos de transporte colectivo, reflecting their origin as shared taxis.

Trenes de Buenos Aires (TBA) was a private company that operated commuter rail services over the 5 ft 6 in broad gauge Sarmiento and Mitre lines of Buenos Aires. The company, owned by Claudio and Mario Cirigliano, also operated long-distance services on the General Mitre Railway to central-western Argentina and on the General Urquiza Railway to northern Argentina and Uruguay on the international Tren de los Pueblos Libres.

Remedios de Escalada is a city located in Buenos Aires Province, Argentina, within Lanús Partido, Gran Buenos Aires. It covers an area of 9.95 km² and the population was 81,465 in 2001; the demonym for its inhabitants is "escaladense."

The General Bartolomé Mitre Railway (FCGBM), named after the former Argentine president Bartolomé Mitre, is one of the six state-owned Argentine railway lines formed after President Juan Perón's nationalisation of the railway network in 1948 and one of the largest of Argentina. The six divisions, managed by Ferrocarriles Argentinos were later broken up during the process of railway privatisation beginning in 1991 during Carlos Menem's presidency.
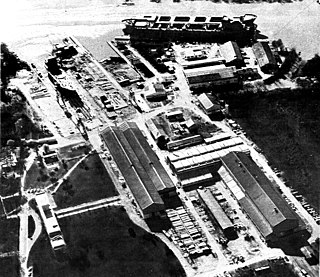
Astilleros Argentinos Río de La Plata S.A. was an Argentine shipyard. Its core business was building and repairing ships and locomotives. It also manufactured pipes, industrial machinery, and tractors. It went out of business in 1994.

Ford Argentina S.C.A. is the Argentine subsidiary of Ford Motor Company founded in Buenos Aires in 1913. Its first products were Model Ts assembled from complete knock down (CKD) kits provided by Ford Motor Company in 1917. Nevertheless, Ford Motor Argentina is best known in more recent times for producing the Ford Focus and, previously, the Argentine version of the Ford Falcon, originally a U.S. model introduced in Argentina in 1961, but adapted to the Argentine market.
Sevel Argentina S.A. was an Argentine automobile company established in 1981 that produced and marketed Fiat, Peugeot, Alfa Romeo, Chevrolet, and Citroën vehicles for the local market until it was dissolved in 1999. The company was created by merging Fiat's and Peugeot's Argentine operations.

Nanque S.A. was an Argentine sports equipment manufacturing company, based in Banfield, Buenos Aires. Founded in 1969, its goal was to manufacture clothing and sportswear for professional and amateur sports, focusing on the association football market, where the company sponsored several teams not only in Argentina but in South and Central America. One of the Nanque's owners, Carlos Portell, was also president of Club Atlético Banfield from 1998 to 2012.

Emprendimientos Ferroviarios S.A. (Emfer) was an Argentine rail rolling stock manufacturer based in San Martín, Buenos Aires. The company also remodelled and repaired rail vehicles and had previously manufactured rolling stock for the Sarmiento and Mitre commuter rail lines in Buenos Aires. The Emfer rail rolling stock ran on the two lines until 2014 when they were replaced with CSR Corporation Limited Electric Multiple Units.

The Sociedad Sportiva Argentina was an Argentine multi-sports club sited in Buenos Aires. The headquarters were located in Florida street nº 183 while the stadium was sited in Palermo, next to Hipódromo Argentino. Originally established in 1899 under the name "Sociedad Hípica Argentina" for the practise of equestrian activities, the Sociedad Sportiva would held a large variety of sport events in several disciplines, such as football, athletics, auto racing, aviation, aerostatics, aeronautics, boxing, bicycle racing, motorcycle racing, polo, rugby union, trot, sulky races, show jumping, among others.

General Motors de Argentina S.R.L. is the Argentine subsidiary of the US-based company General Motors. The company is currently headquartered in Vicente López, Buenos Aires, with its factory located in Alvear, Santa Fe Province.

Fiat SOMECA Concord S.A.C.I was the Argentina subsidiary of Italian automotive manufacturer Fiat Automobiles S.p.A. and the first manufacturer of Fiat vehicles in the country. Established in 1954, the factory produced not only automobiles but railway vehicles through its subsidiary Materfer. Some of Fiat Concord's most emblematic products included the 600, 128, and the 1500 coupé designed by Vignale.

Citroën Argentina S.A. was the Argentine subsidiary of French automotive manufacturer Citroën which produced vehicles of the brand in the country. Established in 1959 and headquartered in Barracas, Buenos Aires, it operated in the country for 30 years producing vehicles until the economic crisis during the military government forced the company to cease its operations.
Stellantis Argentina S.A. is the Argentine subsidiary of international conglomerate Stellantis which produces and markets Citroën, Fiat, and Peugeot vehicles in the country. Established in 2021, the company is successor of several firms that had operated in Argentina as subsidiaries or licensors for these brands, such as Fiat Argentina, and Groupe PSA Argentina.



















