
Linji Yixuan was a Tang dynasty (618-907) Chinese monk and teacher of the Hongzhou school of Chinese Chan (Zen). Linji was the leading figure of Chan Buddhism in the Tang, and the Recorded Sayings of Linji, which contains his teachings, is seen as a major Zen text which exemplifies the iconoclastic and antinomian spirit of Zen. He is also known by the posthumous title Huizhao Chanshi.
Ōbaku is the Amur Corktree. It may refer to:

Mount Putuo is an island in Putuo District, Zhoushan, Zhejiang, China. It is a renowned site in Chinese Buddhism and is the bodhimaṇḍa of the bodhisattva Guanyin.
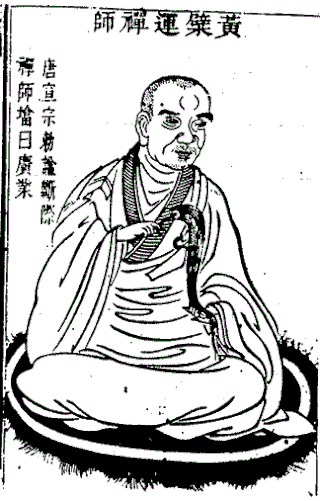
Huángbò Xīyùn was an influential master of Zen Buddhism during the Tang dynasty. He was part of the Hongzhou school of Chan founded by Mazu.

Mount Kōya is a large temple settlement in Wakayama Prefecture, Japan to the south of Osaka. In the strictest sense, Mount Kōya is the mountain name (sangō) of Kongōbu-ji Temple, the ecclesiastical headquarters of the Kōyasan sect of Shingon Buddhism.

Ingen Ryūki was a Chinese poet, calligrapher, and monk of Linji Chan Buddhism from China. He is most known for founding the Ōbaku school of Zen in Japan.
Wanfu Temple is a Buddhist temple on Mount Huangbo in Fuqing, Fujian, China. It is famous as the original temple of Yinyuan Longqi, the temple's 33rd abbot and a Chan master. He later travelled to Japan with his disciple Muyan to found the Japanese Ōbaku school of Zen.

Manpuku-ji is a Buddhist temple located in Uji, Kyoto Prefecture, approximately a 5-minute walk from Ōbaku Station. It is the head temple of the Japanese Ōbaku Zen school, and named after Wanfu Temple in Fujian, China. The mountain is likewise named after Mount Huangbo, where the Chinese temple is situated.
Itsunen Shoyu is famous as a Buddhist monk and painter who helped to establish Chan (Zen) in Japan. He was also the third abbot of Kofukuji Temple. In addition to his skill of painting, he also practices the art of Seal carving and cemented the popularity of this art in Japan.
Sokuhi Nyoitsu was a Buddhist monk of the Ōbaku Zen sect, and was also an accomplished poet and calligrapher. His teacher Ingen Ryūki, Mokuan Shōtō and Sokuhi were together known as the "Three Brushes of Ōbaku" or Ōbaku no Sanpitsu.

Mount Emei, alternatively Mount Omei, is a 3,099-metre-tall (10,167 ft) mountain in Sichuan Province, China, and is the highest of the Four Sacred Buddhist Mountains of China. Mount Emei sits at the western rim of the Sichuan Basin. The mountains west of it are known as Daxiangling. A large surrounding area of countryside is geologically known as the Permian Emeishan Large Igneous Province, a large igneous province generated by the Emeishan Traps volcanic eruptions during the Permian Period.

Mount Wutai, also known by its Chinese name Wutaishan and as Mount Qingliang, is a sacred Buddhist site at the headwaters of the Qingshui in Shanxi Province, China. Its central area is surrounded by a cluster of flat-topped peaks or mesas roughly corresponding to the cardinal directions. The north peak is the highest and is also the highest point in North China.
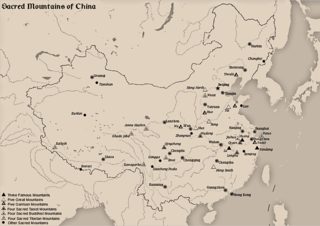
The Sacred Mountains of China are divided into several groups. The Five Great Mountains refers to five of the most renowned mountains in Chinese history, which have been the subjects of imperial pilgrimage by emperors throughout ages. They are associated with the supreme God of Heaven and the five main cosmic deities of traditional Chinese religion. The group associated with Buddhism is referred to as the Four Sacred Mountains of Buddhism, and the group associated with Taoism is referred to as the Four Sacred Mountains of Taoism.

Niuheliang is a Neolithic archaeological site in Liaoning Province, Northeast China, along the middle and upper reaches of the Laoha River and the Yingjin River. Discovered in 1983, the Niuheliang site belongs to the Hongshan culture. It includes evidence of religion, such as a temple, an altar and a cairn.

Mount Jiuhua located in Chizhou, Anhui Province in China is an important Buddhist site and natural scenic spot. It is one of the four famous Buddhist mountains in China, one of the first batch of 5A level scenic spots in China, one of the first batch of natural and cultural heritage sites in China, and the main scenic spot of "two mountains and one lake" tourism development strategy in Anhui Province. The planned area of the scenic spot is 120 square kilometers, and the protected area is 174 square kilometers, which is composed of 11 scenic spots.

Hengshan, also known as Mount Heng, is a mountain in southcentral China's Hunan Province known as the southern mountain of the Five Great Mountains of China. Heng Shan is a mountain range 150 kilometres (93 mi) long with 72 peaks and lies at 27°18′6″N112°41′5″E. The Huiyan Peak is the south end of the peaks, Yuelu Mountain in Changsha City is the north end, and the Zhurong Peak is the highest at 1,300 metres (4,300 ft) above sea level.

Mount Huaguo or Flowers and Fruit Mountain, is a major area featured in the novel Journey to the West. A number of real-world locations have been connected with the Mount Huaguo, although the eponymous mountain in Lianyungang, Jiangsu is most commonly identified as its source of inspiration.

Mount Mogan or Moganshan is a mountain located in Deqing County, Huzhou, Zhejiang Province, China, 60 kilometers from the provincial capital Hangzhou and 200 km from Shanghai. It is part of the Moganshan National Park and at its base is the small town of Moganshan.
Guangjiao Temple is a Buddhist temple located in Xuanzhou District, Xuancheng, Anhui, China. Alongside Huacheng Temple, Cuifeng Temple and Kaihua Temple, it is honoured as the "Four Famous Buddhist Temples in Anhui". It was first built in the Tang dynasty by a prominent Chan master Huangbo Xiyun, and went through many changes and repairs through the following dynasties. Most of the present structures in the temple were repaired or rebuilt between 2004 and 2006.
Mount Huaguo is a mountain located in Haizhou District, Lianyungang, Jiangsu, China. It forms a part of the Yuntai Mountains. The site is best known for being an inspiration for a synonymous legendary mountain in the novel Journey to the West. Its summit, Yunü Peak, is the highest point of Jiangsu province at 625.3 metres (2,052 ft).













