
D'Aguilar National Park is a national park in Queensland, Australia. It contains the D'Aguilar Range and is located along the northwest of the Brisbane metropolitan area. The park is traversed by the winding scenic Mount Nebo Road and Mount Glorious Road.

The Australian Alps montane grasslands is a montane grassland ecoregion of south-eastern Australia, restricted to the montane regions above 1300 metres .

The Mount Lofty Ranges are a range of mountains in the Australian state of South Australia which for a small part of its length borders the east of Adelaide. The part of the range in the vicinity of Adelaide is called the Adelaide Hills and defines the eastern border of the Adelaide Plains.

Esperance mallee is an ecoregion on the south coast of Western Australia, a coastal strip where the predominant vegetation consists of short eucalyptus trees and shrubs.

Hampton is an interim Australian bioregion located in southeastern coastal Western Australia, with a small portion (4%) extending into adjacent South Australia. It has an area of 1,088,198 hectares. The Hampton bioregion is part of the Coolgardie woodlands ecoregion.

Yalgoo is an interim Australian bioregion located in Western Australia. It has an area of 5,087,577 hectares. The bioregion, together with the Avon Wheatbelt and Geraldton Sandplains bioregions, is part of the larger Southwest Australia savanna ecoregion as classified by the World Wildlife Fund.

Eucalyptus cneorifolia, the Kangaroo Island narrow-leaf mallee, is a native tree of Kangaroo Island, South Australia.

The Carpentaria tropical savanna is a tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion in northern Australia.

The Victoria Plains tropical savanna is a tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion in northwestern Australia.

The Coolgardie woodlands is an ecoregion in southern Western Australia. The predominant vegetation is woodlands and mallee scrub. The ecoregion is a transitional zone between the Mediterranean-climate forests, woodlands, and shrublands of Southwest Australia and the deserts and dry scrublands of the Australian interior.

The Eyre Yorke Block, also known as the Eyre and Yorke mallee, is an interim Australian (IBRA) bioregion and a World Wildlife Fund ecoregion covering part of the Eyre Peninsula and all of Yorke Peninsula as well as land to its immediate east in South Australia.

The Tirari–Sturt stony desert is a deserts and xeric shrublands ecoregion in central Australia.
In South Australia, one of the states of Australia, there are many areas which are commonly known by regional names. Regions are areas that share similar characteristics. These characteristics may be natural such as the Murray River, the coastline, desert or mountains. Alternatively, the characteristics may be cultural, such as common land use. South Australia is divided by numerous sets of regional boundaries, based on different characteristics. In many cases boundaries defined by different agencies are coterminous.
Eucalyptus cajuputea, commonly known as the narrow-leaved peppermint box, is a tree or a mallee that is endemic to South Australia. It usually has rough, flaky bark on the trunk, linear to narrow lance-shaped adult leaves, flower buds arranged in groups of seven to eleven, white flowers and smooth, cup-shaped to barrel-shaped fruit.
Bangadilly National Park is a national park located around 20 km west of Bowral in the Southern Highlands of New South Wales. Established in 2001, it is made up of three separate, similarly sized areas of land totalling 2,141 hectares in area. It consists of sandstone plateaus and gorges bordering the Wingecarribee River.

The Southeast Australia temperate forests is a temperate broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion of south-eastern Australia. It includes the temperate lowland forests of southeastern Australia, at the southern end of the Great Dividing Range. Vegetation ranges from wet forests along the coast to dry forests and woodlands inland.

The Tasmanian temperate forests is a temperate broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion in Australia. The ecoregion occupies the eastern portion of the island of Tasmania, which lies south of the Australian mainland.

Kanmantoo is an interim Australian bioregion located in South Australia. It has an area of 812,415 hectares, which includes the Fleurieu Peninsula and Kangaroo Island. The bioregion is part of the Mount Lofty woodlands ecoregion.
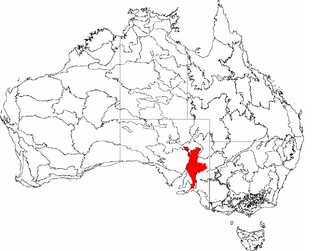
Flinders Lofty Block is an interim Australian bioregion located in South Australia. It has an area of 6,615,765 hectares, which includes the Mount Lofty Ranges and Flinders Ranges.

















