
Mount Temple is a mountain in Banff National Park of the Canadian Rockies of Alberta, Canada.
Mount Walsh is a mountain in Kluane National Park and Reserve in Yukon, Canada.

Major General Sir James Howden MacBrien was a Canadian soldier and Chief of the General Staff, the head of the Canadian Militia from 1920 until 1927.

Pyramid Mountain is a mountain in Jasper National Park, Alberta, Canada, named for its pyramid-like shape. James Hector named the mountain in 1859 due to its appearance from the Athabasca River valley on the eastern side of the peak.

The Columbia Mountains are a group of mountain ranges along the Upper Columbia River in British Columbia, Montana, Idaho and Washington. The mountain range covers 135,952 km². The range is bounded by the Rocky Mountain Trench on the east, and the Kootenai River on the south; their western boundary is the edge of the Interior Plateau. Seventy-five percent of the range is located in Canada and the remaining twenty-five percent in the United States; American geographic classifications place the Columbia Mountains as part of the Rocky Mountains complex, but this designation does not apply in Canada. Mount Sir Sandford is the highest mountain in the range, reaching 3,519 metres (11,545 ft).

Mac. Robertson Land is the portion of Antarctica lying southward of the coast between William Scoresby Bay and Cape Darnley. It is located at 70°00′S65°00′E. In the east, Mac. Robertson Land includes the Prince Charles Mountains. It was named by the British Australian and New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) (1929–1931), under Sir Douglas Mawson, after Sir Macpherson Robertson of Melbourne, a patron of the expedition.
Mount Queen Bess is one of the principal summits of the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains of southern British Columbia. It stands west of Chilko Lake and to the south of Tatlayoko Lake, and crowns a peak-studded ridge to the north of the Homathko Icefield.
Mount Raleigh, elevation 3,132 m (10,276 ft), is one of the principal summits of the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains of southern British Columbia in Canada. It is located just southeast of the confluence of the Southgate and Bishop Rivers, northeast of the head of Bute Inlet, and is the highest summit south of the Bishop River's divide with the Lillooet River at Ring Pass, which is at the southeastern edge of the Lillooet Icefield and just north of the Pemberton Icecap. It is also the highest peak south of the pass between the upper basins of Chilko Lake and the Taseko Lakes, just north of which is Monmouth Mountain at 3,182 m (10,440 ft).

Mount Sir Wilfrid Laurier is the highest peak of the Cariboo Mountains in the east-central interior of British Columbia, Canada. The mountain is part of the Premier Range, which is located just west of Valemount.
Mount Sir MacKenzie Bowell is a 3,301 m (10,830 ft) mountain peak located at co-ordinates 52°49′54″N119°43′48″W in the Premier Range of the Cariboo Mountains in the east-central interior of British Columbia, Canada. The mountain is located between the Kiwa and Tete glaciers.

The Hart Ranges are a major subrange of the Canadian Rockies located in northeastern British Columbia and western Alberta. The mountains constitute the southernmost portion of the Northern Rocky Mountains.

Mount Lyell is a mountain on the Alberta–British Columbia border in western Canada. Comprising five distinct summits, Mount Lyell reaches a height of 3,498 m (11,476 ft). The mountain was named by James Hector in 1858 in recognition of Scottish geologist Sir Charles Lyell.

Mount Sir Sandford is the highest mountain of the Sir Sandford Range and the highest mountain in the Selkirk Mountains of southeastern British Columbia, Canada. It is the 12th highest peak in the province. The mountain was named after Sir Sandford Fleming, a railway engineer for the Canadian Pacific Railway.

MacNaughton Mountain is a mountain located in Essex County, New York, named after James MacNaughton (1851–1905), the grandson of Archibald McIntyre. The mountain is part of the Street Range of the Adirondack Mountains.
Mount Sir Allan MacNab is a mountain located in the Premier Range of British Columbia, Canada. The range is named for Sir Allan MacNab, a Canadian industrialist who was premier of the Province of Canada from 1854 to 1856.

Lotus Flower Tower is a peak in the Cirque of the Unclimbables, Northwest Territories, Canada. The tower is on a ridge one kilometre to the southwest of Mount Sir James MacBrien, and though the tower is not prominent in relation to surrounding peaks, it is noted for its sheer rock walls which are home to classic multi-pitch climbing routes.

Air Marshal William Ross MacBrien, OBE, CD, RCAF (1913–1986), commonly known as Bill MacBrien or Iron Bill, was a senior Royal Canadian Air Force officer during World War II and a senior commander in the 1950s and 60s.
MacBrien is an Irish surname. Notable people with the surname include:
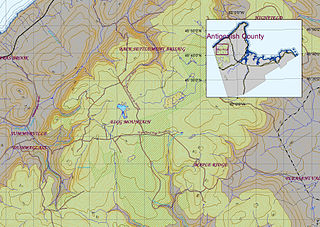
Eigg Mountain is high plateau, part of the highlands of Antigonish County, Nova Scotia, Canada.












