Related Research Articles

Moss Hart was an American playwright, librettist, and theater director.

Hiawatha, also known as Ayenwatha or Aiionwatha, was a precolonial Native American leader and co-founder of the Iroquois Confederacy. He was a leader of the Onondaga people, the Mohawk people, or both. According to some accounts, he was born an Onondaga but adopted into the Mohawks.
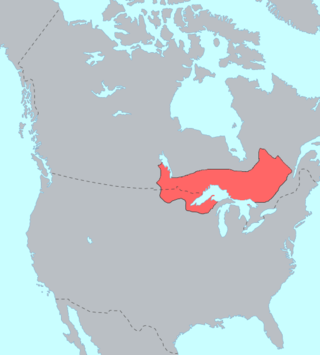
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains. They are Indigenous peoples of the Subarctic and Northeastern Woodlands.

Brother Bear is a 2003 American animated musical fantasy comedy-drama film produced by Walt Disney Feature Animation and released by Walt Disney Pictures. The 44th Disney animated feature film, it was directed by Aaron Blaise and Robert Walker and produced by Chuck Williams, from a screenplay written by Tab Murphy, Lorne Cameron, David Hoselton, and the writing team of Steve Bencich and Ron J. Friedman. The film stars the voices of Joaquin Phoenix, Jeremy Suarez, Rick Moranis, Dave Thomas, Jason Raize, and D.B. Sweeney. Brother Bear follows an Alaska native boy named Kenai as he pursues a bear and kills it, but the Spirits, incensed by this unnecessary death, change Kenai into a bear himself as punishment. In order to be human again, Kenai must travel to a mountain where the Northern lights touch the earth.

The Song of Hiawatha is an 1855 epic poem in trochaic tetrameter by Henry Wadsworth Longfellow which features Native American characters. The epic relates the fictional adventures of an Ojibwe warrior named Hiawatha and the tragedy of his love for Minnehaha, a Dakota woman. Events in the story are set in the Pictured Rocks area of Michigan on the south shore of Lake Superior. Longfellow's poem is based on oral traditions surrounding the figure of Manabozho, but it also contains his own innovations.

Samuel Coleridge-Taylor was a British-Sierra Leonean composer and conductor. Of mixed-race birth, Coleridge-Taylor achieved such success that he was referred to by white New York musicians as the "African Mahler" when he had three tours of the United States in the early 1900s. He was particularly known for his three cantatas on the epic 1855 poem The Song of Hiawatha by American Henry Wadsworth Longfellow. Coleridge-Taylor premiered the first section in 1898, when he was 22.
The baykok is a malevolent spirit from the mythology of the Ojibway nation.

Nanabozho, also known as Nanabush, is a spirit in Anishinaabe aadizookaan, particularly among the Ojibwe. Nanabozho figures prominently in their storytelling, including the story of the world's creation. Nanabozho is the Ojibwe trickster figure and culture hero.

Hiawatha is an unincorporated community and near-ghost town, formerly a coal mining town in southwestern Carbon County, Utah, United States. While the town's former corporate limits were almost entirely within Carbon County, the western part was within the Manti-La Sal National Forest and a very small part extended west into Emery County.
Saugeen First Nation is an Ojibway First Nation band located along the Saugeen River and Bruce Peninsula in Ontario, Canada. The band states that their legal name is the "Chippewas of Saugeen". Organized in the mid-1970s, Saugeen First Nation is the primary "political successor apparent" to the Chippewas of Saugeen Ojibway Territory; the other First Nation that is a part of Chippewas of Saugeen Ojibway Territory is Cape Croker. The Ojibway are of the Algonquian languages family. The First Nation consist of four reserves: Chief's Point 28, Saugeen 29, Saugeen Hunting Grounds 60A, and Saugeen and Cape Croker Fishing Islands 1.

Riding Mountain National Park is a national park in Manitoba, Canada. The park is located within Treaty 2 Territory and sits atop the Manitoba Escarpment. Consisting of a protected area 2,969 km2 (1,146 sq mi), the forested parkland stands in sharp contrast to the surrounding prairie farmland. It was designated a national park because it protects three different ecosystems that converge in the area; grasslands, upland boreal and eastern deciduous forests. It is most easily reached by Highway 10 which passes through the park. The south entrance is at the townsite of Wasagaming, which is the only commercial centre within the park boundaries.

The Midewiwin or the Grand Medicine Society is a secretive religion of some of the Indigenous peoples of the Maritimes, New England and Great Lakes regions in North America. Its practitioners are called Midew, and the practices of Midewiwin are referred to as Mide. Occasionally, male Midew are called Midewinini, which is sometimes translated into English as "medicine man".

John Emerson Moss was an American politician of the Democratic Party, noted for his championing of the federal Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) through multiple sessions of the United States House of Representatives where he served from 1953 to 1978.
The Saugeen Ojibway Nation Territory, also known as Saugeen Ojibway Nation, SON and the Chippewas of Saugeen Ojibway Territory, is the name applied to Chippewas of Nawash Unceded First Nation and Saugeen First Nation as a collective, represented by a joint council. The collective First Nations are Ojibway (Anishinaabe) peoples located on the eastern shores of Lake Huron on the Bruce Peninsula in Ontario, Canada. Though predominantly Ojibway, due to large influx of refugees from the south and west after the War of 1812, the descendants of the Chippewas of Saugeen Ojibway Territory also have ancestry traced to Odawa and Potawatomi peoples.
Jiibayaabooz in a figure in Ojibwe mythology, also known as Chipiapoos or Cheeby-aub-oozoo, meaning "Spirit Rabbit" or "Ghost of Rabbit." The figure also appears in Abenaki mythology Mateguas, meaning "Rabbit." This figure is a trickster spirit and figures prominently in their storytelling, including the story of the world's creation. Depending on the tradition, he was either the second or third son:37 of Wiininwaa ("Nourishment"), a human mother, and E-bangishimog, a spirit father.

Little Hiawatha is a 1937 animated cartoon produced by Walt Disney Productions, inspired by the poem The Song of Hiawatha by Henry Wadsworth Longfellow. It does not appear to have historical correlation to legendary Mohawk leader and peacemaker Hiawatha. It is the last Silly Symphonies short to be released by United Artists.
The Indianist movement was a movement in American classical music that flourished from the 1880s through the 1920s. It was based on attempts by classical composers to incorporate American Indian musical ideas with some of the basic principles of Western music, with the goal of creating a new, truly American national music.

Hiawatha is a 1952 American Western film based on the 1855 epic poem The Song of Hiawatha by Henry Wadsworth Longfellow, centering on Native Americans in pre-Columbian times. Directed by Kurt Neumann, with stars Vincent Edwards and Yvette Dugay, it became the final feature produced by the low-budget Monogram Pictures, a mainstay of Hollywood's Poverty Row.

The Song of Hiawatha, Op. 30, is a trilogy of cantatas written by Samuel Coleridge-Taylor between 1898 and 1900. The first part, Hiawatha's Wedding Feast, was particularly famous for many years and made the composer's name known throughout the world.
Hiawatha, the Messiah of the Ojibway is a 1903 dramatic short film shot in Canada directed by the American pioneering cinematographer and director Joe Rosenthal, based on the Henry Wadsworth Longfellow's famous poem, The Song of Hiawatha, made in Desbarats, Ontario, with a cast of Ojibway First Nations people. According to the Canadian Journal of Film Studies, it was the first dramatic narrative film to be shot in Canada.
References
- Benton-Banai, Edward. The Mishomis Book: The Voice of the Ojibway. Hayward, WI: Indian Country Communications, 1988.
- Johnston, Basil. The Manitous: the spiritual world of the Ojibway. New York: HarperCollins Publishers, 1995.